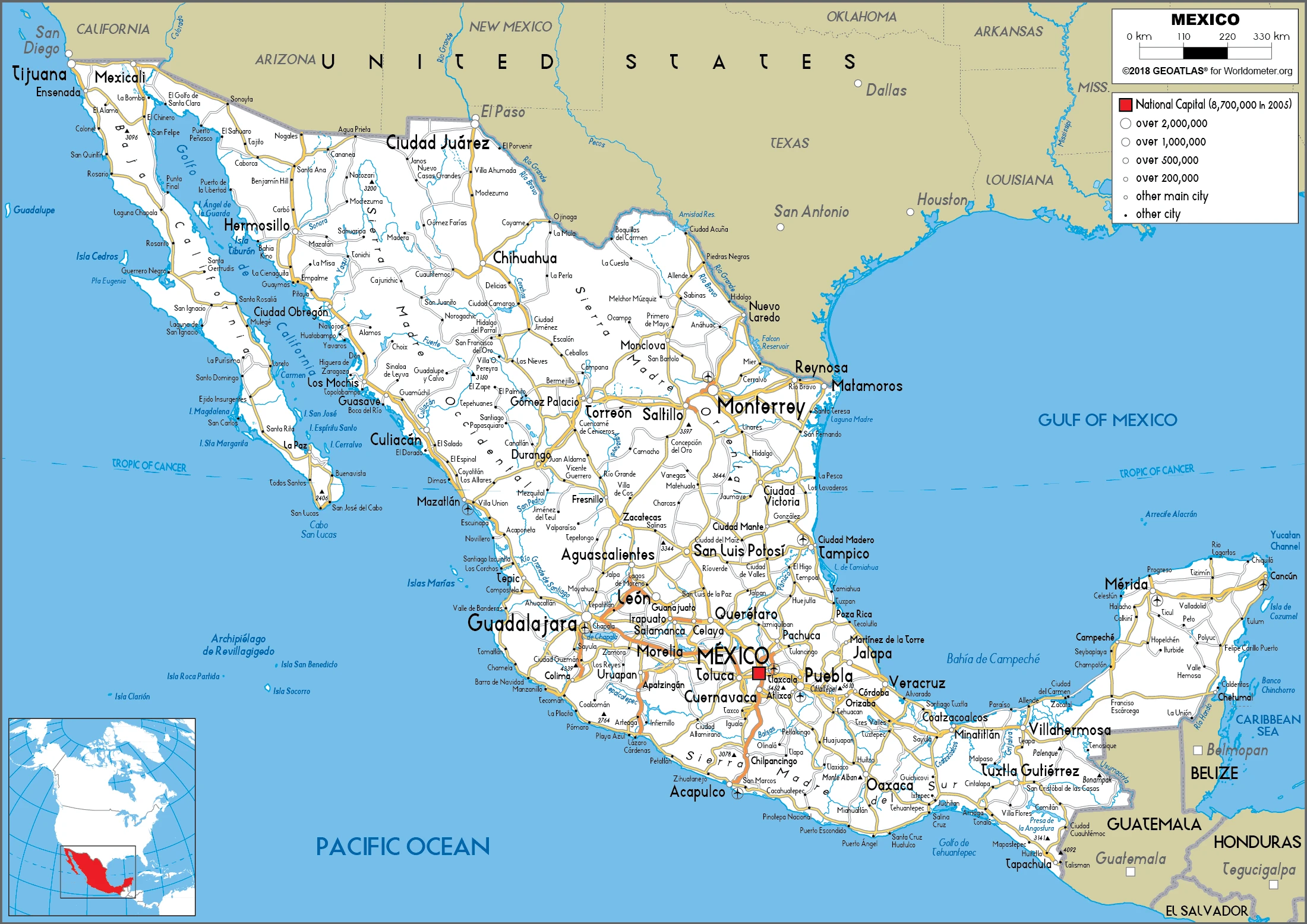
Mexico Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Mexico, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Mexico, North America (4 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico), bordering countries like Belize, Guatemala, US, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this North American state.
Quick links: Google Maps Mexico, Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico) Google maps, Driving Directions Mexico, Printable Road Map.

About Mexico in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Mexico
- The conventional long form of the name: United Mexican States
- Local long form: Estados Unidos Mexicanos
- Local short form: Mexico
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: named after the capital city, whose name stems from the Mexica, the largest and most powerful branch of the Aztecs; the meaning of the name is uncertain.
- The legal system in Mexico: civil law system with US constitutional law influence; judicial review of legislative acts.
