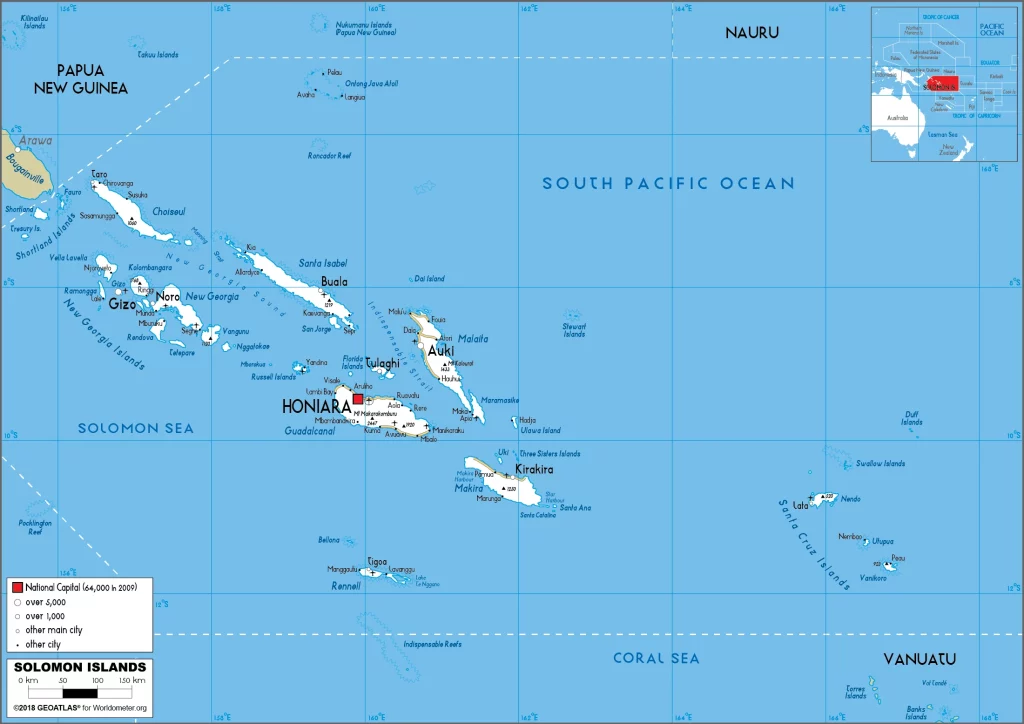
Solomon Islands Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Solomon Islands, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Solomon Islands, Oceania (27 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Honiara, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Oceanian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Solomon Islands, Honiara Google maps, Driving Directions Solomon Islands, Printable Road Map.

About the Solomon Islands in a nutshell
- The battle for Japanese-held Guadalcanal was the first major US offensive in the Pacific War during World War II.
- Conventional short form of the name: Solomon Islands
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Local long form: none
- Local short form: Solomon Islands
- Former name(s): British Solomon Islands
- Etymology: Spanish explorer Alvaro de MENDANA named the isles in 1568 after the wealthy biblical King SOLOMON mistakenly believed that the islands contained great riches.
- The legal system in the Solomon Islands: mixed legal system of English common law and customary law.
- Climate: Northern islands are hot and humid all year round; an excellent season develops farther south. November-April wet season brings cyclones.
- The national symbols are national colors: blue, yellow, green, and white.
- Internet TLD: .sb
The Solomon Islands are located in Oceania and are part of the Melanesian nation. The population of the Solomon Islands is around 690,5 thousand people. The official languages of the Solomon Islands are English and Solomons Pijin. The currency of the Solomon Islands is the Solomon Islands dollar. The climate of the Solomon Islands is tropical, with an average temperature of 27 degrees Celsius.
Background
Settlers from Papua arrived in the Solomon Islands around 30,000 years ago. About 6,000 years ago, Austronesian settlers came to the Solomon Islands, and the two groups mixed extensively. Despite significant inter-island trade, no attempts were made to unite the islands into a single political entity. In 1568, Spanish explorer Alvaro de MENDANA became the first European to spot the islands. After a failed Spanish attempt at creating a permanent European settlement on the islands in the late 1500s, the Solomon Islands remained free of European contact until 1767, when British explorer Philip CARTERET sailed by the islands. The islands were regularly visited by European explorers and American and British whaling ships into the 1800s, followed by missionaries in the 1850s. Germany declared a protectorate over the northern Solomon Islands in 1885, and the UK established a protectorate over the southern islands in 1893. In 1899, Germany transferred its Solomon Islands to the UK in exchange for the UK relinquishing all claims in Samoa.
