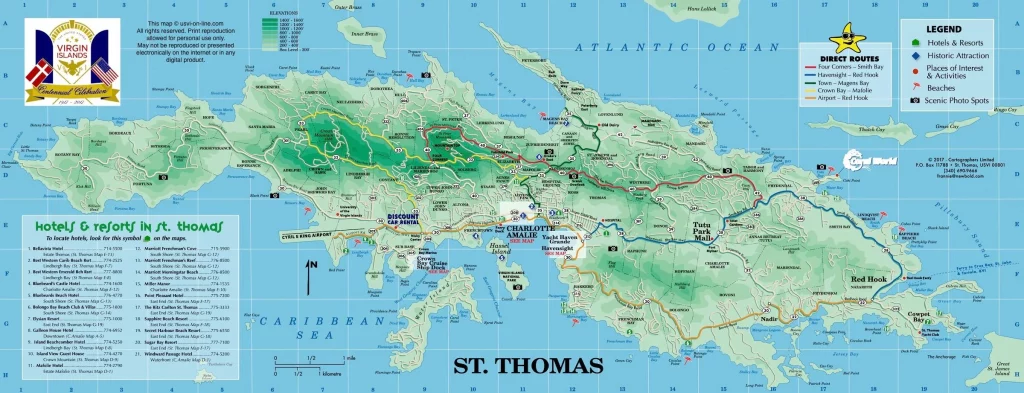
Virgin Islands Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Virgin Islands, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Virgin Islands, Central America, and the Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Charlotte Amalie, bordering countries like none, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Virgin Islands, Charlotte Amalie Google maps, Driving Directions Virgin Islands, Printable Road Map.
About the Virgin Islands in a nutshell

- Conventional short form of the name: Virgin Islands
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Former name(s): Danish West Indies
- Etymology: the myriad islets, cays, and rocks surrounding the major islands reminded Christopher COLUMBUS in 1493 of Saint Ursula and her 11,000 virgin followers (Santa Ursula y las Once Mil Virgenes), which over time shortened to the Virgins (las Virgenes).
- The legal system in the Virgin Islands: US common law.
- Climate: Subtropical, tempered by easterly trade winds, relatively low humidity, slight seasonal temperature variation, rainy season from September to November.
- Internet TLD: .vi
The northern archipelago of the Lesser Antilles was aptly named “Windswept” by the first sailors. All of the islands on the rim of the Caribbean rock plate result from volcanic activity. Active volcanoes continue to threaten the lives of islanders today: on the island of Montserrat, the population has had to be relocated from the south to the north of the island because of the eruptions of Soufrière, which have been renewed since 1995; on Martinique, the explosive eruption of the Mont Pelée volcano on 8 May 1902 swept away the town of Saint-Pierre and all its inhabitants. The eastern part of Guadeloupe, Grande Terre, and the tiny island of Marie Galante is the remains of coral reefs. The World Heritage Site of the Dominican Community, the ‘bubbling lake’ of the Morne Trois Pitons National Park, it’s half a century of steam eruptions, and its heat springs are evidence of post-volcanic activity. The cultural World Heritage Site of Saint Kitts and Nevis is the 17th-18th century fortress at Brimstone Hill National Park, the largest and best-preserved military structure in the Caribbean, the “Gibraltar of the West Indies”. The northern archipelago of the Dutch Antique Islands includes Sínt Eustatius, Saba, and the southern part of the island of Sint Maarten.
Background
The Danes secured control over the southern Virgin Islands of Saint Thomas, Saint John, and Saint Croix during the 17th and early 18th centuries. Sugarcane, produced by African slave labor, drove the island’s economy during the 18th and early 19th centuries. In 1917, the US purchased the Danish holdings, which had been in economic decline since the abolition of slavery in 1848. On 6 September 2017, Hurricane Irma passed over the northern Virgin Islands of Saint Thomas and Saint John. She inflicted severe damage to structures, roads, the airport on Saint Thomas, communications, and electricity. Less than two weeks later, Hurricane Maria passed over the island of Saint Croix in the southern Virgin Islands, inflicting considerable damage with heavy winds and flooding rains.
Geography
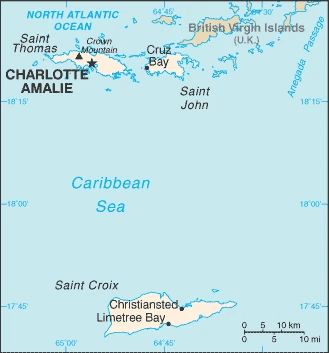
The Virgin Islands are a group of islands in the eastern part of the Caribbean Sea. They are situated between Puerto Rico to their east and the U.S. Virgin Islands to their west, about 3,200 miles from Miami, Florida. Some also consider them part of the Lesser Antilles, a collective name for all the islands located in the Caribbean Sea, including Jamaica, Haiti, Cuba, and others.
This state is located in the Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Puerto Rico, under the coordinates of 18 20 N, 64 50 W, covering an area of 1,910 sq km with a coastline of 188 km. Virgin Islands is Twice the size of Washington, DC.
Mostly hilly to rugged and mountainous with little flat land, with Crown mountain 474 m as the highest point of the Virgin Islands, while the Caribbean Sea 0 m as the lowest point. With 1,910 sq km, the Virgin Islands has 346 sq km of land and a 1,564 sq km water surface area.
