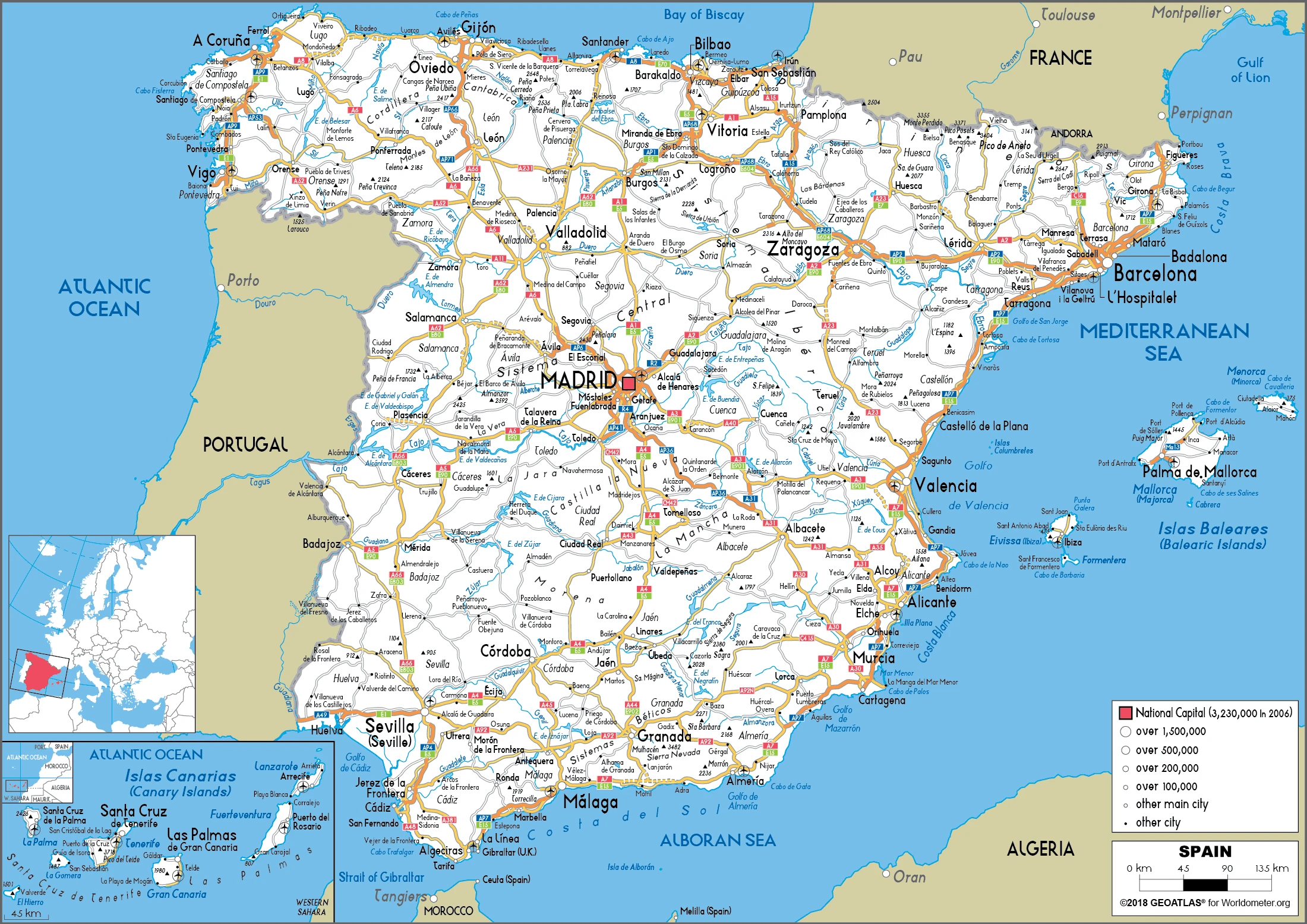
Spain Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Spain, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Spain, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Madrid, bordering countries like Andorra, France, Gibraltar, Portugal, Morocco, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Spain, Madrid Google maps, Driving Directions Spain, Printable Road Map.

About Spain in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Spain
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Spain
- Local long form: Reino de Espana
- Local short form: Espana
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: derivation of the name Espana is uncertain but may come from the Phoenician term span, related to the word spy, meaning to forge metals, so i-spn-ya would mean a place where metals are forged; the ancient Phoenicians long exploited the Iberian Peninsula for its mineral wealth.
- The legal system in Spain: civil law system with regional variations.
- Climate: Maritime in the north. Hotter and drier in the south. The central plateau has an extreme climate.
