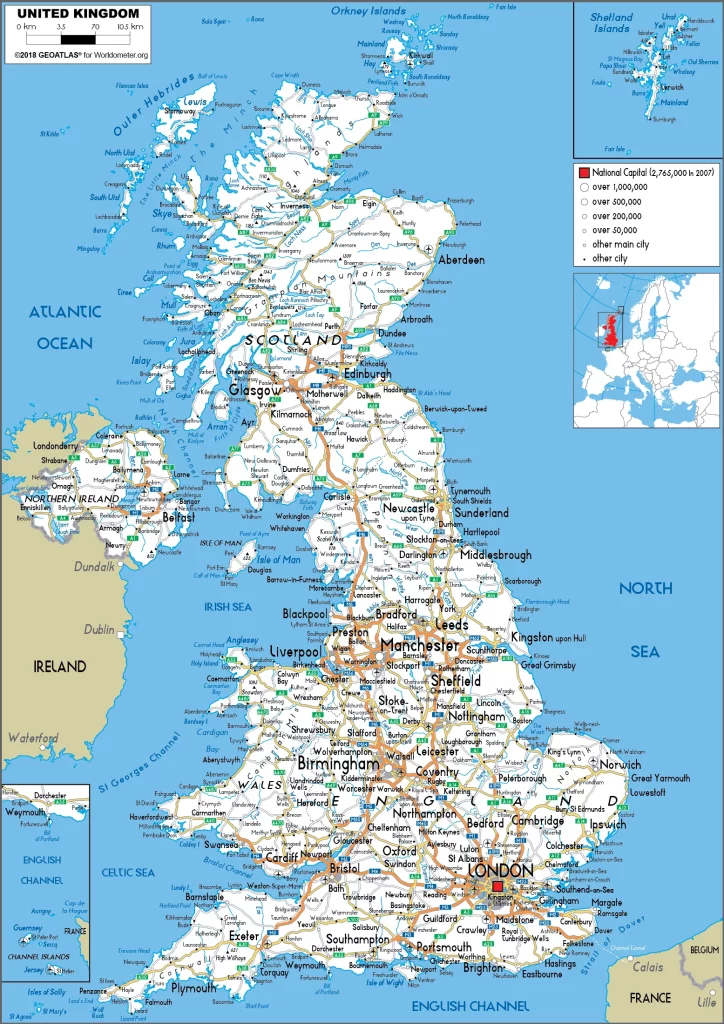
The United Kingdom Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the United Kingdom, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the United Kingdom and Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city London, bordering countries like Ireland, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps United Kingdom, London Google maps, Driving Directions United Kingdom, Printable Road Map.

About the United Kingdom in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: United Kingdom
- The conventional long form of the name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- Etymology: self-descriptive country name; the designation Great Britain, in the sense of Larger Britain, dated back to medieval times and was used to distinguish the island from Little Britain or Brittany in modern France; the name Ireland derives from the Gaelic Eriu, the matron goddess of Ireland (goddess of the land).
- The legal system in the United Kingdom: the common law system has a nonbinding judicial review of Acts of Parliament under the Human Rights Act of 1998.
- Climate: Generally mild, temperate, and highly changeable. Rain is relatively well distributed throughout the year. The west is generally wetter than the east, and the south warmer than the north. Winter snow is expected in upland areas.
- The national symbols are lion (Britain in general); lion, Tudor rose, oak (England); lion, unicorn, thistle (Scotland); dragon, daffodil, leek (Wales); shamrock, flax (Northern Ireland); national colors: red, white, blue (Britain in general); red, white (England); blue, white (Scotland); red, white, green (Wales).
- Internet TLD: .uk
London is a stimulating city full of contradictions. It has more action than most European cities and is a world leader in the latest music, fashion, and food. You should visit some unordinary places like Stonehenge and Oxford University while you’re there.
