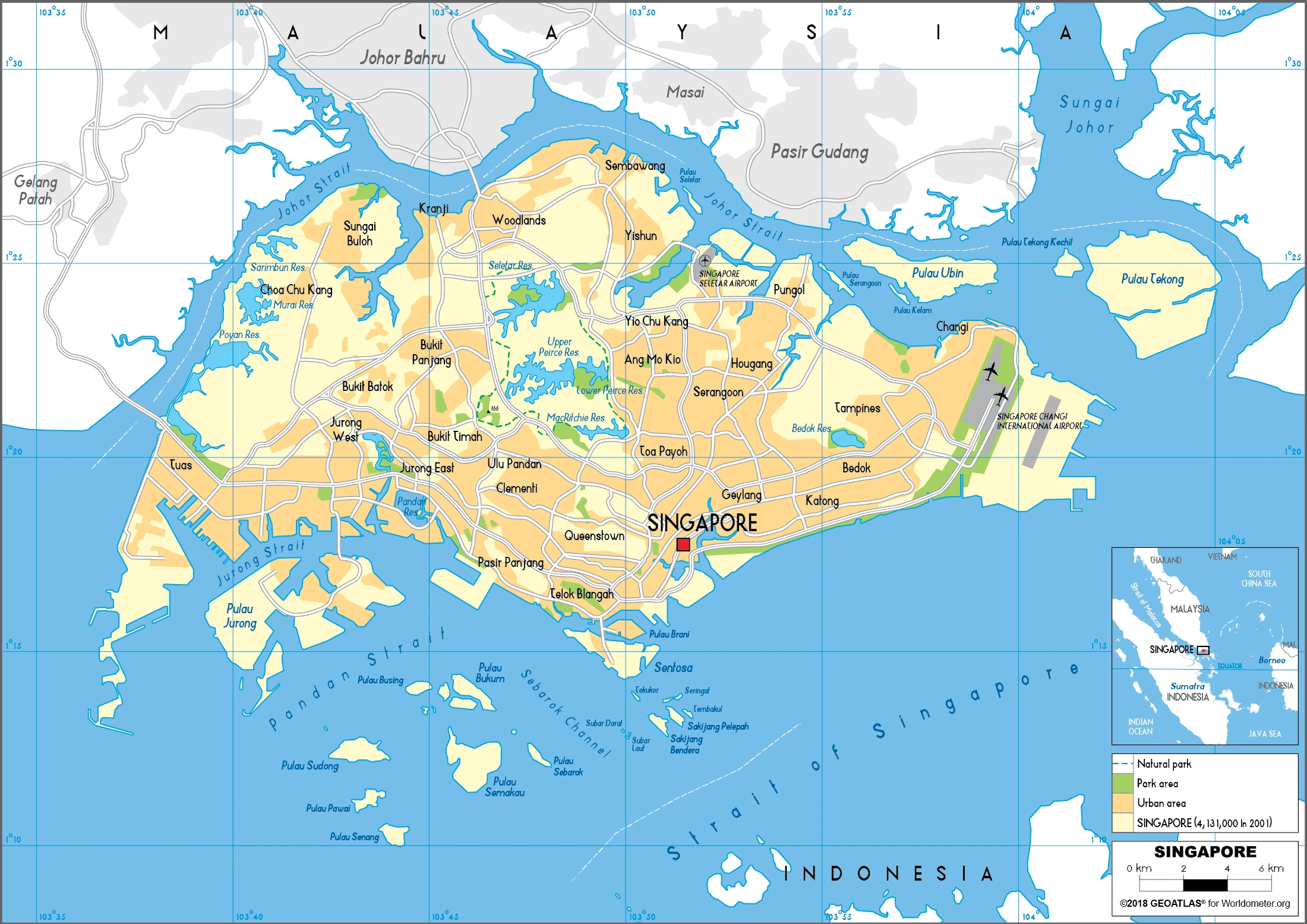
Singapore Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Singapore, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Singapore, Southeast Asia (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Singapore, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Southeastern Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Singapore, Singapore Google maps, Driving Directions Singapore, Printable Road Map.

About Singapore in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Singapore
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Singapore
- Local long form: Republic of Singapore
- Local short form: Singapore
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: name derives from the Sanskrit words Simha (lion) and Pura (city) to describe the city-states leonine symbol.
- The legal system in Singapore: English common law.
- Climate: Equatorial. Hot and humid, with heavy rainfall all year round.
