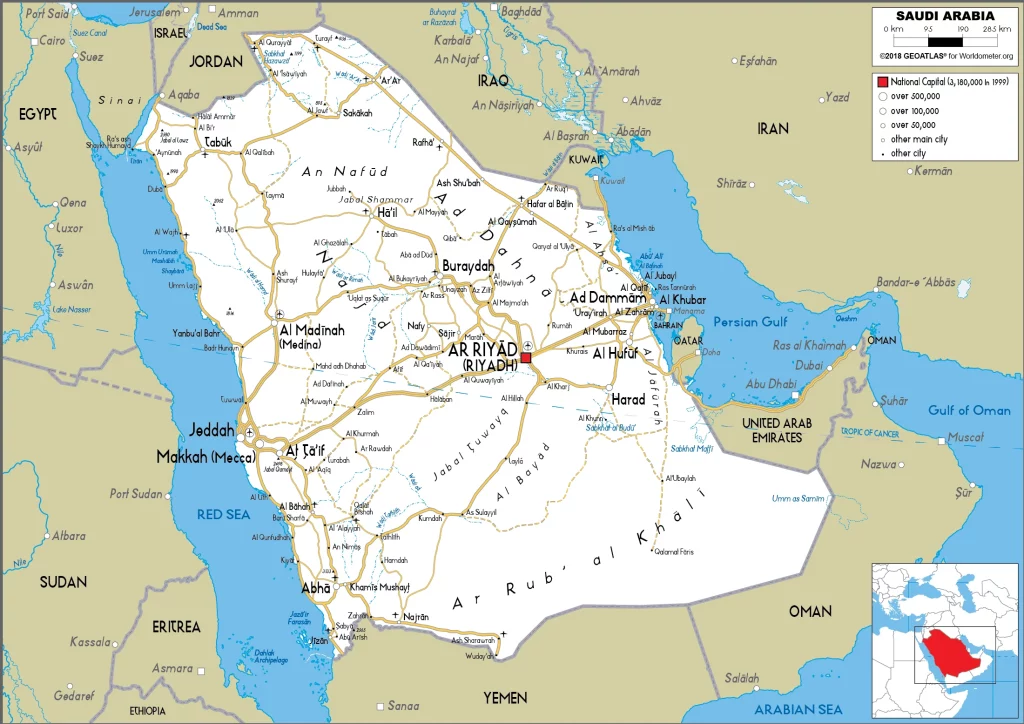
Saudi Arabia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Saudi Arabia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Saudi Arabia, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Riyadh, bordering countries like Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, UAE, Yemen, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Saudi Arabia, Riyadh Google maps, Driving Directions Saudi Arabia, Printable Road Map.

About Saudi Arabia in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Saudi Arabia
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Local long form: Al Mamlakah al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
- Local short form: Al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: named after the country’s ruling dynasty, the House of Saud; the name Arabia can be traced back many centuries B.C. The ancient Egyptians referred to the region as Ar Rabi.
- The legal system in Saudi Arabia: Islamic (sharia) legal system with some Egyptian, French, and customary law elements.
- Climate: In summer, temperatures often soar above 118°F (48°C), but in winter, they may fall below freezing. Rainfall is rare.
- The national symbols are palm trees surmounting two crossed swords; the national colors: are green and white.
- Internet TLD: .sa
The extremely rich desert kingdom is also not a paradise for solo travelers looking for a cheap destination: entry visas are only available to business visitors, pilgrims, or members of a tourist group on an expensive special tour organized by a local travel agency. So Saudi Arabia is not yet rich in tourist attractions in the traditional sense. Riyadh has been the country’s capital since 1932, but until the 1970s, it was second only to Jeddah. But then, thanks to the oil crisis, the country’s revenues multiplied, and the construction that began transformed the capital into a veritable ‘techno oasis’: a veritable glass, steel, and concrete giant. The city’s almost only traditional attraction is the camel market. Jeddah, the ‘Paris of Arabia’, on the Red Sea coast, is one of the rare Saudi cities that has developed around its historic old town rather than on it. Its 200-year-old local history museum is built of Red Sea coral, and the Jeddah Museum houses an archaeological and ethnographic collection. The route to Mecca, the birthplace of the religious founder Mohammed, a holy city sheltered from world tourism and infidels, is mainly via the modern airport of Jeddah. The holy sites around the Islamic holy city, and the city itself, are only accessible to true pilgrims. Gyula Germanus, our renowned explorer of the East, converted to Islam and was able to enter the city that houses the Kaaba stone. Muslims turn to Mecca to pray; every true Muslim makes a pilgrimage to the Kaba Stone once in their life. Taif, a summer capital with a pleasant climate, hiding in the hills above Mecca, is open to foreigners. Its central mosque is a fine example of sophisticated Islamic architecture. The Shubra Palace, built at the end of the 19th century, is the summer residence of the Saudi kings and houses the city museum. The town of Najran, in the south-western corner of the country, on the Yemeni border, has been inhabited for 4,000 years. The former caravan town is now an oasis for smugglers.
