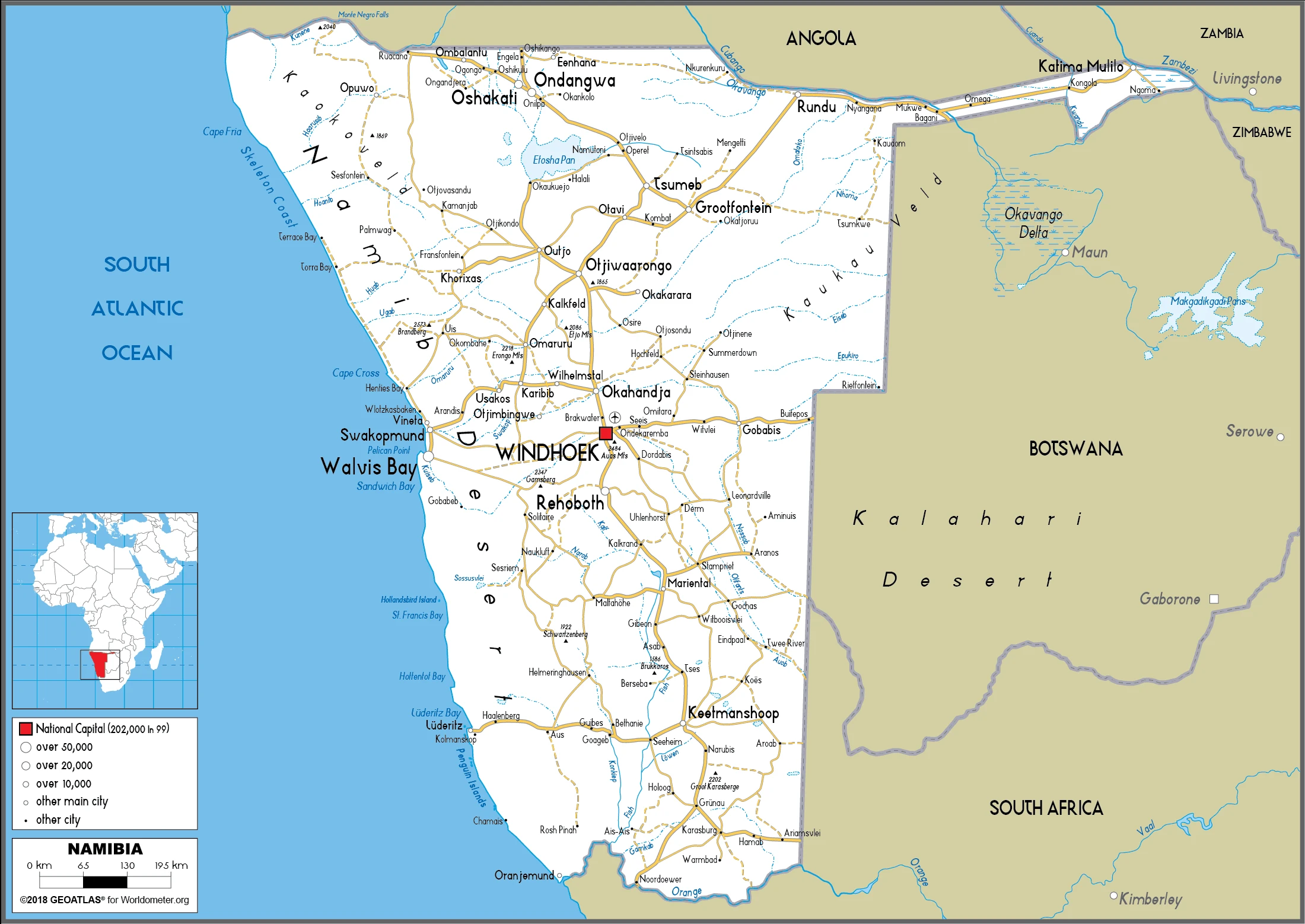
Namibia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Namibia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Namibia, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Windhoek, bordering countries like Angola, Botswana, South Africa, Zambia, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google Maps Namibia, Windhoek Google maps, Driving Directions Namibia, Printable Road Map.