- The national symbols are the Pillars of Hercules; the national colors are red and yellow.
- Internet TLD: .es
A land of rich history and modern creativity, Spain has made amends for the past and thrives in the present day. The sun-soaked beaches, cliffside vineyards, beautiful towns, and splendid palaces reflect an age where culture has flourished alongside technological advances to create a very recent rebirth that has restored sovereignty for Spain. Cultural and artistic innovations have ignited reverence for the country’s age-old customs, experiencing a renaissance in the 21st century.
Only the Ebro and Guadalquivir lowlands give the Iberian Peninsula a slightly greenish appearance, while the ancient land of Mezeta, squeezed between the Pyrenees and the Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, is a dry, plateau-like landscape. Europe’s oldest world heritage site is the 300 000-year-old human remains of the Sierra de Atapuerca. Paintings in the Altamira-bar cave are 25 000 years old, and rock paintings found on the Mediterranean coast are over 6 000 years old. The most notable Roman monuments are the remains of buildings in Segovia, Mérida, Tarraco (formerly Tarragona), the city walls of Lugo, and the abandoned gold mine of Las Médulas. The Moorish monuments of Aragon, the thousand-year-old churches of the Kingdom of Asturias, the Moorish monuments of Granada, Avila, Córdoba, Toledo, Cáceres, Salamanca, and the Moorish monuments of Granada are among the World Heritage sites that preserve the glory of the medieval foreign conquerors and Spanish monarchs, Santiago de Compostela and Cuenca, the Silk Bridge in Valencia, the University of Alcalá de Henares, the Mudejar and Renaissance buildings of Úbeda and Baeza, Seville Cathedral and the Alcazar, as well as the archives of the Archivo General de Indias, the repository of the colonial documents of the New World.
The pastoral heritage includes the Escorial in Madrid, the Cistercian monastery of Poblet, the Colos de Santa Maria de Guadeloupe, the monasteries of St. Milian of Yuso and Suso, the churches of the Boí Valley in the Pyrenees, and the cathedral of Burgos, a stop on the Route of St. James, also a World Heritage Site. In Barcelona, the Art Nouveau buildings of Antonio Ga-udí, the Palau de la Música Catalana and the Hospital de Sant Pau, as well as Bilbao and the Vizcaya Bridge complete the list. The orchards of Aranjuez and Elche’s palm grove of 200,000 date palms are cultural treasures. At the same time, the Donana National Park, the Monté Perdido, and Ibiza marine environment shared with France and the protected areas of the Canary Islands add to the list of natural World Heritage sites.
Over 3000 festivals and feasts take place each year in Spain.
Background
Spain’s powerful world empire of the 16th and 17th centuries ultimately yielded command of the seas to England. Subsequent failure to embrace the mercantile and industrial revolutions caused the country to fall behind Britain, France, and Germany in economic and political power. Spain remained neutral in World War I and II but suffered through a devastating civil war (1936-39). A peaceful transition to democracy following the death of dictator Francisco FRANCO in 1975 and rapid economic modernization (Spain joined the E.U. in 1986) gave Spain a dynamic and rapidly growing economy. They made it a global champion of freedom and human rights. More recently, Spain has emerged from a severe economic recession that began in mid-2008, posting four straight years of GDP growth above the E.U. average. Unemployment has fallen but remains high, especially among youth. Spain is the Eurozone’s fourth-largest economy. The country has faced increased domestic turmoil due to the independence movement in its restive Catalonia region.
Geography
Mountain ranges in the north, center, and south, with a substantial central plateau. Mediterranean lowlands. Verdant valleys in the northwest.
At its unification under Ferdinand and Isabella in 1492, Spain occupied a pivotal position between Europe, Africa, the North Atlantic, and the Mediterranean.
This state is located in Southwestern Europe, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, North Atlantic Ocean, Bay of Biscay, and Pyrenees Mountains, southwest of France, under the coordinates of 40 00 N, 4 00 W, covering an area of 505,370 sq km with a coastline of 4,964 km. Spain is Almost five times the size of Kentucky, slightly more than twice the size of Oregon.
Spain has 1,952.7 km of land boundaries in total and borders (5 nations): Andorra 63 km, France 646 km, Gibraltar 1.2 km, Portugal 1224 km, Morocco (Ceuta) 8 km, and Morocco (Melilla) 10.5 km.
Large, flat to dissected plateau surrounded by rugged hills, Pyrenees mountains in the north, with Pico de Teide (Tenerife) on canary islands 3,718 m as the highest point of Spain, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 660 m throughout the country. With a total of 505,370 sq km, Spain has 498,980 sq km of land and 6,390 sq km of water surface area. The principal river is Tagus (shared with Portugal) – 1,006 km.