Three million Muslims a year make the hajj (pilgrimage) to the holy city of Mecca. Only practicing Muslims are allowed inside the city.
Background
Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and home to Islam’s two holiest shrines, Mecca and Medina. The king’s official title is the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques. The modern Saudi state was founded in 1932 by ABD AL-AZIZ bin Abd al-Rahman Al SAUD (Ibn Saud) after a 30-year campaign to unify most of the Arabian Peninsula. One of his male descendants rules the country today, as required by the country’s 1992 Basic Law. Following Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait in 1990, Saudi Arabia accepted the Kuwaiti royal family and 400,000 refugees while allowing Western and Arab troops to deploy on its soil for the liberation of Kuwait the following year. The continuing presence of foreign troops on Saudi soil after the liberation of Kuwait became a source of tension between the royal family and the public until all operational U.S. troops left the country in 2003. Major terrorist attacks in May and November 2003 spurred a strong ongoing campaign against domestic terrorism and extremism. U.S. troops returned to the Kingdom in October 2019 after attacks on Saudi oil infrastructure. From 2005 to 2015, King ABDALLAH bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud incrementally modernized the Kingdom. Driven by personal ideology and political pragmatism, he introduced a series of social and economic initiatives, including expanding employment and social opportunities for women, attracting foreign investment, increasing the role of the private sector in the economy, and discouraging businesses from hiring foreign workers. These reforms have accelerated under King SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz, who ascended to the throne in 2015 and has since lifted the Kingdom’s ban on women driving and allowed cinemas to operate for the first time in decades.
Saudi Arabia saw some protests during the 2011 Arab Spring but not the level of bloodshed seen in protests elsewhere in the region. Shia Muslims in the Eastern Province protested primarily against the detention of political prisoners, endemic discrimination, and Bahraini and Saudi Government actions in Bahrain. Riyadh took a cautious but firm approach by arresting some protesters but releasing most of them quickly and using its state-sponsored clerics to counter political and Islamist activism. The government held its first-ever elections in 2005 and 2011 when Saudis went to the polls to elect municipal councilors. In December 2015, women were allowed to vote and stand as candidates for the first time in municipal council elections, with 19 women winning seats. After King SALMAN ascended to the throne in 2015, he placed the first next-generation prince, MUHAMMAD BIN NAYIF bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud, as Crown Prince. He designated his son, MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud, as the Deputy Crown Prince. In March 2015, Saudi Arabia led a coalition of 10 countries in a military campaign to restore the legitimate government of Yemen, which had been ousted by Huthi forces allied with former president ALI ABDULLAH al-Salih. The war in Yemen has drawn international criticism for civilian casualties and its effect on its dire humanitarian situation.
In December 2015, then-Deputy Crown Prince MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN announced Saudi Arabia would lead a 34-nation Islamic Coalition to fight terrorism (it has since grown to 41 nations). In May 2017, Saudi Arabia inaugurated the Global Center for Combatting Extremist Ideology (also known as Etidal) as part of its ongoing efforts to counter violent extremism. In June 2017, King SALMAN elevated MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN to Crown Prince. The country remains a leading producer of oil and natural gas and holds about 16% of the world’s proven oil reserves as of 2015. The government continues to pursue economic reform and diversification, particularly since Saudi Arabia’s accession to the WTO in 2005, promoting foreign investment in the Kingdom. In April 2016, the Saudi Government announced a broad set of socio-economic reforms known as Vision 2030. Low global oil prices throughout 2015 and 2016 significantly lowered Saudi Arabia’s governmental revenue. The government cut water, electricity, and gasoline subsidies, reduced government employee compensation packages, and announced limited new land taxes. In coordination with OPEC and some key non-OPEC countries, Saudi Arabia agreed to cut oil output in early 2017 to regulate supply and help elevate global prices.