About Namibia in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Namibia
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Namibia
- Local long form: Republic of Namibia
- Local short form: Namibia
- Former name(s): German South-West Africa (Deutsch-Suedwestafrika), South-West Africa
- Etymology: named for the coastal Namib Desert; the name namib means vast place in the Nama/Damara language.
- The legal system in Namibia: mixed legal system of uncodified civil law based on Roman-Dutch law and customary law.
- Climate: Almost rainless. The coast is usually shrouded in thick fog, unless the hot, dry berg wind is blowing.
- The national symbols are oryx (antelope); national colors: blue, red, green, white, yellow.
- Internet TLD: .na
The land of ancient Africa is still preserved in the former German Southwest Africa. The northward flow of the Benguela Current carries the cold waters of the Antarctic seas to the equator. The current is “responsible” for the desert’s formation, but the fog it creates also sustains all the desert’s inhabitants. The longest river in Namibia’s southern highlands, the Fish River Canyon, is comparable only to the Grand Canyon. The climate in southwest Africa has remained unchanged for millions of years, and the Namib Desert is the oldest on the planet. The Namib-Naukluft National Park comprises several reserves: in the south, the highest dunes on the planet are home to the oldest sand desert, while in the north, the gravel and rock desert is home to the rare and unique plants Welwitschia mirabilis and the quiver tree (Aloé dichotoma). Twyfelfontein’s 27 000-year-old rock paintings testify that the sleds or busmen have inhabited this land since ancient times. The houses of the German colonial settlements have been preserved, and the German street names of Windhoek and Swakopmund are reminiscent of the turn of the century.
Namib is the Earths oldest and one of its driest deserts.
Background
Various ethnic groups occupied southwestern Africa before Germany established a colony over most of the territory in 1884. South Africa occupied the colony, then known as German Southwest Africa, in 1915 during World War I and administered it as a mandate until after World War II, when it annexed the territory. In 1966, the Marxist South-West Africa Peoples Organization (SWAPO) guerrilla group launched a war of independence for the area that became Namibia. Still, it was not until 1988 that South Africa agreed to end its administration with a UN peace plan for the entire region. Namibia gained independence in 1990 and has been governed by SWAPO since, though the party has dropped much of its Marxist ideology. In a landslide victory, President Hage GEINGOB was elected in 2014, replacing Hifikepunye POHAMBA, who stepped down after serving two terms. SWAPO retained its parliamentary supermajority in the 2014 elections. In the 2019 elections, GEINGOB was reelected but by a substantially reduced majority, and SWAPO narrowly lost its supermajority in parliament. Namibia gained independence in 1990.
Geography
The Namib Desert stretches along the coastal strip. Inland, a ridge of mountains rises to 8000 ft (2500 m). The Kalahari Desert lies in the east.
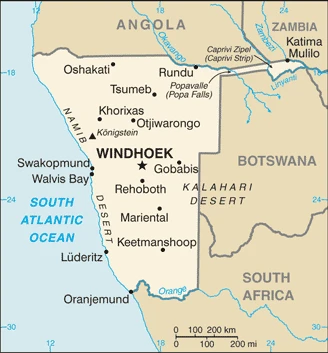
Located in southwestern Africa, Namibia gained independence from South Africa in 1990, after 24 years of armed struggle. It regained the territory of Walvis Bay in 1994.
This state is located in Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola and South Africa, under the coordinates of 22 00 S, 17 00 E, covering an area of 824,292 sq km with a coastline of 1,572 km. Namibia is Almost seven times the size of Pennsylvania, slightly more than half the size of Alaska.
