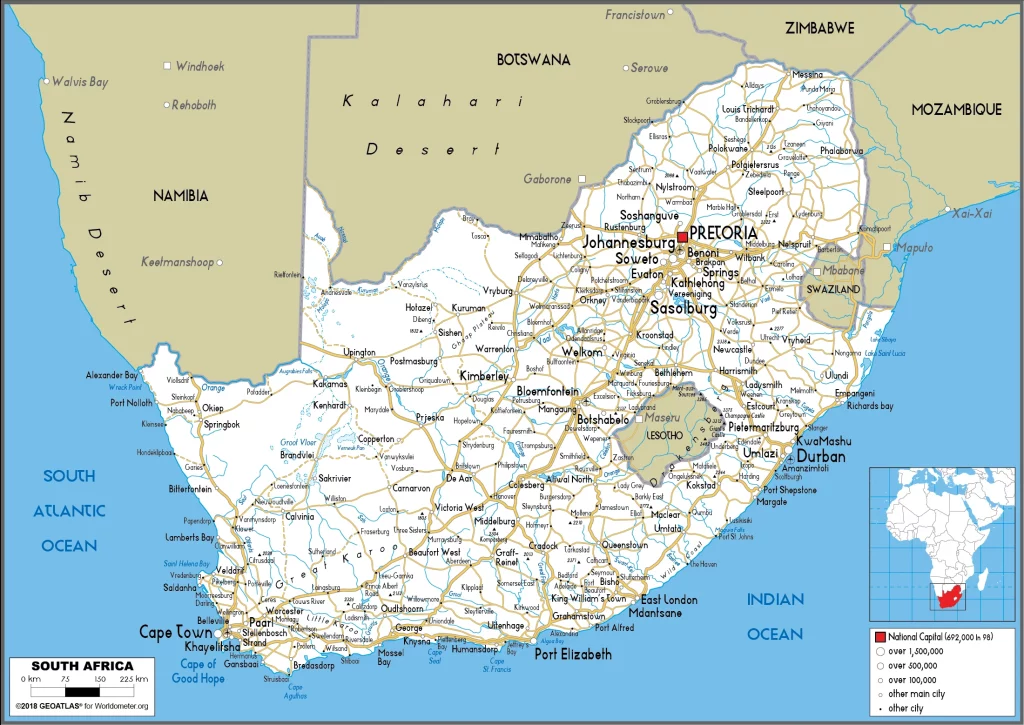
South Africa Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like South Africa, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to South Africa, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Pretoria (administrative capital), Cape Town (legislative capital), Bloemfontein (judicial capital), bordering countries like Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, Eswatini, Zimbabwe, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google Maps South Africa, Pretoria Google maps, Driving Directions South Africa, Printable Road Map.

About South Africa in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: South Africa
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of South Africa
- Former name(s): Union of South Africa
- Etymology: self-descriptive name from the country’s location on the continent; Africa is derived from the Roman designation of the area corresponding to present-day Tunisia Africa terra, which meant Land of the Afri (the tribe resident in that area), but which eventually came to mean the entire continent.
- The legal system in South Africa: mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and customary law.
- Climate: Warm, temperate, and dry. Cape Town has a Mediterranean climate. Semiarid in the west.
- The national symbols are springbok (antelope), king protea flower; national colors: red, green, blue, yellow, black, white.
- Internet TLD: .za
“In one country, the whole world”, proclaims the South African brochures. And that’s no exaggeration – the country, thirteen times our size, boasts half a hundred national parks and nature reserves, four natural and five cultural World Heritage sites. These attractions represent millions of years of African natural history.