Geography
Mostly desert or semidesert plateau. Mountain ranges in the west run parallel to the Red Sea and drop steeply to a coastal plain.
Occupying most of the Arabian Peninsula, Saudi Arabia covers an area the size of western Europe. It is the worlds largest oil producer and has a significant petrochemicals industry.
This state is located in the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen, under the coordinates of 25 00 N, 45 00 E, covering an area of 2,149,690 sq km with a coastline of 2,640 km. Saudi Arabia is Slightly more than one-fifth the size of the U.S.
Saudi Arabia has 4,272 km of land boundaries in total and borders (7 nations): Iraq 811 km, Jordan 731 km, Kuwait 221 km, Oman 658 km, Qatar 87 km, UAE 457 km, Yemen 1307 km.
Mostly sandy desert, with as Sarawat range, 3,000 m as the highest point of Saudi Arabia, while Persian Gulf 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 665 m throughout the country. With a total of 2,149,690 sq km, Saudi Arabia has 2,149,690 sq km of land and 0 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: The significant watersheds for Saudi Arabia are the Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf), Tigris, and Euphrates (918,044 sq km).
Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the world without a river; extensive coastlines on the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea allow for considerable shipping (especially of crude oil) through the Persian Gulf and Suez Canal.
The climate in Saudi Arabia is as follows: Harsh, desert with great temperature extremes.
When you visit Saudi Arabia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Frequent sand and dust storms and volcanism: despite many volcanic formations, there has been little activity in the past few centuries; volcanoes include Harrat Rahat, Harrat Khaybar, Harrat Lunayyir, and Jabal Yar.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Saudi Arabia: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Saudi or Saudi Arabian people: desertification, depletion of underground water resources, the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies have prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities, coastal pollution from oil spills; air pollution; waste management.
Google Maps Saudi Arabia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Riyadh found under the coordinates 24 39 N, 46 42 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia, located in the northwest of the Arabian Peninsula. It is home to millions of people, making it one of the most populated cities in the Middle East. Riyadh is also famous for its huge malls, which attract people from all over Saudi Arabia to shop. It has been the country’s seat of government since King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud designated it to be the nation’s capital in 1957, and today it holds about half of the total population of Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia became independent on 23 September 1932 (unification of the Kingdom), and its national holiday is Saudi National Day (Unification of the Kingdom), 23 September (1932).
Administrative divisions: 13 regions (manatiq, singular – mintaqah); Al Bahah, Al Hudud ash Shamaliyah (Northern Border), Al Jawf, Al Madinah al Munawwarah (Medina), Al Qasim, Ar Riyad (Riyadh), Ash Sharqiyah (Eastern), Asir, Hail, Jazan, Makkah al Mukarramah (Mecca), Najran, Tabuk.
People and society
Most Saudis are Sunni Muslims who embrace sharia (Islamic law) and follow Islam’s strictly orthodox Wahhabi interpretation in their daily lives. Women are obliged to wear the veil, cannot hold a driver’s license, and have no role in public life. The al-Saud family rules with absolute power. Supported by the religious establishment, it controls all political life and makes few concessions to any calls for broader public participation.
The population in Saudi Arabia is 34,783,757 (July 2021 estimate). Note: immigrants make up 38.3% of the total population, according to U.N. data (2019), with an average of 1.62% (2021 estimate) change. That means Saudi Arabia is the No. 41 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 30.8 years median age (33 years for males and 33 years for women), Saudi Arabia ranks No. 119 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Saudi(s) (noun) or Saudi or Saudi Arabian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Arab 90%, Afro-Asian 10%.
They speak Arabic (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Muslim (official; citizens are 85-90% Sunni and 10-15% Shia), other (includes Eastern Orthodox, Protestant, Roman Catholic, Jewish, Hindu, Buddhist, and Sikh) (2012 estimate) note: despite having a large expatriate community of various faiths (more than 30% of the population), most forms of public religious expression inconsistent with the government-sanctioned interpretation of Sunni Islam are restricted; non-Muslims are not allowed to have Saudi citizenship, and non-Muslim places of worship are not permitted (2013).