- The national symbols are lion, merlion (mythical half lion-half fish creature), and orchid; national colors: red and white.
- Internet TLD: .sg
Singapore was established in the early 19th century on an island occupying an important strategic position on the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, a former British colony at a single latitude north of the equator. It became independent in 1965 after two years of loose association with neighboring Malaysia (now Malaysia). A modern metropolis of four million people, it is the gateway to world trade with Australia and a major international business center. It is a cosmopolitan city: in the crowded streets of Chinatown, fortune tellers, calligraphic sign painters, and temple sacrifices are as much a part of everyday life as the vendors selling saris, spices, and images of Hindu gods in the Little India district, or the Sultan’s Mosque muezzin’s call to prayer echoing through the tiny shops of the nearby Arab Street. Not only from the colors and sounds but also the smells wafting from the small bakeries and street stalls, a stranger can tell which neighborhood he is in even with his eyes closed. Every month of the year, the mini-state has a festival or religious holiday. And suppose you want to escape the crowded city for a nature escape. In that case, you can visit Singapore’s largest tropical rainforest, the Bükit Timah Reserve, home to 800 species of native plants, monkeys, and tropical birds.
Background
A Malay trading port known as Temasek existed on the island of Singapore by the 14th century. The settlement changed hands several times in the ensuing centuries and was eventually burned in the 17th century and fell into obscurity. The British founded modern Singapore as a trading colony on the site in 1819. It joined the Malaysian Federation in 1963 but was ousted two years later and became independent. Singapore subsequently became one of the world’s most prosperous countries with strong international trading links (its port is one of the world’s busiest cargo handled) and with a per capita GDP equal to that of the leading nations of Western Europe.
Geography
Little remains of the original vegetation on Singapore Island. The other 54 much smaller islands are little more than swampy jungle.
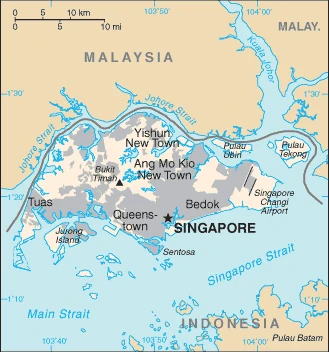
Linked to the southernmost tip of the Malay peninsula by a causeway, Singapore was established as a trading settlement in 1819. It is now one of Asias most important commercial centers.
This state is located in Southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia, under the coordinates of 1 22 N, 103 48 E, covering an area of 719 sq km with a coastline of 193 km. Singapore is Slightly more than 3.5 times the size of Washington, DC.
Low-lying, gently undulating central plateau, with Bukit Timah 166 m as the highest point of Singapore, while Singapore Strait 0 m as the lowest point in the country. With a total of 719 sq km, Singapore has 709.2 sq km of land and 10 sq km of water surface area.
The focal point for Southeast Asian sea routes; consists of about 60 islands, by far the largest of which is Pulau Ujong; land reclamation has removed many former islands and created several new ones.
The climate in Singapore is as follows: Tropical, hot, humid, and rainy, with two distinct monsoon seasons – northeastern monsoon (December to March) and Southwestern monsoon (June to September), and inter-monsoon – frequent afternoon and early evening thunderstorms.
The natural hazards shall be considered when you visit Singapore: Flash floods.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Singapore: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Singapore people: water pollution, industrial pollution; limited natural fresh water resources; limited land availability, present waste disposal problems; air pollution; deforestation; seasonal smoke/haze resulting from forest fires in Indonesia.
Google Maps Singapore
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Singapore found under the coordinates 1 17 N, 103 51 E, applying the time zone UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Singapore is a small, densely populated island city-state with over 5 million people. It is one of the most developed countries in Asia and has been an essential global finance center since World War II. Singapore’s development and prosperity can be attributed to its strategy of “self-help”, which relies on skills and education acquired by citizens themselves. The country has been described as ‘the Switzerland of Asia’. As its economy has grown, it has become known for its investment climate, efficient public transport system, and safety.
Singapore became independent on 9 August 1965 (from Malaysian Federation), and its national holiday is National Day, 9 August (1965).
Administrative divisions: no first-order administrative divisions; there are five community development councils: Central Singapore Development Council, North East Development Council, North West Development Council, South East Development Council, and South West Development Council (2019).
People and society
Chinese majority includes old-established English-speaking Straits Chinese and more recent immigrants. The median income is highest in Indian households and lowest in Malay households. Significant expatriate workforce. Aging population: cash incentives and more extended maternity leave aim to boost the birth rate. Society is highly regulated; official campaigns aim to improve public behavior. Crime is low; punishment can be severe. Living standards are among the world’s highest.