Strategic location along with approaches to the Strait of Gibraltar; Spain controls several territories in northern Morocco, including the enclaves of Ceuta and Melilla and the islands of Penon de Velez de la Gomera, Penon de Alhucemas, and Islas Chafarinas; Spain’s Canary Islands are one of four North Atlantic archipelagos that make up Macaronesia; the others are Azores (Portugal), Madeira (Portugal), and Cabo Verde.
The climate in Spain is as follows: Temperate, clear, hot summers in the interior, more moderate and cloudy along the coast, cloudy, cold winters in the interior, partly cloudy and cool along the coast.
When you visit Spain, the natural hazards shall be considered: Periodic droughts, occasional flooding, volcanism: volcanic activity in the canary islands, located off Africa’s northwest coast; Teide (3,715 m) has been deemed a decade volcano by the international association of volcanology and chemistry of the interior of the earth, worthy of study due to its tumultuous history and proximity to human populations; La Palma (2,426 m), which last erupted in 1971, is the most active of the canary island’s volcanoes; Lanzarote is the only other historically active volcano.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Spain: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Spanish people: pollution of the Mediterranean Sea from raw sewage and effluents from the offshore production of oil and gas; water quality and quantity nationwide; air pollution; deforestation; desertification.
Google Maps Spain
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Madrid found under the coordinates 40 24 N, 3 41 W, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Madrid is the capital of Spain and one of the most important cities in Europe. It has a rich history and many famous monuments, including the Plaza Mayor, and excellent shopping areas, restaurants, and cultural attractions. Madrid is also a city where you will find plenty of opportunities to enjoy nature, with many parks and walking trails nearby. One famous suburb near Madrid is the city of Toledo, which is known for its architecture and fiestas, including the Semana Santa. Madrid was founded in 1173 on a swampy piece of land.
Spain became independent in 1492; the Iberian peninsula was characterized by a variety of independent kingdoms before the Muslim occupation that began in the early 8th century A.D. and lasted nearly seven centuries; the small Christian redoubts of the north began the reconquest almost immediately, culminating in the seizure of Granada in 1492; this event completed the unification of several kingdoms and is traditionally considered the forging of present-day Spain, and its national holiday is National Day (Hispanic Day), 12 October (1492).
Administrative divisions: 17 autonomous communities (comunidades autonomas, singular – comunidad autonoma) and 2 autonomous cities (ciudades autonomas, singular – ciudad autonoma); Andalucia; Aragon; Asturias; Canarias (Canary Islands); Cantabria; Castilla-La Mancha; Castilla-Leon; Cataluna (Castilian), Catalunya (Catalan), Catalonha (Aranese) Catalonia; Ceuta*; Comunidad Valenciana (Castilian), Comunitat Valenciana (Valencian) Valencian Community; Extremadura; Galicia; Illes Baleares (Balearic Islands); La Rioja; Madrid; Melilla*; Murcia; Navarra (Castilian), Nafarroa (Basque) Navarre; Pais Vasco (Castilian), Euskadi (Basque) Basque Country note: the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla plus three small islands of Islas Chafarinas, Penon de Alhucemas, and Penon de Velez de la Gomera, administered directly by the Spanish central government, are all along the coast of Morocco and are collectively referred to as Places of Sovereignty (Plazas de Soberania).
People and society
A robust ethnic regionalism, suppressed under Franco’s fascist regime, now flourishes. There are 17 autonomous regions. People remain churchgoing, though Roman Catholic teachings on social issues are often disregarded. Spanish women are increasingly emancipated, with solid political representation.
The population in Spain is 47,260,584 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.03% (2021 estimate) change. That means Spain is the No. 30 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 43.9 years median age (42.7 years for males and 42.7 years for women), Spain ranks No. 19 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Spaniard(s) (noun) or Spanish (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Spanish 84.8%, Moroccan 1.7%, Romanian 1.2%, other 12.3% (2021 estimate). Note: data represent population by country of birth.
They speak Castilian Spanish (official language nationwide) 74%, Catalan (official language in Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, and the Valencian Community (where it is known as Valencian)) 17%, Galician (official language in Galicia), 7%, Basque (official language in the Basque Country and the Basque-speaking area of Navarre) 2%, Aranese (official language in the northwest corner of Catalonia (Vall dAran) along with Catalan, <5,000 speakers) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 58.2%, atheist 16.2%, agnostic 10.8%, other 2.7%, non-believer 10.5%, unspecified 1.7% (2021 estimate). We can conclude the following about the population in Spain: With the notable exception of Madrid, Sevilla, and Zaragoza, the largest urban agglomerations are found along the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts. Numerous smaller cities are spread throughout the interior, reflecting Spain’s agricultural heritage. The very dense settlement around the capital of Madrid and the port city of Barcelona. In Spain, we are talking about 81.1% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 6.669 million, Madrid (capital city), 5.624 million, Barcelona, 835,000 Valencia (2021).