The Vredefort Dome, dating back 2 billion years, is 190 km in diameter and is the oldest meteorite impact remains found on Earth. The protected area of the Cape Floristic Reserve is one of the richest in plant species in the world. Less than half a percent of the continent is home to one-fifth of Africa’s plant species, including many indigenous species. The Greater St. Lucia Wetland Park is the largest wetland in southern Africa, combining coastal, shallow water, estuarine, and savannah habitats. The 4.5 million-year-old hominid remains found around Sterkfontein and Swartkrand are probably the oldest. On the sandstone cliffs of uKhahlamba – Drakensberg Park, sub-Saharan Africa’s most extensive outdoor rock art gallery spanning 4,000 years is on display. On a hilltop at the confluence of the Limpopo and Shashe rivers lie the remains of Mapungubwe’s Bantu civilization, which flourished between the 10th and 14th centuries. Near Cape Town, Robben Island prison, which operated until the late 20th century, was used to hold political prisoners.
Over the last century, South Africa has produced over half of the worlds gold.
Background
Some of the earliest human remains in the fossil record are found in South Africa. By about A.D. 500, Bantu-speaking groups began settling into what is now northeastern South Africa, displacing Khoisan-speaking groups to the southwest. Dutch traders landed at the southern tip of present-day South Africa in 1652 and established a stopover point on the spice route between the Netherlands and the Far East, founding the city of Cape Town. After the British seized the Cape of Good Hope area in 1806, many of the settlers of Dutch descent (Afrikaners, also called Boers (farmers) at the time) trekked north to found their republics, Transvaal and Orange Free State. In the 1820s, several decades of wars began as the Zulus expanded their territory, moving out of what is today southeastern South Africa, clashing with other indigenous peoples, and expanding European settlements.
The discovery of diamonds (1867) and gold (1886) spurred wealth and immigration from Europe. The Anglo-Zulu War (1879) resulted in incorporation of the Zulu kingdom’s territory into the British Empire. Subsequently, the Afrikaner republics were incorporated into the British Empire after their defeat in the Second South African War (1899-1902). However, the British and the Afrikaners ruled together in 1910 under the Union of South Africa, which became a republic in 1961 after a whites-only referendum. In 1948, the National Party was voted into power and instituted a policy of apartheid billed as separate development of the races – which favored the white minority at the expense of the black majority and other non-white groups. The African National Congress (ANC) led the opposition to apartheid and many top ANC leaders, such as Nelson MANDELA, spent decades in South Africa’s prisons. Internal protests, insurgency, and boycotts by some Western nations and institutions led to the regime’s eventual willingness to negotiate a peaceful transition to majority rule.
The first multiracial elections in 1994 following the end of apartheid ushered in majority rule under an ANC-led government. South Africa has since struggled to address apartheid-era imbalances in wealth, housing, education, and health care. Jacob ZUMA became president in 2009 and was reelected in 2014 but resigned in February 2018 after numerous corruption scandals and gains by opposition parties in municipal elections in 2016. His successor, Cyril RAMAPHOSA, has progressed in reining corruption, though many challenges persist. In May 2019 national elections, the country’s sixth since the end of apartheid, the ANC won a majority of parliamentary seats, delivering RAMAPHOSA a five-year term.
Geography
Much of the interior is grassy veld. Desert in the west and far north. Mountains east, south, and west.
After 80 years of white minority rule, South Africa held its first multiracial, multiparty elections in 1994. Victory for the blacks marked the symbolic overturning of long years of apartheid.
This state is located in Southern Africa, at the southern tip of the continent of Africa, under the coordinates of 29 00 S, 24 00 E, covering an area of 1,219,090 sq km with a coastline of 2,798 km. South Africa is slightly less than twice the size of Texas.
South Africa has 5,244 km of land boundaries in total and borders (6 nations): Botswana 1969 km, Lesotho 1106 km, Mozambique 496 km, Namibia 1005 km, Eswatini 438 km, Zimbabwe 230 km.
Vast interior plateau rimmed by rugged hills and narrow coastal plain, with Ntheledi (Mafadi) 3,450 m as the highest point of South Africa, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation of 1,034 m throughout the country. With a total of 1,219,090 sq km, South Africa has 1,214,470 sq km of land and 4,620 sq km of water surface area.
