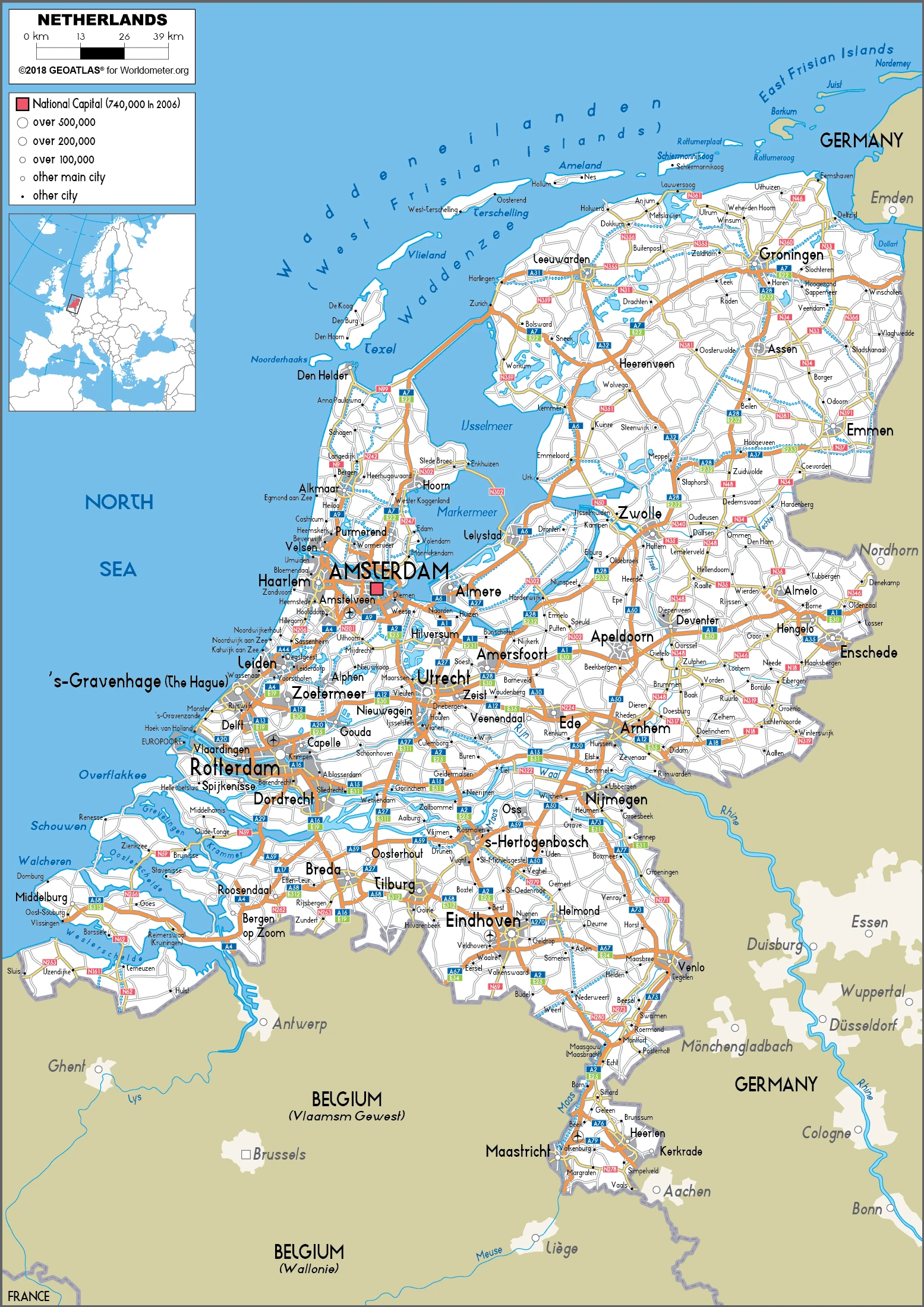
Netherlands Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Netherlands, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Netherlands, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Amsterdam, bordering countries like Belgium, Germany, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Netherlands, Amsterdam Google maps, Driving Directions Netherlands, Printable Road Map.