- Climate: The plateau and high mountains are warm for much of the year. The Pacific coast is tropical: storms occur mostly in March and December. The Northwest is dry.
- The national symbols are golden eagle, national colors: are green, white, and red.
- Internet TLD: .mx
The common language, similar history, and ancient cultures link Mexico to Latin America, ¡11 Central America. However, most of Mexico’s territory is geographically and geographically part of North America, with the continent ending only in the Tehuantepec isthmus. In the California Peninsula, the Parti-Cordillera continues into the Pacific Ocean, and the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, which form the geological skeleton of the country at 4,000-5,000 meters, are a continuation of the Rocky Mountains, the North American Cordillera and encircle the Mexican highlands. Here, at 2,800 meters above sea level, the high indigenous cultures of ancient and medieval times flourished and where one of the most populous capitals on the planet, the ‘breathtaking’ Mexico City, was founded. The Yucatán Peninsula’s vast limestone plateau, covered in tropical rainforest, is a testament to the Mayan civilization. The mysterious relics of pre-Columbian times, the ruined cities of the various indigenous cultures, the architectural wonders of the colonial period, and the natural treasures of California and the Yucatán Peninsula – 26 (!) World Heritage sites, in all – are among the universal treasures of humanity.
More people cross the US-Mexican border each year illegally or legally than any other border in the world.
Background
The site of several advanced Amerindian civilizations – including the Olmec, Toltec, Teotihuacan, Zapotec, Maya, and Aztec – Mexico was conquered and colonized by Spain in the early 16th century. Administered as the Viceroyalty of New Spain for three centuries, it achieved independence early in the 19th century. Elections held in 2000 marked the first time since the 1910 Mexican Revolution that an opposition candidate – Vicente FOX of the National Action Party (PAN) – defeated the party in government, the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI). He was succeeded in 2006 by another PAN candidate Felipe CALDERON, but Enrique PENA NIETO regained the presidency for the PRI in 2012. Left-leaning anti-establishment politician and former mayor of Mexico City (2000-05) Andres Manuel LOPEZ OBRADOR, from the National Regeneration Movement (MORENA), became president in December 2018. The global financial crisis in late 2008 caused a massive economic downturn in Mexico the following year, although growth returned quickly in 2010. Ongoing economic and social concerns include low real wages, high underemployment, inequitable income distribution, and few advancement opportunities for the largely indigenous population in the impoverished southern states. Since 2007, Mexico’s powerful drug-trafficking organizations have bloody feuding, resulting in thousands of drug-related homicides.
Geography
Coastal plains along the Pacific and Atlantic seaboard rise to a high arid central plateau. To the east and west are the Sierra Madre mountain ranges. Limestone lowlands form the projecting Yucatan peninsula.
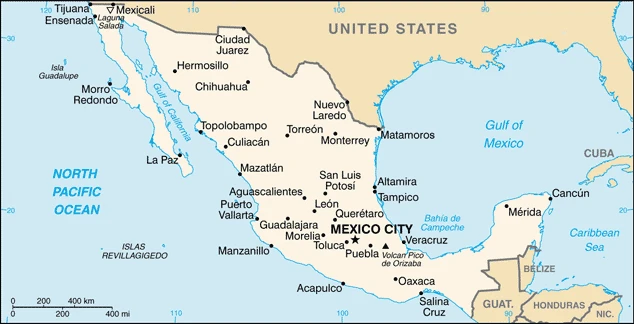
Mexico stretches from the US border southward into the ancient Aztec and Mayan heartlands. Independence from Spain came in 1836. One in five Mexicans lives in the sprawling capital.
This state is located in North America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, between Belize and the United States and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Guatemala and the United States, under the coordinates of 23 00 N, 102 00 W, covering an area of 1,964,375 sq km with a coastline of 9,330 km. Mexico is slightly less than three times the size of Texas.
Mexico has 4,389 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (3 nations): Belize 276 km, Guatemala 958 km, US 3155 km.
High, rugged mountains, low coastal plains, high plateaus, and desert, with Volcan pico de Orizaba 5,636 m as the highest point of Mexico, while Laguna Salada -10 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 1,111 m throughout the country. With a total of 1,964,375 sq km, Mexico has 1,943,945 sq km of land and 20,430 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Laguna de Chapala – 1,140 sq km (a freshwater lake), Laguna de Terminos – 1,550 sq km (saltwater lake), while the major rivers are: Rio Grande river mouth (shared with the US [s]) – 3,057 km, Colorado river mouth (shared with the US) – 2,333 km. The significant watersheds for Mexico are the Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Gulf of Mexico) Rio Grande/Bravo (607,965 sq km), Pacific Ocean drainage: (Gulf of California) Colorado (703,148 sq km). The significant watersheds for Mexico are the Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains Aquifers.