The principal rivers are Orange (shared with Lesotho and Namibia) – 2,092 km, Limpopo river source (shared with Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique m) – 1,800 km, Vaal – 1,210 km. The significant watersheds for South Africa are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Orange (941,351 sq km).
South Africa surrounds Lesotho and almost completely surrounds Eswatini.
The climate in South Africa is primarily semiarid, subtropical along the east coast, with sunny days and cool nights.
When you visit South Africa, the natural hazards shall be considered: Prolonged droughts volcanism: the volcano forming Marion Island in the Prince Edward Islands, which last erupted in 2004, is South Africa’s only active volcano.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting South Africa: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, and schistosomiasis.
Current environmental issues affecting the South African people: lack of important arterial rivers or lakes requires extensive water conservation and control measures; growth in water usage outpacing supply; pollution of rivers from agricultural runoff and urban discharge; air pollution resulting in acid rain; deforestation; soil erosion; land degradation; desertification; solid waste pollution; disruption of the fragile ecosystem has resulted in significant floral extinctions.
Google Maps South Africa
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Pretoria (administrative capital); Cape Town (legislative capital); Bloemfontein (judicial capital) found under the coordinates 25 42 S, 28 13 E, applying the time zone UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital city of South Africa and the administrative, financial, and commercial center of Gauteng is Pretoria. Situated in the African bushveld, Pretoria was founded in 1886 when it replaced Mafeking as the capital of the Transvaal Colony. Its proximity to Johannesburg has made it a popular location for businesses. The capital city of South Africa and the administrative, financial, and commercial center of Gauteng is Pretoria. Situated in the African bushveld, Pretoria was founded in 1886 when it replaced Mafeking as the capital of the Transvaal Colony. Its proximity to Johannesburg has made it a popular location for businesses.
South Africa became independent on 31 May 1910 (Union of South Africa formed from four British colonies: Cape Colony, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State); 22 August 1934 (Status of the Union Act); 31 May 1961 (republic declared); 27 April 1994 (majority rule), and its national holiday is Freedom Day, 27 April (1994).
Administrative divisions: 9 provinces; Eastern Cape, Free State, Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Northern Cape, North West, Western Cape.
People and society
The majority black population now dominates politically, but the minority white community still controls the economy. A small black middle class is growing, but unemployment among blacks remains high. Over five million people are HIV-positive, but social attitudes hamper the fight against AIDS. Violent crime is a problem.
The population in South Africa is 56,978,635 (July 2021 estimate). Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected, with an average of 0.95% (2021 estimate) change. That means South Africa is the No. 26 on the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 28 years median age (27.9 years for males and 27.9 years for women), South Africa ranks No. 142 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the South African(s) (noun) or South African (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Black African 80.9%, Colored 8.8%, White 7.8%, Indian/Asian 2.5% (2018 estimate). Note: color is a term used in South Africa, including on the national census, for persons of mixed-race ancestry who developed a distinct cultural identity over several hundred years.
They speak isiZulu (official language) 25.3%, isiXhosa (official language) 14.8%, Afrikaans (official language) 12.2%, Sepedi (official language) 10.1%, Setswana (official language) 9.1%, English (official language) 8.1%, Sesotho (official language) 7.9%, Xitsonga (official language) 3.6%, siSwati (official language) 2.8%, Tshivenda (official language) 2.5%, isiNdebele (official language) 1.6%, other (includes Khoi, Nama, and San languages) 2% languages and practice the following religions: Christian 86%, ancestral, tribal, animist, or other traditional African religions 5.4%, Muslim 1.9%, other 1.5%, nothing in particular 5.2% (2015 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in South Africa: The population is concentrated along the southern and southeastern coast and inland around Pretoria. This population distribution map shows that the eastern half of the country is more densely populated than the west. In South Africa, we are talking about 67.8% (2021) of the total population is living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 9.897 million, Johannesburg (Includes Ekurhuleni), 4.710 million, Cape Town (Legislative Capital), 3.176 million, Durban, 2.655 million, Pretoria (Administrative Capital), 1.267 million, Port Elizabeth, 909,000 West Rand (2021).