About the Netherlands in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Netherlands
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Local long form: Koninkrijk der Nederlanden
- Local short form: Nederland
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the country name means the lowlands and refers to the geographic features of the land being both flat and downriver from higher areas (i.e., at the estuaries of the Scheldt, Meuse, and Rhine Rivers; only about half of the Netherlands is more than 1 meter above sea level).
- The legal system in the Netherlands: civil law system is based on the French system; the constitution does not permit judicial review of acts of the States-General.
- Climate: Mild, rainy winters, and cool summers. Gales from the North Sea is expected in fall and winter.
- The national symbols are lion and tulip, while the national color: is orange.
- Internet TLD: .nl
Holland was once underwater, and today a significant portion of the country is below sea level. Some of this land has risen over time and been recovered through Dutch ingenuity or hard work. Today, Holland has spectacular landscapes and green areas with silver accents throughout.
Amsterdam is one of the highlights of the Netherlands and is also a popular destination among backpackers worldwide. It’s a central cultural and economic hub that offers easy access to other noteworthy towns, such as Haarlem, Zandvoort, Zaanse Schans, Volendam, and Marken.
Visit Delft, home of The Dutch Royalty and Vermeer. Not to mention Leiden, the heart of the Pilgrim Fathers.
The Zuidersee, once a rippling lake where Lake IJssel used to be, is now cut off from the sea by a 30-kilometer-long barrier, and the cut-off areas are being drained and cultivated – polders are being laid. In the Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt estuaries, storm surges did not spare the settlements on the islands between the rivers even in the second half of the 20th century. In the southwestern province of Zeeland in the Netherlands, the Delta Plan was implemented by damming the estuaries between the islands.
The constant struggle with the sea is also a constant reminder of the Netherlands’ world heritage. Schokland and its environs, which once extended into the Zuiderseeb as a peninsula, were conquered by the sea in the 15th century and only reclaimed in the 20th century during pondering. Amsterdam’s 135 km long system of dykes is now the only one of 45 dykes that once existed throughout the country. The pumping windmills of Kinderdijk and Elshout testify to the industrial development and ingenuity of the inhabitants of the medieval Netherlands, while the Wouda pumping station near Lemmer is the largest ever built and still steam-powered – a feat of early 20th-century engineering. The Beemster polder was first conquered in the 17th century and has remained almost untouched by modernization since then – the oldest drying area in the Netherlands. Its settlements are great examples of neoclassical and Renaissance design. Modern architecture is represented by the Rietveld Schröder House in Utrecht, built-in 1924, a World Heritage Site.
In 2002, the Netherlands became the first country to legalize euthanasia.
Background
The Dutch United Provinces declared their independence from Spain in 1579. During the 17th century, they became a leading seafaring and commercial power, with settlements and colonies worldwide. After a 20-year French occupation, the Kingdom of the Netherlands was formed in 1815. In 1830, Belgium seceded and formed a separate kingdom. The Netherlands remained neutral in World War I but suffered German invasion and occupation in World War II. The Netherlands is a modern, industrialized nation and a significant exporter of agricultural products. The country was a founding member of NATO and the EEC (now the EU) and participated in introducing the euro in 1999. In October 2010, the former Netherlands Antilles was dissolved, and the three most minor islands – Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba – became special municipalities in the Netherlands administrative structure. The larger islands of Sint Maarten and Curacao joined the Netherlands and Aruba as constituent countries forming the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
In February 2018, the Sint Eustatius island council (governing body) was dissolved and replaced by a government commissioner to restore the integrity of public administration. According to the Dutch Government, the intervention will be as short and as long as needed.
Geography
Mainly flat, with 27% of the land below sea level and protected by dunes, dikes, and canals. There are a few low hills in the south and east.
Astride the delta of five major rivers in northwest Europe, the Netherlands built its historic wealth on maritime trade. Rotterdam is Europes largest port.
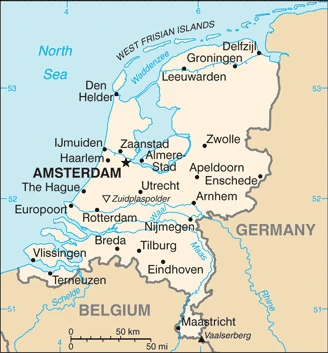
This state is located in Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between Belgium and Germany, under the coordinates of 52 31 N, 5 46 E, covering an area of 41,543 sq km with a coastline of 451 km. The Netherlands is Slightly less than twice the size of New Jersey.