The UK tried encouraging plantation farming, but few Europeans were willing to go to the Solomon Islands. The UK left most services – such as education and medical services – to missionaries. In 1942, Japan invaded the Solomon Islands, and significant battles against Allied forces during the Guadalcanal Campaign proved a turning point in the Pacific war. World War II destroyed large parts of the Solomon Islands, and a nationalist movement emerged near the war’s end. By 1960, the British relented to allow for some local autonomy. The islands were granted self-government in 1976 and independence two years later under Prime Minister Sir Peter KENILOREA. In 1999, longstanding ethnic tensions between ethnic Guale in Honiara and ethnic Malaitans in Honiaras suburbs erupted in civil war, leading thousands of Malaitans to take refuge in Honiara and Guale to flee the city. In 2000, newly-elected Prime Minister Manasseh SOGAVARE focused on peace agreements and distributing resources equally among groups, but his actions bankrupted the government in 2001 and led to SOGAVAREs ouster. In 2003, the Solomon Islands requested international assistance to reestablish law and order.
The Australian-led Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI), which ended in 2017, was generally effective in improving the security situation. In 2006, riots broke out in Honiara, and the city’s Chinatown burned over allegations that the prime minister took money from China. SOGAVARE was reelected prime minister for a fourth time following elections in 2019 and that same year announced the Solomon Islands would switch diplomatic recognition from Taiwan to China.
Geography
The six largest islands are volcanic, mountainous, and thickly forested. Flat coastal plains provide the only cultivable land.
The Solomons archipelago comprises several hundred coral reef islands in the southwestern Pacific. Most of the population lives on the six largest islands.
This state is located in Oceania, a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea, under the coordinates of 8 00 S, 159 00 E, covering an area of 28,896 sq km with a coastline of 5,313 km. The Solomon Islands is Slightly smaller than Maryland.
Mostly rugged mountains with some low coral atolls, Mount Popomanaseu at 2,335 m is the Solomon Islands’ highest point, and the Pacific Ocean at 0 m is the lowest point. With a total of 28,896 sq km, the Solomon Islands has 27,986 sq km of land and 910 sq km of water surface area.
Strategic location on sea routes between the South Pacific Ocean, the Solomon Sea, and the Coral Sea.
The climate in the Solomon Islands is as follows: Tropical monsoon, few temperature and weather extremes.
When you visit the Solomon Islands, the natural hazards shall be considered: Tropical cyclones, but rarely destructive; geologically active region with frequent earthquakes, tremors, and volcanic activity; tsunamis volcanism: Tinakula (851 m) has frequent eruption activity, while an eruption of Savo (485 m) could affect the capital Honiara on nearby Guadalcanal.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Solomon Islands: high (2020) degree of risk, bacterial diarrhea, and malaria.
Current environmental issues affecting the Solomon Islander people: deforestation, soil erosion, many of the surrounding coral reefs are dead or dying, effects of climate change, and rising sea levels.
Google Maps the Solomon Islands
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Honiara found under the coordinates 9 26 S, 159 57 E, applying the time zone UTC+11 (16 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Honiara is the capital city of the Solomon Islands. It’s located in the center of the country, at an elevation of about 6 meters. At full occupancy, Honiara has a population of around 45,000 people. The local government is based in the national parliament building in Regina, with all significant ministries also headquartered there. It covers an area of 15 sq km area.
Solomon Islands became independent on 7 July 1978 (from the UK), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 7 July (1978).
Administrative divisions: 9 provinces and 1 city; Central, Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Honiara, Isabel, Makira and Ulawa, Malaita, Rennell and Bellona, Temotu, Western.
People and society
Almost all Solomon Islanders are Melanesian. Animist beliefs exist alongside Christianity. Tensions are regional; Guadalcanal natives (Isatabu) fought against immigrant Malaitan workers in the 1998 – 2000 conflict, displacing thousands and ruining the economy. In 2003, Australian-led peacekeepers arrived. A new devolved “state system” has granted outlying islands more autonomy and brought a semblance of stability.
