Panama Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Panama, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Panama, Central America and the Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Panama City, bordering countries like Colombia, Costa Rica, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Panama, Panama City Google maps, Driving Directions Panama, Printable Road Map.

About Panama in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Panama
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Panama
- Local long form: Republica de Panama
- Local short form: Panama
- Etymology: named after the capital city, named after a former indigenous fishing village.
- The legal system in Panama: civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court of Justice.
- Climate: Hot and humid, with heavy rainfall in the May-December wet season. Cooler at high altitudes.
- The national symbols are the harpy eagle; the national colors: are blue, white, and red.
- Internet TLD: .pa
Panama is the southernmost country in the entire Central American continent and the closest to the equator. It has the narrowest land bridge in the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The first plans to cut the isthmus date back to 1529, when the Church blocked the project. In 1879, France’s attempt to build the bridge failed because of bribes, embezzlement, and ‘Panamaze’. After another quarter of a century, the United States helped to create the independent state of Panama in the former Colombian isthmus and then bought the 10-mile-wide strip of land for $10 million, on which the gigantic construction could begin in 1904.
In August 1914, the great dream was finally realized: the Panama Canal was completed. The difference in water levels between the two oceans of about one and a half meters and the Culebra watershed were bridged by constructing a multi-stage lock system. On 31 December 1999, the United States handed over the Canal Zone to the Republic of Panama. Since the 16th century, two of Panama’s world cultural heritage sites have guarded the two terminals of the shortest route across the isthmus (and, since 1914, the canal): Panama City, which controlled the Pacific, and the fortress of Portobelo, which controlled the Caribbean port.
At the ‘other three ends’ of the country are three natural world heritage sites: to the west, in the highest and most massive range of the Central American Cordillera, the Talamanca Mountains, well over 3,700 m above sea level, is La Amistad International Park, which belongs to both Costa Rica and Panama. Its special protection is due to its pristine virgin forests and unparalleled biodiversity. In the eastern corner of the country, the impenetrable tropical rainforest, swamps, sandy beaches, and sandstone beaches of Darién National Park cover almost 6,000 km2, at the junction of the isthmus and the South American mainland, and in the south, Panama’s newest natural world heritage site, Coiba National Park, which occupies 38 islands in the Gulf of Chiriqui and the surrounding maritime area.
The Panama Canal shortens the sea route between the east coast of the US and Japan by 3000 miles (4800 km).
Background
Explored and settled by the Spanish in the 16th century, Panama broke with Spain in 1821 and joined a union of Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela – named the Republic of Gran Colombia. When the latter dissolved in 1830, Panama remained part of Colombia. With US backing, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903. It promptly signed a treaty with the US allowing for the construction of a canal and US sovereignty over a strip of land on either side of the structure (the Panama Canal Zone). The Panama Canal was built by the US Army Corps of Engineers between 1904 and 1914. In 1977, an agreement was signed to transfer the Canal from the US to Panama by the end of the century. Certain portions of the Zone and increasing responsibility for the Canal were turned over in the subsequent decades. With US help, dictator Manuel NORIEGA was deposed in 1989. The entire Panama Canal, the area supporting the Canal, and the remaining US military bases were transferred to Panama by 1999. An ambitious expansion project to more than double the Canal’s capacity – allowing for more Canal transits and larger ships – was carried out between 2007 and 2016.
Geography
Lowlands along both coasts, with savanna-covered plains and rolling hills. Mountainous interior. Swamps and rainforests in the east.
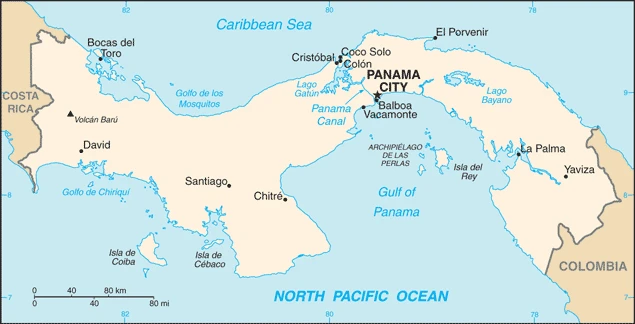
A Spanish colony until 1821, Panama is the southernmost country in Central America. The colossal Panama Canal (under US control until 2000) links the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
This state is located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica, under the coordinates of 9 00 N, 80 00 W, covering an area of 75,420 sq km with a coastline of 2,490 km. Panama is slightly smaller than South Carolina.
Panama has 687 km of land boundaries and borders (2 nations): Colombia 339 km, and Costa Rica 348 km.
Interior mostly steep, rugged mountains with dissected, upland plains, coastal plains with rolling hills, with Volcan Baru 3,475 m as the highest point of Panama, while Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 360 m throughout the country. With 75,420 sq km, Panama has 74,340 sq km of land and 1,080 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Laguna de Chiriqui – 900 sq km (saltwater lake).
Strategic location on the eastern end of isthmus forming land bridge connecting North and South America; controls Panama Canal that links North Atlantic Ocean via the Caribbean Sea with North Pacific Ocean.