The Netherlands has 1,053 km of land boundaries and borders (2 nations): Belgium 478 km, Germany 575 km.
Mostly coastal lowland and reclaimed land (polders), some hills in the southeast, with Mount scenery (on the island of Saba in the Caribbean, now considered an integral part of the Netherlands following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles) 862 m as the highest point of Netherlands, while Zuidplaspolder -7 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 30 m throughout the country. With a total of 41,543 sq km, the Netherlands has 33,893 sq km of land and 7,650 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Rhine (shared with Switzerland, Germany, and France) – 1,233 km. The significant watersheds for the Netherlands are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Rhine-Maas (198,735 sq km).
Located at the mouths of three major European rivers (the Rhine, Maas or Meuse, and Schelde), about a quarter of the country lies below sea level, and only about half of the land exceeds one meter above sea level.
The climate in the Netherlands is as follows: Temperate, marine, cool summers, and mild winters.
When you visit the Netherlands, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flooding volcanism: mount scenery (887 m), located on the island of Saba in the Caribbean, last erupted in 1640; round hill (601 m), a dormant volcano is also known as the quill, is located on the island of st. Eustatius in the Caribbean; these islands are at the northern end of the volcanic island arc of the lesser Antilles that extends south to Grenada.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Netherlands: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Dutch people: water and air pollution are significant environmental problems; pollution of the country’s rivers from industrial and agricultural chemicals, including heavy metals, organic compounds, nitrates, and phosphates; air pollution from vehicles and refining activities.
Google Maps Netherlands
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Amsterdam found under the coordinates 52 21 N, 4 55 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Amsterdam is the capital and most populous city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It’s a city of almost 900,000 people. It is famous for its many canals, beautiful architecture, liberal policies, the big flower market, and some of the finest art museums in the world! From its beginning, in the year 1275, Amsterdam was known for its strategic position and trade. The city increased when Prince William of Orange (the leader of the Protestant rebellion against King Philip II) took control and established it as the Dutch Republic’s capital in 1581.
The Netherlands became independent on 23 January 1579 (the northern provinces of the Low Countries concluded the Union of Utrecht breaking with Spain; on 26 July 1581, they formally declared their independence with an Act of Abjuration; however, it was not until 30 January 1648 and the Peace of Westphalia that Spain recognized this independence), and its national holiday is Kings Day (birthday of King WILLEM-ALEXANDER), 27 April (1967).
Administrative divisions: 12 provinces (provincies, singular – provincie), 3 public entities (openbare lichamen, singular – openbaar lichaam (Dutch); entidatnan publiko, singular – entidat publiko (Papiamento)); Bonaire, Drenthe, Flevoland, Fryslan (Friesland), Gelderland, Groningen, Limburg, Noord-Brabant (North Brabant), Noord-Holland (North Holland), Overijssel, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Utrecht, Zeeland (Zealand), Zuid-Holland (South Holland) note 1: the Netherlands is one of four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands; the other three, Aruba, Curacao, and Sint Maarten, are all islands in the Caribbean; while all four parts are considered equal partners, in practice, most of the Kingdoms affairs are administered by the Netherlands, which makes up about 98% of the Kingdoms total land area and population, note 2: although Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius are officially incorporated into the country of the Netherlands under the broad designation of public entities, Dutch Government sources regularly apply to them the more descriptive term of special municipalities; Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius are collectively referred to as the Caribbean Netherlands.
People and society
The Dutch have a long history of welcoming immigrants from former colonies and refugees seeking asylum. However, lack of integration is now raising fears about the failing asylum system, immigrant crime, and militant Islam. The population is primarily urban, and the density is high. The state does not try to impose a particular morality on its citizens. Laws concerning sexuality, narcotics-taking, and euthanasia are among the worlds most liberal.
The population in the Netherlands is 17,337,403 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.37% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Netherlands is the No. 69 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 42.8 years median age (41.6 years for males and 41.6 years for women), the Netherlands ranks No. 32 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Dutchman (men), Dutchwoman (women) (noun) or Dutch (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Dutch 76.9%, EU 6.4%, Turkish 2.4%, Moroccan 2.3%, Indonesian 2.1%, German 2.1%, Surinamese 2%, Polish 1%, other 4.8% (2018 estimate).