We can conclude the following about the population in Saudi Arabia: Historically, a population that was primarily nomadic or semi-nomadic, the Saudi population has become more settled since petroleum was discovered in the 1930s. Most of the economic activities – and with it the country’s population – are concentrated in a wide area across the middle of the peninsula, from ad Dammam in the East, through Riyadh in the interior, to mecca-medina in the west near the red sea. In Saudi Arabia, we talk about 84.5% (2021) of the total population lives in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 7.388 million, Riyadh (capital city), 4.697 million, Jeddah, 2.079 million, Mecca, 1.518 million, Medina, 1.279 million, Ad Dammam, 1.279 million, Hufuf-Mubarraz (2021).
Industry
Vast oil and natural gas reserves. A third of workers are foreign. Attractive jobs for young Saudis are scarce, however.
Saudi Arabia has an oil-based economy with strong government controls over major economic activities. It possesses about 16% of the world’s proven petroleum reserves, ranks as the largest exporter of petroleum, and plays a leading role in OPEC. The petroleum sector accounts for roughly 87% of budget revenues, 42% of GDP, and 90% of export earnings., Saudi Arabia is encouraging the growth of the private sector to diversify its economy and employ more Saudi nationals. Approximately 6 million foreign workers play an essential role in the Saudi economy, particularly in the oil and service sectors; at the same time, however, Riyadh is struggling to reduce unemployment among its nationals. Saudi officials are mainly focused on employing its large youth population. In 2017, the Kingdom incurred a budget deficit estimated at 8.3% of GDP, financed by bond sales and drawing down reserves.
Although the Kingdom can finance high deficits for several years by drawing down its considerable foreign assets or borrowing, it has cut capital spending, reduced subsidies on electricity, water, and petroleum products, and recently introduced a value-added tax of 5%. In January 2016, Crown Prince and Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN announced that Saudi Arabia intends to list shares of its state-owned petroleum company, ARAMCO – another move to increase revenue and outside investment. The government has also looked at privatization and diversification of the economy more closely in the wake of a diminished oil market. Historically, Saudi Arabia has focused diversification efforts on power generation, telecommunications, natural gas exploration, and petrochemical. More recently, the government has approached investors about expanding the role of the private sector in the health care, education, and tourism industries. While Saudi Arabia has emphasized their diversification goals for some time, current low oil prices may force the government to make more drastic changes ahead of its long-run timeline.
Saudi Arabia is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, and copper.
The main industrial sectors are crude oil production, petroleum refining, basic petrochemicals, ammonia, industrial gases, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), cement, fertilizer, plastics, metals, commercial ship repair, commercial aircraft repair, and construction.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in crude petroleum, refined petroleum, polymers, industrial alcohols, and natural gas (2019), partnering with these nations: China 20%, India 11%, Japan 11%, South Korea 9%, United States 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $184.11 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). A global rank of the export values resulted in Saudi Arabia’s position of 32.
Land use in Saudi Arabia: 0.5% (2018 estimate) forest, 18.8% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1.5% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 80.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 79.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 16,200 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Saudi Arabia are milk, dates, poultry, fruit, watermelons, barley, wheat, potatoes, eggs, and tomatoes.
The country typically needs to import: cars, broadcasting equipment, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, and telephones (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 18%, United Arab Emirates 12%, United States 9%, Germany 5% (2019) in a sum value of $179.8 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $218.94 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $209.59 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Saudi Arabia 31.
Saudi Arabia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Saudi Arabia, the Middle East bordering the Persian Gulf, and the Red Sea north of Yemen. We published some basic information about its capital Riyadh, and the Saudi or Saudi Arabian nation.
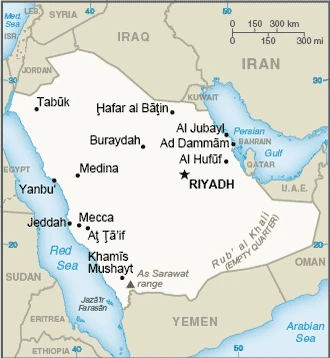
Are you interested in visiting Saudi Arabia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Saudi Arabia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Saudi Arabia
Did you know about Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia is a Middle Eastern country bordered by the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf. It is a significant oil producer and has the second-largest oil reserves. The country is also home to Islam’s holiest sites, Mecca and Medina. Saudi Arabia has a population of over 34 million people.
Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia and is its largest city. It is located in the central-western part of the country on the Arabian Peninsula. The climate in Riyadh is hot and dry, with temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius. The city is home to several important government buildings, embassies, and large businesses.
After virtually visiting Saudi Arabia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, UAE, and Yemen.
If you liked our Google map and Saudi Arabia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.