The climate in Panama is as follows: Tropical maritime, hot, humid, cloudy, prolonged rainy season (May to January), and short dry season (January to May).
When you visit Panama, the natural hazards shall be considered: Occasional severe storms and forest fires in the Darien area.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Panama: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea, dengue fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Panamanian people: water pollution from agricultural runoff threatens fishery resources; deforestation of tropical rain forest; land degradation and soil erosion threatens siltation of the Panama Canal; air pollution in urban areas; mining threatens natural resources.
Google Maps Panama
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Panama City is found under the coordinates 8 58 N, 79 32 W, applying the time zone UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Panama City is the capital of Panama and its largest city. It is located on the North Pacific coast of Central America. Panama City is a hub for finance, commerce, and trade between South America and North America. It is also known for the Canal, which links the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Panama became independent on 3 November 1903 (from Colombia; it became independent from Spain on 28 November 1821), and its national holiday is Independence Day (Separation Day), 3 November (1903).
Administrative divisions: 10 provinces (provincias, singular – provincia) and 4 indigenous regions (comarcas); Bocas del Toro, Chiriqui, Cocle, Colon, Darien, Embera-Wounaan, Guna Yala, Herrera, Los Santos, Naso Tjer Di, Ngobe-Bugle, Panama, Panama Oeste, Veraguas.
People and society
A multiethnic society dominated by people of mixed SpanishAmerindian origin (mestizo). Amerindians live in remote areas. The Panama Canal and former US military bases (the last of which closed in 1999) have given society a cosmopolitan outlook, but Catholicism and the extended family remain strong. Wealth is unevenly divided. Money laundering, narcotics trafficking, and corruption are rife.
The population in Panama is 3,928,646 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.16% (2021 estimate) change. That means Panama is the No. 129 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 30.1 years median age (29.6 years for males and 29.6 years for women), Panama ranks No. 122 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Panamanian(s) (noun) or Panamanian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Mestizo (mixed Amerindian and White) 65%, Native American 12.3% (Ngabe 7.6%, Kuna 2.4%, Embera 0.9%, Bugle 0.8%, other 0.4%, unspecified 0.2%), Black or African descent 9.2%, Mulatto 6.8%, White 6.7% (2010 estimate).
They speak Spanish (official language), indigenous languages (including Ngabere (or Guaymi), Buglere, Kuna, Embera, Wounaan, Naso (or Teribe), and Bri Bri), Panamanian English Creole (similar to Jamaican English Creole; a mixture of English and Spanish with elements of Ngabere; also known as Guari Guari and Colon Creole), English, Chinese (Yue and Hakka), Arabic, French Creole, other (Yiddish, Hebrew, Korean, Japanese); languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 48.6%, Evangelical 30.2%, other 4.7%, agnostic 0.2%, atheist 0.2%, none 12.3%, unspecified 3.7% (2018 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Panama: Population is concentrated towards the center of the country, particularly around the canal, but a sizeable segment of the populace also lives in the far west around David. The eastern third of the country is sparsely inhabited. In Panama, we are talking about 68.8% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.899 million, Panama City (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Colón Free Trade Zone: worlds second-largest. Income from the canal (expansion project underway) and merchant ships sailing under the flag of Panama. Banana and shrimp exports.
Panama’s dollar-based economy rests primarily on a well-developed services sector that accounts for more than three-quarters of GDP. Services include operating the Panama Canal, logistics, banking, the Colon Free Trade Zone, insurance, container ports, flagship registry, and tourism, and Panama is a center for offshore banking. Panama’s transportation and logistics services sectors and infrastructure development projects have boosted economic growth; however, public debt surpassed $37 billion in 2016 because of excessive government spending and public works projects. The US-Panama Trade Promotion Agreement was approved by Congress and signed into law in October 2011, and entered into force in October 2012., Future growth will be bolstered by the Panama Canal expansion project that began in 2007 and was completed in 2016 at $5.3 billion – about 10-15% of current GDP. The expansion project more than doubled the Canal’s capacity, enabling it to accommodate high-capacity vessels such as tankers and neo-Panamax vessels too large to traverse the existing canal. The US and China are the top users of the Canal., Strong economic performance has not translated into broadly shared prosperity, as Panama has the second-worst income distribution in Latin America. About one-fourth of the population lives in poverty; however, from 2006 to 2012, poverty was reduced by 10 percentage points.
Panama is rich in the following natural resources: Copper, mahogany forests, shrimp, and hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are construction, brewing, cement, other construction materials, and sugar milling.
The country’s export sectors are robust in refined petroleum, copper, bananas, ships, coal tar oil, and packaged medicines (2019), partnering with these nations: Ecuador 20%, Guatemala 14%, China 8%, United States 6%, Netherlands 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $20.18 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Panama’s position of 82.
Land use in Panama: 43.6% (2018 estimate) forest, 25.9% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 7.3% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 30.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 2.5% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 20.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 321 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Panama are sugar cane, bananas, rice, poultry, milk, plantains, pineapples, maize, beef, and pork.