Industry
Africa’s largest, most developed economy. Leading mineral producer, notably metals, diamonds, coal. Tourism is also vital. The wealth gap has widened: jobs, housing, and better access to essential services are needed to fight poverty.
South Africa is a middle-income emerging market with an abundant supply of natural resources; well-developed financial, legal, communications, energy, and transport sectors; and a stock exchange that is Africa’s most significant and among the top 20 globally. Economic growth has decelerated in recent years, slowing to an estimated 0.7% in 2017. Unemployment, poverty, and inequality – among the highest globally – remain a challenge. Official unemployment is roughly 27% of the workforce and runs significantly higher among black youth. Even though the country’s modern infrastructure supports a relatively efficient distribution of goods to major urban centers throughout the region, unstable electricity supplies retard growth. Eskom, the state-run power company, is building three new power stations and is installing new power demand management programs to improve power grid reliability but has been plagued with accusations of mismanagement and corruption and faces an increasingly high debt burden., South Africa’s economic policy has focused on controlling inflation while empowering a broader economic base; however, the country faces structural constraints that limit economic growth, such as skills shortages, declining global competitiveness, and frequent work stoppages due to strike action. The government faces growing pressure from urban constituencies to improve the delivery of essential services to low-income areas, increase job growth, and provide university-level education at affordable prices. Political infighting among South Africa’s ruling party and the volatility of the rand risk economic growth. International investors are concerned about the country’s long-term economic stability; in late 2016, most major international credit rating agencies downgraded South Africa’s international debt to junk bond status.
South Africa is rich in natural resources: gold, chromium, antimony, coal, iron ore, manganese, nickel, phosphates, tin, rare earth elements, uranium, gem diamonds, platinum, copper, vanadium, salt, natural gas.
The main industrial sectors are typically mining (the world’s largest producer of platinum, gold, chromium), automobile assembly, metalworking, machinery, textiles, iron and steel, chemicals, fertilizer, foodstuffs, and commercial ship repair.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in gold, platinum, cars, iron products, coal, manganese, diamonds (2019), partnering with these nations: China 15%, the United Kingdom 8%, Germany 7%, United States 6%, India 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $93.01 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in South Africa’s position of 42.
Land use in South Africa: 7.6% (2018 estimate) forest, 13% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 9.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 79.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.3% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 69.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 16,700 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of South Africa are sugar cane, maize, milk, potatoes, grapes, poultry, oranges, wheat, soybeans, and beef.
The country typically needs to import: crude petroleum, refined petroleum, cars and vehicle parts, gold, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 18%, Germany 11%, United States 6%, India 5% (2019) in a sum value of $77.86 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $103.12 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $108.91 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in South Africa 45.
South Africa Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about South Africa, Southern Africa, at the southern tip of the continent of Africa. We published some basic information about its capital Pretoria (administrative capital), Cape Town (legislative capital), Bloemfontein (judicial capital), and the South African nation.
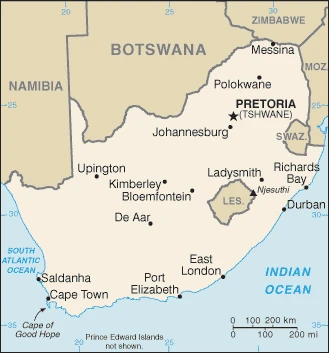
Are you interested in visiting South Africa and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of South Africa below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of South Africa
Did you know about South Africa?
South Africa is a country located in the southern part of Africa. It has a diverse culture and population, with many different languages and religions. Farmers use traditional methods to grow crops like sorghum, maize, and sugar cane. South African cuisine includes recipes using these ingredients and other foods like ostrich meat and crocodile.
After virtually visiting South Africa, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, Eswatini, and Zimbabwe.
If you liked our Google map and South Africa information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.