The country is most often referred to as Britain or England, occupying the whole of the British Isles and one-sixth of the island of Ireland. Its World Heritage Sites well represent the significant stages in the history of the United Kingdom. Stonehenge and the megaliths of Avebury are the most notable monuments of the prehistoric era, while Hadrian’s Wall marks the northernmost frontier of the Roman Empire. The Roman Baths and Georgian palaces of Bath, the fortifications and cathedrals of Durham, Gwynedd, and Canterbury, London’s Tower and Westminster of the Middle Ages, Blenheim Palace, Studley Royal Park, and Kew Royal Botanic Gardens embody the aristocratic splendor of the modern age, as does Edinburgh’s Old Town with its towering castle and neo-Classical-Sicist new town.
The Maritime Museum complex in Greenwich is a testament to England’s role in the world of exploration and science in the 17th and 18th centuries, while the Blaenavon area, Ironbridge Iron Bridge, the mines of Cornwall and Devon, the industrial buildings of Saltaire, the mills of the Derwent Valley and the village of New Lanark in Scotland are all monuments to the Industrial Revolution. The historic port of Liverpool once handled the trade of a world empire. The white cliffs of Dover are the symbol of the ‘Foggy Albion’. Northern Ireland’s Antrim Highlands coastline, the ‘Stairway of Giants’, is the evocative name for some 40,000 basalt organs. The four-island volcanic archipelago of St Kilda in the Outer Hebrides, the megalithic structures, stone circles, and unexplored tombs and settlement remains found in the Orkney Islands are evidence of a Neolithic culture dating back 5,000 years.
The UK has no formal written constitution but a stable government system based on Parliament, which originated as a check on royal power in the 13th century.
Background
Historically, the United Kingdom has played a leading role in developing parliamentary democracy and advancing literature and science. At its zenith in the 19th century, the British Empire stretched over one-fourth of the earth’s surface. The first half of the 20th century saw the UK’s strength seriously depleted in two world wars and the Irish Republics’ withdrawal from the Union. The second half witnessed the dismantling of the Empire and the UK rebuilding itself into a modern and prosperous European nation. As one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council and a founding member of NATO and the Commonwealth, the UK pursues a global approach to foreign policy. The Scottish Parliament, the National Assembly for Wales, and the Northern Ireland Assembly were established in 1998. The UK was an active member of the EU after its accession in 1973, although it chose to remain outside the Economic and Monetary Union. However, motivated partly by frustration at a remote bureaucracy in Brussels and massive migration into the country, UK citizens, on 23 June 2016, narrowly voted to leave the EU. The UK became the first country to depart the EU on 31 January 2020, after prolonged negotiations on EU-UK economic and security relationships had been hammered out.
Geography
Rugged uplands dominate the landscape of Scotland, Wales, and northern England. All the peaks in the United Kingdom over 4000 ft (1219 m) are in highland Scotland. The Pennine mountains, known as the “backbone of England,” run the length of northern England. Lowland England rises into several ranges of rolling hills, and there is an interconnected system of rivers and canals. Over 600 islands, many uninhabited, lie west and north of the Scottish mainland.
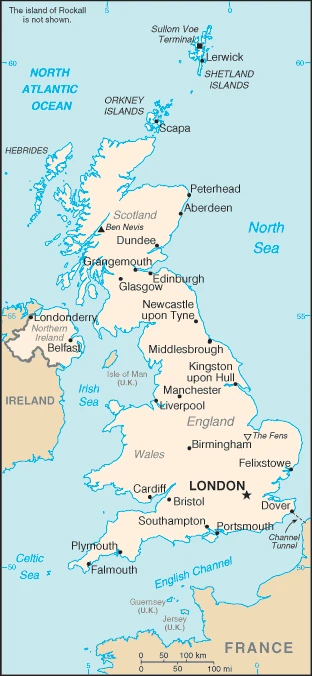
Separated from continental Europe by the English Channel, the UK consists of Great Britain (England, Wales, and Scotland), several smaller islands, and Northern Ireland.
This state is located in Western Europe, islands – including the northern one-sixth of the island of Ireland – between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, northwest of France, under the coordinates of 54 00 N, 2 00 W, covering an area of 243,610 sq km with a coastline of 12,429 km. The United Kingdom is twice the size of Pennsylvania, slightly smaller than Oregon.
The United Kingdom has 499 km of land boundaries and borders (1 nation): Ireland has 499 km.