The population in Singapore is 5,866,139 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.95% (2021 estimate) change. That means Singapore is the No. 114 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 35.6 years median age (35.4 years for males and 35.4 years for women), Singapore ranks No. 82 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Singaporean(s) (noun) or Singapore (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Chinese 74.3%, Malay 13.5%, Indian 9%, other 3.2% (2020 estimate). Note: data represent population by self-identification; the population is divided into four categories: Chinese, Malay (includes indigenous Malays and Indonesians), Indian (includes Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, or Sri Lankan), and other ethnic groups (includes Eurasians, Caucasians, Japanese, Filipino, Vietnamese).
They speak English (official language) 48.3%, Mandarin (official language) 29.9%, other Chinese dialects (includes Hokkien, Cantonese, Teochew, Hakka) 8.7%, Malay (official language) 9.2%, Tamil (official language) 2.5%, other 1.4% languages and practice the following religions: Buddhist 31.1%, Christian 18.9%, Muslim 15.6%, Taoist 8.8%, Hindu 5%, other 0.6%, none 20% (2020 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Singapore: Most of the urbanization is along the southern coast, with relatively dense population clusters found in the central areas. In Singapore, we are talking about 100% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 5.992 million, Singapore (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Wealth from success as an entrepôt and center of high-tech industries, such as electronics and pharmaceuticals. Leads research in new biotechnologies. All food, energy, and water are imported. Worst-ever recession in 2008-2009.
Singapore has a highly developed and booming free-market economy. It enjoys an open and corruption-free environment, stable prices, and a per capita GDP higher than most developed countries. Unemployment is deficient. The economy depends heavily on exports, particularly electronics, petroleum products, chemicals, medical and optical devices, pharmaceuticals, and Singapore’s vibrant transportation, business, and financial services sectors. The economy contracted 0.6% in 2009 due to the global financial crisis but has continued to grow since 2010. Growth from 2012 to 2017 was slower than during the previous decade due to slowing structural growth – as Singapore reached high-income levels – and weak global demand for exports. Growth recovered to 3.6% in 2017 with a strengthening global economy. The government attempts to restructure Singapore’s economy to reduce its dependence on foreign labor, raise productivity growth, and increase wages amid slowing labor force growth and an aging population. Singapore has attracted significant investments in advanced manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and medical technology production and will continue efforts to strengthen its position as Southeast Asia’s leading financial and technology hub. Singapore is a signatory of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and a party to the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) negotiations with nine other ASEAN members plus Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, and New Zealand. In 2015, Singapore formed, with the other ASEAN members, the ASEAN Economic Community.
Singapore is rich in the following natural resources: Fish and deepwater ports.
The main industrial sectors are electronics, chemicals, financial services, oil drilling equipment, petroleum refining, biomedical products, scientific instruments, telecommunication equipment, processed food and beverages, ship repair, offshore platform construction, and entrepot trade.
The country’s export sectors are robust in integrated circuits, refined petroleum, gold, gas turbines, and packaged medicines (2019), partnering with these nations: China 15%, Hong Kong 13%, Malaysia 9%, United States 8%, Indonesia 7%, India 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $599.2 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Singapore’s position of 10.
Land use in Singapore: 3.3% (2018 estimate) forest, 95.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 0.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 0% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 0 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Singapore are poultry, eggs, vegetables, pork, duck meat, spinach, pig offals, bird eggs, pig fat, and cabbages.
The country typically needs to import: integrated circuits, refined petroleum, crude petroleum, gold, and gas turbines (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 16%, Malaysia 11%, United States 9%, Taiwan 7%, Japan 5%, Indonesia 5% (2019) in a sum value of $490.68 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $552.71 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $557.49 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Singapore 12.
Singapore Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Singapore, Southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia. We published some basic information about its capital Singapore and the Singapore nation.
Are you interested in visiting Singapore and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Singapore below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Singapore
Did you know about Singapore?
Singapore is one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world. It has a very modern culture, and it is considered one of the safest places to live. All residents have access to free healthcare and education system ranked as the best in the world, and they can get internet access through their mobile devices for only S$14 per month. There are no laws restricting social media use or other online activities in this country. It also has strict data protection laws, which means that your information won’t be sold to third parties without your knowledge.
After virtually visiting Singapore, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Indonesia and Malaysia.
If you liked our Google map and Singapore information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.