Strategic location on the southern border of the US; Mexico is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world’s earthquakes and some 75% of the world’s volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire.
The climate in Mexico is as follows: It Varies from tropical to desert.
When you visit Mexico, the natural hazards shall be considered: Tsunamis along the pacific coast, volcanoes and destructive earthquakes in the center and south, and hurricanes on the Pacific, Gulf of Mexico, and Caribbean coasts. Volcanism: volcanic activity in the central-southern part of the country; the volcanoes in Baja California are mostly dormant; Colima (3,850 m), which erupted in 2010, is Mexico’s most active volcano and is responsible for causing periodic evacuations of nearby villagers; it has been deemed a decade volcano by the international association of volcanology and chemistry of the interior of the earth, worthy of study due to its tumultuous history and proximity to human populations; Popocatepetl (5,426 m) poses a threat to Mexico City; other historically active volcanoes include Barcena, Ceboruco, el Chichon, Michoacan-Guanajuato, Pico de Orizaba, San Martin, Socorro, and Tacana; see note 2 under geography – note.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Mexico: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A, and dengue fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Mexican people: a scarcity of hazardous waste disposal facilities; rural to urban migration; natural freshwater resources scarce and polluted in the north, inaccessible and poor quality in the center and extreme southeast; raw sewage and industrial effluents polluting rivers in urban areas; deforestation; widespread erosion; desertification; deteriorating agricultural lands; severe air and water pollution in the national capital and urban centers along US-Mexico border; land subsidence in Valley of Mexico caused by groundwater depletion note: the government considers the lack of clean water and deforestation national security issues.
Google Maps Mexico
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico) found under the coordinates 19 26 N, 99 08 W, applying the time zone UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in April; ends last Sunday in October.
Mexico City is a vibrant, modern metropolis. It has become the center of government and culture for Mexico in the past century. It is home to beautiful buildings and unique traditions that bring together Spanish colonial architecture, indigenous Aztec art, and Mexican barrio culture.
Mexico became independent on 16 September 1810 (declared independence from Spain), 27 September 1821 (recognized by Spain), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 16 September (1810).
Administrative divisions: 32 states (estados, singular – estado); Aguascalientes, Baja California, Baja California Sur, Campeche, Chiapas, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Colima, Cuidad de Mexico, Durango, Guanajuato, Guerrero, Hidalgo, Jalisco, Mexico, Michoacan, Morelos, Nayarit, Nuevo Leon, Oaxaca, Puebla, Queretaro, Quintana Roo, San Luis Potosi, Sinaloa, Sonora, Tabasco, Tamaulipas, Tlaxcala, Veracruz, Yucatan, Zacatecas.
People and society
Mexico is the 10th most populous country globally, with over 130 million people. Five major geographical regions are home to different cultures and languages, including Spanish. Mexico City is the capital of Mexico, and it’s also one of the largest cities in the world, with over 8 million people living there.
Most Mexicans are mestizos of Spanish-Amerindian descent. Rural Amerindians are segregated mainly from Hispanic society, and most live in poverty, though the state promotes their culture. The Zapatista movement backs indigenous rights. Few women in male-dominated politics and business. Narcotics-related violent crime is rising.
The population in Mexico is 130,207,371 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.04% (2021 estimate) change. That means Mexico is the No. 10 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 29.3 years median age (28.2 years for males and 28.2 years for women), Mexico ranks No. 132 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Mexican(s) (noun) or Mexican (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Mestizo (Amerindian-Spanish) 62%, predominantly Amerindian 21%, Amerindian 7%, other 10% (primarily European) (2012 estimate). Note: Mexico does not collect census data on ethnicity.
They speak Spanish only 92.7%, Spanish and indigenous languages 5.7%, indigenous only 0.8%, unspecified 0.8%; note -indigenous languages include various Mayan, Nahuatl, and other regional languages (2005 estimate)major-language sample(s): La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la Fuente indispensable de información básica. They speak the Spanish language and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 82.7%, Pentecostal 1.6%, Jehovah’s Witness 1.4%, other Evangelical Churches 5%, other 1.9%, none 4.7%, unspecified 2.7% (2010 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Mexico: Most of the population is found in the middle of the country between the states of Jalisco and Veracruz. Approximately a quarter of the population lives in and around Mexico City. In Mexico, we are talking about 81% (2021) of the total population living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 21.919 million; Mexico City (capital city), 5.259 million; Guadalajara, 4.956 million; Monterrey, 3.245 million; Puebla, 2.522 million; Toluca De Lerdo, 2.181 million, Tijuana (2021).