Primarily rugged hills and low mountains, level to rolling plains in east and southeast, with Ben Nevis 1,345 m as the highest point of United Kingdom, while The Fens -4 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 162 m throughout the country. With a total of 243,610 sq km, the United Kingdom has 241,930 sq km of land and 1,680 sq km of water surface area.
Lies near vital North Atlantic sea lanes, only 35 km from France, and linked by tunnel under the English Channel (the Channel Tunnel or Chunnel); because of its heavily indented coastline, no location is more than 125 km from tidal waters.
The climate in the United Kingdom is as follows: Temperate, moderated by prevailing southwest winds over the North Atlantic current, more than one-half of the days are overcast.
When you visit the United Kingdom, the natural hazards shall be considered: Winter windstorms; floods.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the United Kingdom: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the British people: air pollution improved but remains a concern, particularly in the London region; soil pollution from pesticides and heavy metals; decline in marine and coastal habitats brought on by pressures from housing, tourism, and industry.
Google Maps the United Kingdom
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: London found under the coordinates 51 30 N, 0 05 W, applying the time zone UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
London is the capital of England and one of the largest cities in the UK. The word London originally meant “the area covered by water,” and it’s fair to say that London is a city that has been at the forefront of technology from the beginning, even becoming one of the first towns in Europe to have gas street lighting. Nowadays, London is one of the most important cities in the world. It is a major financial center with immense cultural diversity, traditions, and attractions. The city is renowned for its vibrant nightlife, attractive architecture, and rich history.
The United Kingdom became independent on no official date of independence: 927 (minor English kingdoms unite); 3 March 1284 (enactment of the Statute of Rhuddlan uniting England and Wales); 1536 (Act of Union formally incorporates England and Wales); 1 May 1707 (Acts of Union formally unite England, Scotland, and Wales as Great Britain); 1 January 1801 (Acts of Union formally unite Great Britain and Ireland as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland); 6 December 1921 (Anglo-Irish Treaty formalizes partition of Ireland; six counties remain part of the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland); 12 April 1927 (Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act establishes the current name of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland), and its national holiday is the UK does not celebrate one particular national holiday.
Administrative divisions: England: 26 two-tier counties, 32 London boroughs and 1 City of London or Greater London, 36 metropolitan districts, 56 unitary authorities (including 4 single-tier counties); two-tier counties: Buckinghamshire, Cambridgeshire, Cumbria, Derbyshire, Devon, Dorset, East Sussex, Essex, Gloucestershire, Hampshire, Hertfordshire, Kent, Lancashire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire, Norfolk, Northamptonshire, North Yorkshire, Nottinghamshire, Oxfordshire, Somerset, Staffordshire, Suffolk, Surrey, Warwickshire, West Sussex, Worcestershire London boroughs and City of London or Greater London: Barking and Dagenham, Barnet, Bexley, Brent, Bromley, Camden, Croydon, Ealing, Enfield, Greenwich, Hackney, Hammersmith and Fulham, Haringey, Harrow, Havering, Hillingdon, Hounslow, Islington, Kensington and Chelsea, Kingston upon Thames, Lambeth, Lewisham, City of London, Merton, Newham, Redbridge, Richmond upon Thames, Southwark, Sutton, Tower Hamlets, Waltham Forest, Wandsworth, Westminster metropolitan districts: Barnsley, Birmingham, Bolton, Bradford, Bury, Calderdale, Coventry, Doncaster, Dudley, Gateshead, Kirklees, Knowlsey, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, North Tyneside, Oldham, Rochdale, Rotherham, Salford, Sandwell, Sefton, Sheffield, Solihull, South Tyneside, St. Helens, Stockport, Sunderland, Tameside, Trafford, Wakefield, Walsall, Wigan, Wirral, Wolverhampton unitary authorities: Bath and North East Somerset; Bedford; Blackburn with Darwen; Blackpool; Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole; Bracknell Forest; Brighton and Hove; City of Bristol; Central Bedfordshire; Cheshire East; Cheshire West and Chester; Cornwall; Darlington; Derby; Dorset; Durham County; East Riding of