Namibia has 4,220 km of land boundaries in total and borders (4 nations): Angola 1427 km, Botswana 1544 km, South Africa 1005 km, Zambia 244 km.
Primarily high plateau, Namib desert along the coast, Kalahari desert in the east, with Konigstein on Brandenberg 2,573 m as the highest point of Namibia, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 1,141 m throughout the country. With a total of 824,292 sq km, Namibia has 823,290 sq km of land and 1,002 sq km of water surface area.
The principal rivers are Zambezi (shared with Zambia), Angola, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique) – 2,740 km, Orange river mouth (shared with Lesotho and South Africa) – 2,092 km, Okavango (shared with Angola and Botswana) – 1,600 km. The significant watersheds for Namibia are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Orange (941,351 sq km), Indian Ocean drainage: Zambezi (1,332,412 sq km) Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Okavango Basin (863,866 sq km).
The Namib Desert, after which the country is named, is considered to be the oldest desert in the world; Namibia is the first country in the world to incorporate the protection of the environment into its constitution; some 14% of the land is protected, including virtually the entire Namib Desert coastal strip; Namib-Naukluft National Park (49,768 sq km), is the largest game park in Africa and one of the largest in the world.
The climate in Namibia is as follows: Desert, hot, dry, rainfall sparse, and erratic.
When you visit Namibia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Prolonged periods of drought.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Namibia: degree of risk: high (2020), bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever, malaria, schistosomiasis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Namibian people: depletion and degradation of water and aquatic resources; desertification; land degradation; loss of biodiversity and biotic resources; wildlife poaching.
Google Maps Namibia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Windhoek found under the coordinates 22 34 S, 17 05 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in September; ends first Sunday in April.
It is currently home to the largest concentration of Namibians in the country. Much of this population came from Ovamboland, and following a long period of colonial rule, Windhoek became a more permanent settlement with many different ethnic groups living in it. The Dutch Reformed Church founded Windhoek in 1892 after they built a mission station there, becoming the first Europeans to settle in Ovamboland. Windhoek has a warm climate, with hot temperatures and high humidity.
Namibia became independent on 21 March 1990 (from the South African mandate), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 21 March (1990).
Administrative divisions: 14 regions; Erongo, Hardap, //Karas, Kavango East, Kavango West, Khomas, Kunene, Ohangwena, Omaheke, Omusati, Oshana, Oshikoto, Otjozondjupa, Zambezi;.
People and society
Ovambo, the leading ethnic group, lives mainly in the more populated north. Some 100,000 whites, many of German descent, are centered around Windhoek and still control the economy. The minority San and Khoi bushmen are among the oldest human communities globally. Homosexual rights are restricted.
The population in Namibia is 2,678,191 (July 2021 estimate). Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected, with an average of 1.83% (2021 estimate) change. That means Namibia is the No. 142 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 21.8 years median age (21.1 years for males and 21.1 years for women), Namibia ranks No. 183 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Namibian(s) (noun) or Namibian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Ovambo 50%, Kavangos 9%, Herero 7%, Damara 7%, mixed European and African ancestry 6.5%, European 6%, Nama 5%, Caprivian 4%, San 3%, Baster 2%, Tswana .5%.
They speak Oshiwambo languages 49.7%, Nama/Damara 11%, Kavango languages 10.4%, Afrikaans 9.4% (also a common language), Herero languages 9.2%, Zambezi languages 4.9%, English (official language) 2.3%, other African languages 1.5%, other European languages 0.7%, other 1% (2016 estimate). Note: Namibia has 13 recognized national languages, including 10 indigenous African languages and 3 European languages, and practices the following religions: Christian 80% to 90% (at least 50% Lutheran), indigenous beliefs 10% to 20%.
We can conclude the following about the population in Namibia: Population density is very low, with the most extensive clustering found in the extreme north-central area along the border with Angola, as shown in this population distribution map. In Namibia, we are talking about 53% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 446,000 Windhoek (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Varied mineral resources, notably uranium and diamonds. Rich offshore fishing grounds. High unemployment. HIV/AIDS epidemic. One of Africas most skewed distributions of wealth.