They speak Dutch (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 23.6%, Protestant 14.9% (includes Dutch Reformed 6.4%, Protestant Church of The Netherlands 5.6%, Calvinist 2.9%), Muslim 5.1%, other 5.6% (includes Hindu, Buddhist, Jewish), none 50.7% (2017 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the Netherlands: An area known as the Randstad, anchored by the cities of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, the Hague, and Utrecht, is the most densely populated region. The north tends to be less dense, though sizeable communities can be found. In the Netherlands, we are talking about 92.6% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.158 million, Amsterdam (capital city), 1.012 million, Rotterdam (2021).
Industry
Major trading hub. High-profile multinationals. Diverse industrial base: chemicals, machinery, electronics, and metals. Costly social welfare system.
The Netherlands, the sixth-largest economy in the European Union, plays a vital role as a European transportation hub, with a consistently high trade surplus, stable industrial relations, and low unemployment. Industry focuses on food processing, chemicals, petroleum refining, and electrical machinery. A highly mechanized agricultural sector employs only 2% of the labor force but provides large surpluses for food processing and underpins the country’s status as the world’s second-largest agricultural exporter. The Netherlands is part of the eurozone, and as such, its monetary policy is controlled by the European Central Bank. The Dutch financial sector is highly concentrated, with four commercial banks possessing over 80% of banking assets and four times the Dutch GDP size. In 2008, during the financial crisis, the government budget deficit hit 5.3% of GDP. After a protracted recession from 2009 to 2013, unemployment doubled to 7.4%, and household consumption contracted for four years. Economic growth began inching forward in 2014. Since 2010, Prime Minister Mark Rutte’s government has implemented significant austerity measures to improve public finances. It has instituted broad structural reforms in key policy areas, including the labor market, the housing sector, the energy market, and the pension system. In 2017, the government budget returned to a surplus of 0.7% of GDP, with economic growth of 3.2%, and GDP per capita finally surpassed pre-crisis levels. The fiscal policy announced by the new government in the 2018-2021 coalition plans for increases in government consumption and public investment, fueling domestic demand and household consumption and investment. The new government’s policy also plans to increase demand for workers in the public and private sectors, forecasting a further decline in the unemployment rate, which hit 4.8% in 2017.
The Netherlands is rich in natural resources: Natural gas, petroleum, peat, limestone, salt, sand and gravel, and arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically agroindustries, metal and engineering products, electrical machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum, construction, microelectronics, and fishing.
The country’s export sectors are robust in refined petroleum, packaged medicines, broadcasting equipment, photography equipment, and computers (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 20%, Belgium 12%, United Kingdom 9%, France 7%, United States 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $719.78 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in the Netherlands’s position of 7.
Land use in Netherlands: 10.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 34.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 29.8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 55.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 24.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 4,860 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the Netherlands are milk, potatoes, sugar beet, pork, onions, wheat, poultry, tomatoes, carrots/turnips, and beef.
The country typically needs to import: crude petroleum, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, computers, and cars (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 15%, China 11%, Belgium 9%, United States 8%, Russia 7%, the United Kingdom 5% (2019) in a sum value of $622.66 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $661.18 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $677.38 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Netherlands 7.
Netherlands Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the Netherlands, and Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between Belgium and Germany. We published some basic information about its capital Amsterdam, and the Dutch nation.
Are you interested in visiting the Netherlands and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Netherlands below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of the Netherlands
Did you know about the Netherlands?
The Netherlands is one of the most densely populated countries in Europe. The busiest and largest airport in the country is Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. Most people can speak Dutch, but many languages are spoken throughout the country, such as French, German, English, and Spanish.
The Netherlands occupies roughly the north-western quarter of the country, divided into North and South Holland. It borders Belgium, Germany, and Luxembourg. The country is a constitutional monarchy; Beatrix (queen of the Netherlands since 1980) is head of state.
After virtually visiting the Netherlands, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Belgium and Germany.
If you liked our Google map and the Netherlands information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.