The population of the Solomon Islands is 690,598 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.75% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Solomon Islands is the No. 167 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 23.5 years median age (23.2 years for males and 23.2 years for women), the Solomon Islands ranks No. 176 on the globe’s median age list.
The people living in this country are the Solomon Islander(s) (noun) or Solomon Islander (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Melanesian 95.3%, Polynesian 3.1%, Micronesian 1.2%, other 0.3% (2009 estimate).
They speak Melanesian pidgin (in much of the country is lingua franca), English (official language but spoken by only 1%-2% of the population), 120 indigenous languages, and practice the following religions: Protestant 73.4% (Church of Melanesia 31.9%, South Sea Evangelical 17.1%, Seventh Day Adventist 11.7%, United Church 10.1%, Christian Fellowship Church 2.5%), Roman Catholic 19.6%, other Christian 2.9%, other 4%, unspecified 0.1% (2009 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the Solomon Islands: Most of the population lives along the coastal regions. About one in five live in urban areas; of these, some two-thirds reside in Honiara, the largest town and chief port. In the Solomon Islands, we are talking about 25.1% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 82,000 Honiara (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Subsistence farming and fishing sustain 75% of people. Cash crops are copra and cocoa. Gold deposits. Civil conflict bankrupted the government, closed the primary gold mine, and cut trade links. Forests have been depleted.
Most of the population depends on agriculture, fishing, and forestry for at least part of its livelihood. Most manufactured goods and petroleum products must be imported. The islands are rich in undeveloped mineral resources such as lead, zinc, nickel, and gold. Before the arrival of The Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI), severe ethnic violence, the closure of key businesses, and an empty government treasury culminated in economic collapse. RAMSIs efforts, which concluded in Jun 2017, to restore law and order and economic stability have led to modest growth as the economy rebuilds.
The Solomon Islands is rich in natural resources: Fish, forests, gold, bauxite, phosphates, lead, zinc, and nickel.
The main industrial sectors are fish (tuna), mining, and timber.
The country’s export sectors are influential in lumber, fish, aluminum, palm oil, and cocoa beans (2019), partnering with these nations: China 65%, Italy 9%, and India 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $430 million. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global export rank, values resulted in the Solomon Islands’ position of 192.
Land use in Solomon Islands: 78.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 17.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 0.7% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 3.9% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 2.9% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 0.3% (2018 estimate). The area of the irrigated land is 0 sq km NA (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the Solomon Islands are oil palm fruit, sweet potatoes, coconuts, taro, yams, fruit, pulses nes, vegetables, cocoa, and cassava.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, fish, insulated wiring, broadcasting equipment, and excavation machinery (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 24%, Australia 13%, South Korea 12%, Singapore 12%, Malaysia 10% (2019) in a sum value of $560 million. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $750 million. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $750 million. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global list of imports resulted in Solomon Islands 201.
The Solomon Islands Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the Solomon Islands, Oceania, a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea. We published some basic information about its capital Honiara, and the Solomon Islander nation.
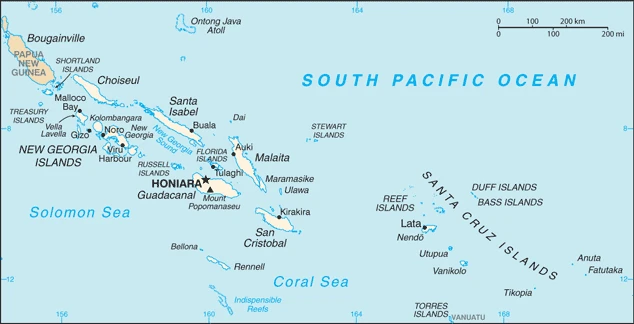
Are you interested in visiting the Solomon Islands and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Solomon Islands below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Solomon Islands
Did you know about the Solomon Islands?
The Solomon Islands are a group of over 900 islands in the South Pacific. They are home to unique animals, including the world’s most giant lizard, the monitor lizard. The Solomon Islands are also home to one of the world’s rarest birds, the critically endangered black-faced spoonbill. The spoonbill is so rare that there are only an estimated 600 individuals left in the wild. The Solomon Islands are a beautiful and unique place worth visiting.
After virtually visiting the Solomon Islands, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and the Solomon Islands information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.