Namibia’s economy is heavily dependent on extracting and processing minerals for export. Mining accounts for about 12.5% of GDP but provides more than 50% of foreign exchange earnings. Rich alluvial diamond deposits make Namibia a primary source of gem-quality diamonds. Marine diamond mining is increasingly important as the terrestrial diamond supply has dwindled. The rising cost of mining diamonds, especially from the sea, has reduced profit margins with increased diamond production in Russia and China. Namibian authorities have emphasized adding value to raw materials, doing more in-country manufacturing, and exploiting the services market, especially in the logistics and transportation sectors. Namibia is one of the world’s largest producers of uranium. The Chinese-owned Husab uranium mine began producing uranium ore in 2017 and is expected to reach total production in August 2018 and produce 15 million pounds of uranium a year. Namibia also produces large quantities of zinc and is a smaller producer of gold and copper.
Namibia’s economy remains vulnerable to world commodity price fluctuations and drought., Namibia usually imports about 50% of its cereal requirements; in drought years, food shortages are problematic in rural areas. A high per capita GDP relative to the region obscures one of the world’s most unequal income distributions; the current government has prioritized exploring wealth redistribution schemes while maintaining a pro-business environment. GDP growth in 2017 slowed to about 1%, however, due to contractions in both the construction and mining sectors and an ongoing drought. Growth is expected to recover modestly in 2018., A five-year Millennium Challenge Corporation compact ended in September 2014. As an upper-middle-income country, Namibia is ineligible for a second compact. The Namibian economy is closely linked to South Africa, with the Namibian dollar pegged one-to-one to the South African rand. Namibia receives 30%-40% of its revenues from the Southern African Customs Union (SACU); volatility in the size of Namibia’s annual SACU allotment and global mineral prices complicates budget planning.
Namibia is rich in the following natural resources: Diamonds, copper, uranium, gold, silver, lead, tin, lithium, cadmium, tungsten, zinc, salt, hydropower, fish, note, suspected deposits of oil, coal, and iron ore.
The main industrial sectors are meatpacking, fish processing, dairy products, pasta, beverages, mining (diamonds, lead, zinc, tin, silver, tungsten, uranium, copper).
The country’s export sectors are solid in copper, diamonds, uranium, thorium, gold, radioactive chemicals, fish (2019), partnering with these nations: China 27%, South Africa 18%, Botswana 8%, Belgium 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $3.56 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Namibia’s position of 140.
Land use in Namibia: 8.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 44% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 47.2% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 46.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 80 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Namibia are roots/tubers nes, milk, maize, onions, beef, grapes, fruit, pulses nes, vegetables, millet.
The country typically needs to import: copper, refined petroleum, delivery trucks, diamonds, cars (2019), partnering with the following nations: South Africa 47%, Zambia 16% (2019) in a sum value of $4.54 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $5.77 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $6.33 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Namibia 145.
Namibia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Namibia, Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola and South Africa. We published some basic information about its capital Windhoek, and the Namibian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Namibia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Namibia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Namibia
Did you know about Namibia?
Namibia’s landscape consists of deserts in the east, Savannah in the central part of the country, and Kalahari Desert vegetation to the west. The Berlin Conference in 1884-85 set boundaries for countries in Africa. As a result, Germany colonized Namibia until 1920, when South Africa took over. In 1990, Namibia became independent and today has a stable economy and a democratic government.
Namibia has many plants and animals that are endemic to the region. Some examples are Hoodia Gordonii, the African penguin, and the Fish eagle. The country’s symbol is the elephant, showing its concern for wildlife conservation.
After virtually visiting Namibia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Angola, Botswana, South Africa, Zambia.
If you liked our Google map and Namibia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.