Industry
Exports food, wine. Few natural resources. Large fishing fleet. Tourism, and the motor industry, were hit by the global downturn, soaring unemployment since the abrupt end of a construction boom. The austerity program aims to cut debt and deficits. A target for economic migrants from Africa.
After a prolonged recession that began in 2008 in the wake of the global financial crisis, Spain marked the fourth full year of positive economic growth in 2017, with economic activity surpassing its pre-crisis peak, mainly because of increased private consumption. The financial crisis of 2008 broke 16 consecutive years of economic growth for Spain, leading to an economic contraction that lasted until late 2013. In that year, the government successfully shored up its struggling banking sector – heavily exposed to the collapse of Spain’s real estate boom – with the help of an EU-funded restructuring and recapitalization program. Until 2014, contraction in bank lending, fiscal austerity, and high unemployment constrained domestic consumption and investment. The unemployment rate rose from a low of about 8% in 2007 to more than 26% in 2013, but labor reforms prompted a modest reduction to 16.4% in 2017. High unemployment strained Spain’s public finances, as spending on social benefits increased while tax revenues fell.
Spain’s budget deficit peaked at 11.4% of GDP in 2010, but Spain gradually reduced the deficit to about 3.3% of GDP in 2017. Public debt has increased substantially from 60.1% of GDP in 2010 to nearly 96.7% in 2017., Strong export growth helped bring Spain’s current account into surplus in 2013 for the first time since 1986 and sustained Spain’s economic growth. Increasing labor productivity and an internal devaluation resulting from moderating labor costs and lower inflation have improved Spain’s export competitiveness and generated foreign investor interest in the economy, restoring FDI flows., In 2017, the Spanish government’s minority status constrained its ability to implement controversial labor, pension, health care, tax, and education reforms. The European Commission expects the government to meet its 2017 budget deficit target and anticipates that expected economic growth in 2018 will help the government meet its deficit target. Spain’s borrowing costs are dramatically lower since their peak in mid-2012, and increased economic activity has generated a modest level of inflation, at 2% in 2017.
Spain is rich in natural resources: Coal, lignite, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, uranium, tungsten, mercury, pyrites, magnesite, fluorspar, gypsum, sepiolite, kaolin, potash, hydropower, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically textiles and apparel (including footwear), food and beverages, metals and metal manufacturers, chemicals, shipbuilding, automobiles, machine tools, tourism, clay and refractory products, footwear, and pharmaceuticals, medical equipment.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in cars and vehicle parts, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, delivery trucks, clothing, and apparel (2019), partnering with these nations: France 15%, Germany 11%, Portugal 8%, Italy 8%, United Kingdom 7%, United States 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $392.85 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Spain’s position of 18.
Land use in Spain: 36.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 9.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 24.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 54.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 9.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 20.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 38,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Spain are barley, milk, wheat, olives, grapes, tomatoes, pork, maize, oranges, and sugar beet.
The country typically needs to import: crude petroleum, cars and vehicle parts, packaged medicines, natural gas, refined petroleum (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 13%, France 11%, China 8%, Italy 7% (2019) in a sum value of $373.67 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $444.31 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $460.98 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Spain at 18.
Spain Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Spain, Southwestern Europe, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, North Atlantic Ocean, Bay of Biscay, and Pyrenees Mountains, southwest of France. We published some basic information about its capital Madrid, and the Spanish nation.
Are you interested in visiting Spain and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Spain below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Spain
Did you know about Spain?
Spain has a long, exciting history. It was ruled by the Romans and later the Moors. In 1492, Christopher Columbus successfully discovered America, and the Spanish created colonies in South America. The Spanish Inquisition was one of the darkest periods in their history. They also had an empire with colonies in Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
Spain has many different regions that offer unique to travelers looking for new experiences. Situated on the southern coast of Europe, Catalonia offers a beach experience and is home to Barcelona, one of Spain’s most important cities. It also has a rich history and culture as it was ruled at various points by Romans, Visigoths, Franks, and Arabs. Seville is located in Andalusia and boasts that it’s the world’s largest producer of sugarcane!
After virtually visiting Spain, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Andorra, France, Gibraltar, Portugal, and Morocco.
If you liked our Google map and Spain information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.