Industry
Mexico is home to the world’s seventh-largest economy. It is one of the United States’ largest trading partners. Mexicans enjoy more than twice as much purchasing power as those in other Latin American countries. Mexico has been the number one source of legal immigrants since 1964, providing labor to industries that would otherwise be unable to find qualified employees.
One of the world’s largest oil producers. Corn, fruit, vegetables, and sugar are cash crops. NAFTA has boosted exports but exposes farmers to subsidized US competition. Wealth disparity. Hit hard by the 2008-2009 global downturn and swine flu crisis.
Mexico’s $2.4 trillion economy, the 11th most significant globally – has become increasingly oriented toward manufacturing since the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) entered into force in 1994. Per capita income is roughly one-third that of the US; income distribution remains highly unequal., Mexico has become the US’s second-largest export market and third-largest source of imports. In 2017, two-way trade in goods and services exceeded $623 billion. Mexico has free trade agreements with 46 countries, putting more than 90% of its trade under free trade agreements. In 2012, Mexico formed the Pacific Alliance with Peru, Colombia, and Chile. Mexico’s current government, led by President Enrique PENA NIETO, has emphasized economic reforms, passing and implementing total energy, financial, fiscal, and telecommunications reform legislation, among others, with the long-term aim of improving competitiveness and economic growth across the Mexican economy.
Since 2015, Mexico has held public auctions of oil and gas exploration and development rights and long-term electric power generation contracts. Mexico has also issued permits for private sector import, distribution, and retail sales of refined petroleum products to attract private investment into the energy sector and boost production., Since 2013, Mexico’s economic growth has averaged 2% annually, falling short of private-sector expectations that President PENA NIETOs sweeping reforms would bolster economic prospects. Growth is predicted to remain below potential given falling oil production, weak oil prices, structural issues such as low productivity, high inequality, a large informal sector employing over half of the workforce, the weak rule of law, and corruption. Mexico’s economy remains vulnerable to uncertainty surrounding the future of NAFTA because the United States is its top trading partner. The two countries share integrated supply chains and potential shifts in domestic policies following the inauguration of a new president in December 2018.
Mexico is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, silver, antimony, copper, gold, lead, zinc, natural gas, and timber.
The main industrial sectors are typically food and beverages, tobacco, chemicals, iron and steel, petroleum, mining, textiles, clothing, motor vehicles, consumer durables, and tourism.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars and vehicle parts, computers, delivery trucks, crude petroleum, and insulated wiring (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 75% (2019). The export trade resulted in $434.93 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Mexico’s position of 16.
Land use in Mexico: 33.3% (2018 estimate) forest, 11.8% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 11.8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 54.9% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops is 1.4% (2018 estimate), and permanent pasture is 41.7% (2018 estimate). The summed area of the irrigated land is 65,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Mexico are sugar cane, maize, milk, oranges, sorghum, tomatoes, poultry, wheat, green chilies/peppers, and eggs.
The country typically needs to import: integrated circuits, refined petroleum, cars and vehicle parts, office machinery/parts, and telephones (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 54%, China 14% (2019) in a sum value of $410.66 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $495.79 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $505.05 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Mexico’s 16.
Mexico Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Mexico, and North America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, between Belize and the United States, and bordering the North Pacific Ocean between Guatemala and the United States. We published some basic information about its capital Mexico City (Ciudad de Mexico), and the Mexican nation.
Are you interested in visiting Mexico and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Mexico below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Mexico
Did you know about Mexico?
Mexico is the 4th largest country and has the 15th largest economy globally. Its population consists of over 130 million people; it is ten times larger than New York City’s.
Mexico is a beautiful country that has lots of diverse terrains and cultures. The climates depend on the region, but it’s typically tropical. Mexico has a coast on the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, so many beaches have beautiful water. Some of Mexico’s most popular tourist destinations are Cancun, La Paz, Guadalajara, Cabo San Lucas, and Cozumel.
One of the most interesting is that Mexico is home to some of the world’s most ancient civilizations and archaeological sites.
Travel tips for Mexico
Mexico is a fascinating country that’s guaranteed to offer something for everyone. During your visit, you’ll discover beautiful natural landscapes, get an insight into the rich culture and history and meet some of the friendliest people in the world. Learn more here: Mexico Travel Tips, Facts, and Advice.
After virtually visiting Mexico, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Belize, Guatemala, and the United States.
If you liked our Google map and Mexico information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.