The country typically needs to import: ships, refined petroleum, crude petroleum, tanker ships, and packaged medicines (2019), partnering with the following nations: China, 21%, the United States, 19%, Japan, 16%, Colombia, 6%, Ecuador 5% (2019) in a sum value of $17.41 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $27.38 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $28.9 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). Note: includes the Colon Free Zone. This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Panama 92.
Panama Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Panama, Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. We published some basic information about its capital Panama City, and the Panamanian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Panama and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Panama below to overview the route network.
Printable map of Panama
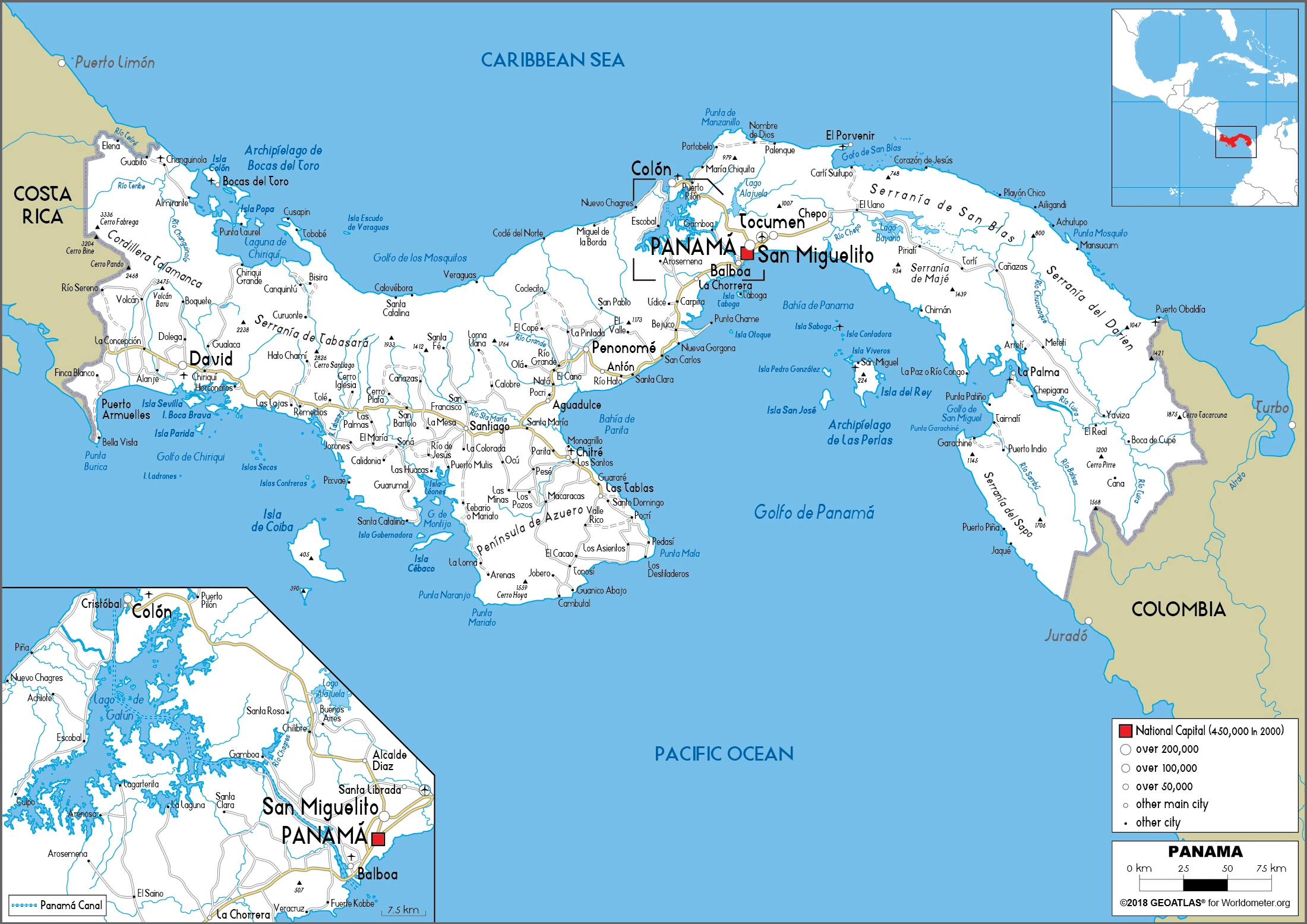
Did you know about Panama?
Panama is a small country located in Central America. It has just over 3,9 million people, making it the smallest country in the region and the world’s fourth-smallest by total area. Costa Rica borders the country to the north, Colombia to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. The Panama Canal provides easy access to shipping routes between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Panama is home to many exciting attractions, including the Panama Canal. The canal is one of the most important transportation links globally and was built by the United States to connect North America with Asia.
Did you know that Panama is one of the most popular tax havens globally? This small country has a lot to offer, including low taxes and a stable government. Panama is also well known for its safe and secure environment. The country has a low crime rate, and it’s considered one of the most peaceful countries in the world. It’s also a great place to do business because of its stable economy and efficient government.
After virtually visiting Panama, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Colombia and Costa Rica.
If you liked our Google map and Panama information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.