Yorkshire; Halton; Hartlepool; Herefordshire; Isle of Wight; Isles of Scilly; City of Kingston upon Hull; Leicester; Luton; Medway; Middlesbrough; Milton Keynes; North East Lincolnshire; North Lincolnshire; North Somerset; Northumberland; Nottingham; Peterborough; Plymouth; Portsmouth; Reading; Redcar and Cleveland; Rutland; Shropshire; Slough; South Gloucestershire; Southampton; Southend-on-Sea; Stockton-on-Tees; Stoke-on-Trent; Swindon; Telford and Wrekin; Thurrock; Torbay; Warrington; West Berkshire; Wiltshire; Windsor and Maidenhead; Wokingham; York Northern Ireland: 5 borough councils, 4 district councils, 2 city councils; borough councils: Antrim and Newtownabbey; Ards and North Down; Armagh City, Banbridge, and Craigavon; Causeway Coast and Glens; Mid and East Antrim district councils: Derry City and Strabane; Fermanagh and Omagh; Mid Ulster; Newry, Murne, and Down city councils: Belfast; Lisburn and Castlereagh Scotland: 32 council areas; council areas: Aberdeen City, Aberdeenshire, Angus, Argyll and Bute, Clackmannanshire, Dumfries and Galloway, Dundee City, East Ayrshire, East Dunbartonshire, East Lothian, East Renfrewshire, City of Edinburgh, Eilean Siar (Western Isles), Falkirk, Fife, Glasgow City, Highland, Inverclyde, Midlothian, Moray, North Ayrshire, North Lanarkshire, Orkney Islands, Perth and Kinross, Renfrewshire, Shetland Islands, South Ayrshire, South Lanarkshire, Stirling, The Scottish Borders, West Dunbartonshire, West Lothian Wales: 22 unitary authorities; unitary authorities: Blaenau Gwent, Bridgend, Caerphilly, Cardiff, Carmarthenshire, Ceredigion, Conwy, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Isle of Anglesey, Merthyr Tydfil, Monmouthshire, Neath Port Talbot, Newport, Pembrokeshire, Powys, Rhondda Cynon Taff, Swansea, The Vale of Glamorgan, Torfaen, Wrexham.
People and society
Scottish and Welsh people have a stronger sense of separate identity than the English; Scotland and Wales have some self-government, as does Northern Ireland. In 2014 Scotland rejected independence in a referendum. Other ethnic minorities account for 5% of the population; more than half were born in the UK. Asian women, in particular, can be socially isolated. Asians and West Indians in most cities face deprivation and social stress, but white working-class youths were also evident when inner-city rioting erupted in 2011. Income inequality is greater now than in 1884 when records began. In critical areas such as policing, multiethnic recruitment has made little progress. Marriage is in decline. Over 40% of all births occur outside marriage, but most are to cohabiting couples. Single-parent households account for just over a quarter of all families.
The population of the United Kingdom is 67.081 million. United Kingdom (June 2020 estimate) constituent countries by percentage of total population: England 84.3% Scotland 8.1% Wales 4.7% Northern Ireland 2.8%, with an average of 0.48% (2021 estimate) change. That means the United Kingdom is the No. 22 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 40.6 years median age (39.6 years for males and 39.6 years for women), the United Kingdom ranks No. 50 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Briton(s), British (collective plural) (noun) or British (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White 87.2%, Black/African/Caribbean/Black British 3%, Asian/Asian British: Indian 2.3%, Asian/Asian British: Pakistani 1.9%, mixed 2%, other 3.7% (2011 estimate).
They speak English. Note: the following are recognized regional languages: Scots (about 30% of the population of Scotland), Scottish Gaelic (about 60,000 speakers in Scotland), Welsh (about 20% of the population of Wales), Irish (about 10% of the population of Northern Ireland), Cornish (some 2,000 to 3,000 people in Cornwall) (2012 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Christian (includes Anglican, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian, Methodist) 59.5%, Muslim 4.4%, Hindu 1.3%, other 2%, unspecified 7.2%, none 25.7% (2011 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the United Kingdom: The core of the population lives in and around London, with significant clusters found in central Britain around Manchester and Liverpool, in the Scottish lowlands between Edinburgh and Glasgow, southern wales in and around Cardiff, and far eastern, northern Ireland centered on Belfast. In the United Kingdom, we are talking about 84.2% (2021) of the population living in cities. Most reside in the following municipalities: 9.426 million, London (capital city), 2.750 million, Manchester, 2.626 million, Birmingham, 1.902 million, West Yorkshire, 1.681 million, Glasgow, 936,000 Southampton/Portsmouth (2021).