An important location along the Anegada Passage – a key shipping lane for the Panama Canal; Saint Thomas has one of the best natural deepwater harbors in the Caribbean.
The climate in the Virgin Islands is as follows: Subtropical, tempered by easterly trade winds, relatively low humidity, slight seasonal temperature variation, rainy season from September to November.
When you visit the Virgin Islands, the natural hazards shall be considered: Several hurricanes in recent years; frequent and severe droughts and floods; occasional earthquakes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Virgin Islands: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Virgin Islander people: lack of natural freshwater resources; protection of coral reefs; solid waste management; coastal development; increased boating and overfishing.
Google Maps Virgin Islands
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Charlotte Amalie found under the coordinates 18 21 N, 64 56 W, applying the time zone UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Charlotte Amalie is the capital of the US Virgin Islands. It is a city on St Thomas founded in 1666 by Danish nobleman Peter Turner. It is home to many beautiful beaches, diverse cuisine, and fantastic entertainment options. Charlotte Amalie is also known as the “City of Seven Hills.”
Virgin Islands became independent on none (territory of the US), and its national holiday is Transfer Day (from Denmark to the US), 31 March (1917).
Administrative divisions: none (territory of the US); the US Government defines no first-order administrative divisions, but there are 3 islands in the second-order; Saint Croix, Saint John, and Saint Thomas.
People and society
The population of the Virgin Islands is 105,870 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.42% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Virgin Islands is the No. 191 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 41.8 years median age (40.6 years for males and 40.6 years for women), the Virgin Islands ranks No. 42 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Virgin Islander(s) (US citizens) (noun) or Virgin Islander (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Black 76%, White 15.6%, Asian 1.4%, other 4.9%, mixed 2.1% (2010 estimate). Note: 17.4% self-identify as Latino.
They speak English 71.6%, Spanish or Spanish Creole 17.2%, French or French Creole 8.6%, other 2.5% (2010 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 59% (Baptist 42%, Episcopalian 17%), Roman Catholic 34%, other 7%.
We can conclude the following about the population in the Virgin Islands: While overall population density throughout the islands is relatively low, concentrations appear around charlotte Amalie on st. Thomas and Christiansted on st. Croix. In the Virgin Islands, we are talking about 96% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 52,000 Charlotte Amalie (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Tourism, trade, other services, and rum production are the primary economic activities of the US Virgin Islands (USVI), accounting for most of its GDP and employment. The USVI receives between 2.5 and 3 million tourists a year, mostly from visiting cruise ships. The islands are vulnerable to damage from storms, as evidenced by the destruction from two major hurricanes in 2017. Recovery and rebuilding have continued, but full recovery from these back-to-back hurricanes is years away. The USVI government estimates it will need $7.5 billion, almost twice the territory’s GDP, to rebuild it. The agriculture sector is small, and most food is imported. In 2016, government spending (both federal and territorial) accounted for about 27% of GDP, while exports of goods and services, including spending by tourists, accounted for nearly 47%. Federal programs and grants, including rum tax cover-over totaling $482.3 million in 2016, contributed 32.2% of the territory’s total revenues. The economy picked up 0.9% in 2016 and appeared to be progressing before the 2017 hurricanes severely damaged the territory’s infrastructure and the economy.
The Virgin Islands is rich in the following natural resources: Pleasant climate beaches foster tourism.
The main industrial sectors are tourism, watch assembly, rum distilling, construction, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
The country’s export sectors are robust in refined petroleum, jewelry, recreational boats, watches, and rum (2019), partnering with these nations: Haiti 14%, Guadeloupe 7%, Malaysia 7%, Martinique 7%, Barbados 7%, the British Virgin Islands 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.81 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2016 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in the Virgin Islands’s position of 156.
Land use in Virgin Islands: 57.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 31.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 11.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 2.9% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 5.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the Virgin Islands are fruit, vegetables, sorghum, and Senepol cattle.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, crude petroleum, rubber piping, jewelry, and beer (2019), partnering with the following nations: India 18%, Algeria 14%, South Korea 9%, Argentina 9%, Sweden 7%, Brazil 5% (2019) in a sum value of $2.489 billion (2016 estimate) $1.549 billion (2015 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Virgin Islands 166.
The Virgin Islands Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the Virgin Islands, the Caribbean, and the islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Puerto Rico. We published basic information about its capital Charlotte Amalie, and the Virgin Islander nation.
Are you interested in visiting the Virgin Islands and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Virgin Islands below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of the Virgin Islands
Did you know about the Virgin Islands?
Christopher Columbus discovered this small island country in 1493. It comprises three major islands, St. Croix, St. Thomas, and St. John. The Virgin Islands are the most extensive U.S. territories in the Caribbean and are found in the North Atlantic Ocean between Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands. The Virgin Islands are one of the most beautiful places in the Caribbean. Many names call them, but they’re called “the Virgins”. The Virgin Islands were home to Christopher Columbus, and he named the island that he first landed on “Virgin”. Each island has its unique natural beauty. Due to climate and terrain, each island is a little different from the last.
Founded in 1670, Charlotte Amalie is the largest settlement on the islands. The town was once a Danish colony but was taken over by the US after the Treaty of Paris in 1873. It is now one of America’s smallest states, with just over 36,000 people.
After virtually visiting the Virgin Islands, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and the Virgin Islands information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.