Industry
World leader in financial services, pharmaceuticals, and defense industries. Strong multinationals. Precision engineering and high-tech industries, including biotechnology and telecommunications. The energy sector is based on declining North Sea oil and natural gas reserves. Innovative in computer software development. Flexible working practices. The long-term decline of the manufacturing sector, heavy industries, and car manufacturing were partially offset by rising financial and other services. Nonparticipant in euro. High government, corporate, and consumer debt levels: banks made significant losses in the 2007-2009 global downturn. Bailouts and stimulus packages pushed the governments finances further into the red. Tackling the deficit by cuts in spending puts pressure on growth strategy and social programs, with rising unemployment.
The UK, leading trading power and financial center, is the third-largest European economy after Germany and France. Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanized, and efficient by European standards, producing about 60% of food needs with less than 2% of the labor force. The UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil resources, but its oil and natural gas reserves are declining; the UK has been a net energy importer since 2005. Services, particularly banking, insurance, and business services, are key drivers of British GDP growth. Manufacturing, meanwhile, has declined in importance but still accounts for about 10% of economic output. In 2008, the global financial crisis hit the economy particularly hard due to the importance of its financial sector. Falling home prices, high consumer debt, and the global economic slowdown compounded the UK’s economic problems, pushing the economy into recession in the latter half of 2008 and prompting the then BROWN (Labour) government to implement several measures to stimulate the economy and stabilize the financial markets.
Facing burgeoning public deficits and debt levels, in 2010, the then CAMERON-led coalition government (between Conservatives and Liberal Democrats) initiated an austerity program, which has continued under the Conservative government. However, the deficit remains one of the highest in the G7, standing at 3.6% of GDP as of 2017, and the UK has pledged to lower its corporation tax from 20% to 17% by 2020. The UK had a debt burden of 90.4% of GDP in 2017. The UK economy has begun to slow since the referendum vote to leave the EU in June 2016. A sustained depreciation of the British pound has increased consumer and producer prices, weighing on consumer spending without spurring a meaningful increase in exports. The UK has an extensive trade relationship with other EU members through its single market membership. Economic observers have warned that the exit will jeopardize its position as the central location for European financial services. The UK is slated to leave the EU in January 2020.
The United Kingdom is rich in the following natural resources: Coal, petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, lead, zinc, gold, tin, limestone, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, potash, silica sand, slate, and arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically machine tools, electric power equipment, automation equipment, railroad equipment, shipbuilding, aircraft, motor vehicles and parts, electronics and communications equipment, metals, chemicals, coal, petroleum, paper and paper products, food processing, textiles, clothing, other consumer goods.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars, gas turbines, gold, crude petroleum, and packaged medicines (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 15%, Germany 10%, China 7%, Netherlands 7%, France 7%, Ireland 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $741.95 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global export rank, values resulted in the United Kingdom’s position of 6.
Land use in the United Kingdom: 11.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 17.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 25.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 71% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.2% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 45.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 950 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the United Kingdom are wheat, milk, barley, sugar beet, potatoes, rapeseed, poultry, oats, pork, and beef.
The country typically needs to import: gold, cars, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, and broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 13%, China 10%, United States 8%, Netherlands 7%, France 6%, Belgium 5% (2019) in a sum value of $752.77 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $914.96 billion. This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in the United Kingdom 6.
United Kingdom Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the United Kingdom, Western Europe, and islands – including the northern one-sixth of the island of Ireland – between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, northwest of France. We published some basic information about its capital London, and the British nation.
Are you interested in visiting the United Kingdom and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the United Kingdom below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of the United Kingdom
Did you know about the United Kingdom?
England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland make up the United Kingdom. These four countries are in the northeastern part of Europe and are separated from mainland Europe by the English Channel. The United Kingdom comprises more than 80 islands, including Great Britain, Ireland, and many smaller ones. The Union Jack flag is part of the British Flag, also known as the Union Jack.
After visiting the United Kingdom, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, and Scotland.
If you liked our Google map and the United Kingdom information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.