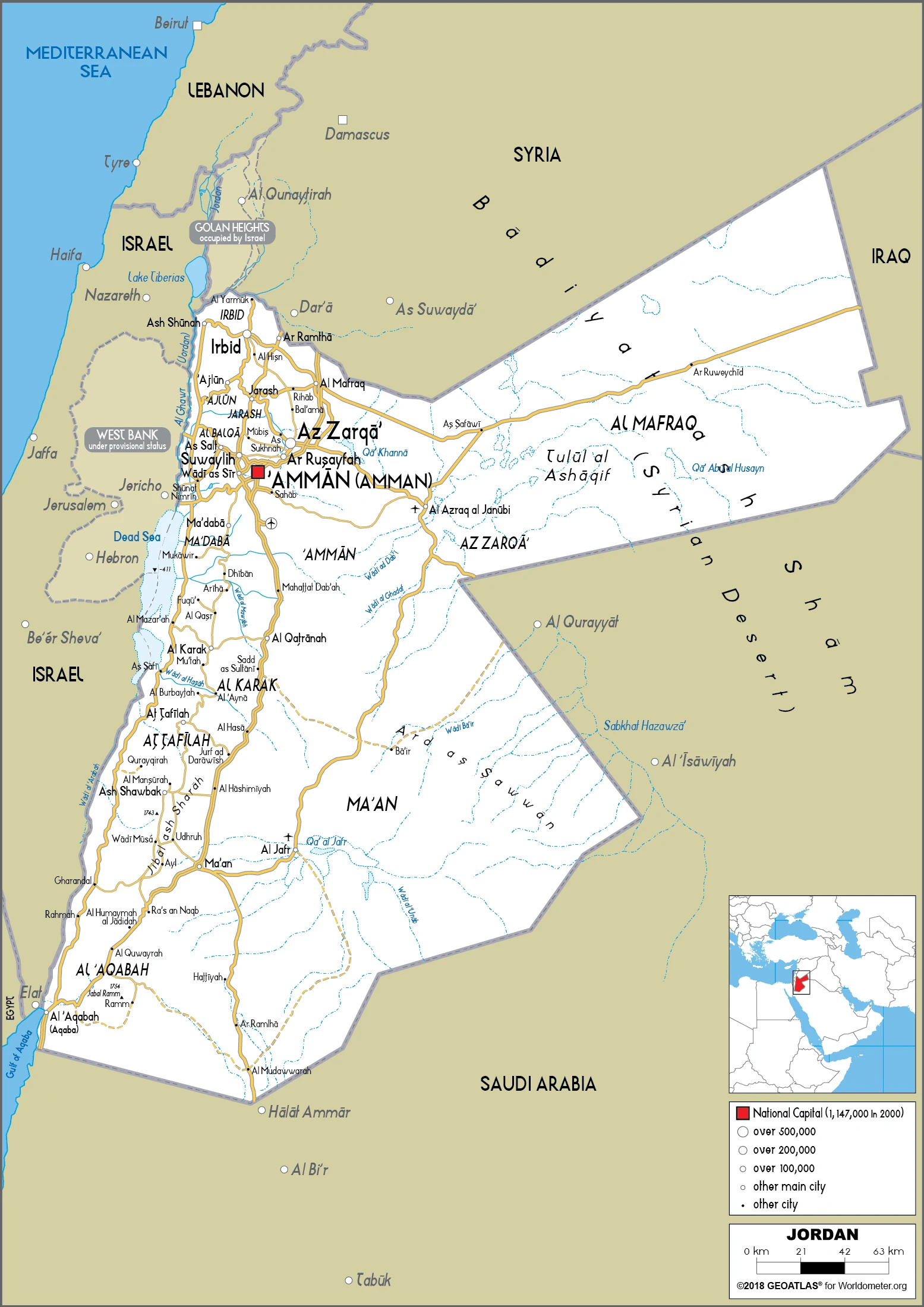
Jordan Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Jordan, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Jordan, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Amman, bordering countries like Iraq, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Syria, West Bank, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Jordan, Amman Google maps, Driving Directions Jordan, Printable Road Map.

About Jordan in a nutshell
- The Nabataean ruins of the ancient city of Petra attract thousands of tourists every year.
- Conventional short form of the name: Jordan
- The conventional long form of the name: Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
- Local long form: Al Mamlakah al Urduniyah al Hashimiyah
- Local short form: Al Urdun
- Former name(s): Transjordan
- Etymology: named for the Jordan River, which makes up part of Jordans northwest border.
- The legal system in Jordan: mixed system developed from codes instituted by the Ottoman Empire (based on French law), British common law, and Islamic law.
- Climate: Hot, dry summers. Cool, wet winters. Areas below sea level very hot in summer, and warm in winter.
- The national symbols are eagle; national colors: black, white, green, red.
- Internet TLD: .jo
The history of the Muslim Arab country parallels that of Palestine. Its borders were drawn by the British after the Second World War (legend has it that the eastern borderline was drawn in a slightly curly way because Winston Churchill had one too many drinks after lunch…). The surface of Jordan can be divided into three major areas: the fertile Jordan River valley, the Syrian-Arab plateau with its large settlements, and the deserts along the borders of Syria, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia. Jordan’s short coastline – the Gulf of Aqaba – is a popular tourist destination. Tourism, which started in the third millennium, has become a significant source of income for the Jordanian economy. Its World Heritage Sites are unique assets, representing thousands of years of history and culture. Petra, inhabited since prehistoric times, is the former monumental trading city of the Nabataeans, built and carved into the walls of the gorges thousands of years ago, combining oriental traditions with elements of Hellenic architecture. The superimposed Roman, Byzantine, and early Islamic ruins of Um er-Rasas, dating from the 3rd to the 9th century AD, have only been partially excavated. The desert fortress and palace of Quseir Amra was the residence of the Umayyad caliphs in the early 8th century AD. The Old City and walls of Jerusalem, the holy city of the three world religions, on the border of Jordan and Israel, were inscribed on the World Heritage List by Jordan based on a Jordanian nomination.
Background
Following World War, I and the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire, the League of Nations awarded Britain the mandate to govern much of the Middle East. Britain demarcated a semi-autonomous region of Transjordan from Palestine in the early 1920s. The area gained its independence in 1946 and, after that, became The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. The country’s long-time ruler, King HUSSEIN (1953-99), successfully navigated competing pressures from the major powers (US, USSR, and UK), various Arab states, Israel, and a large internal Palestinian population. Jordan lost the West Bank to Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. King HUSSEIN in 1988 permanently relinquished Jordanian claims to the West Bank. In 1994 he signed a peace treaty with Israel. King ABDALLAH II, King Hussein’s eldest son, assumed the throne following his father’s death in 1999. He has implemented modest political reforms, including the passage of a new electoral law in early 2016 and an effort to devolve some authority to governorate- and municipal-level councils following subnational elections in 2017. In 2016, the Islamic Action Front, the political arm of the Jordanian Muslim Brotherhood, returned to the National Assembly with 15 seats after boycotting the previous two elections in 2010 and 2013.
Geography
Mostly desert plateaus, with occasional salt pans. The lowest parts lie along the eastern shores of the Dead Sea and the Jordan River.
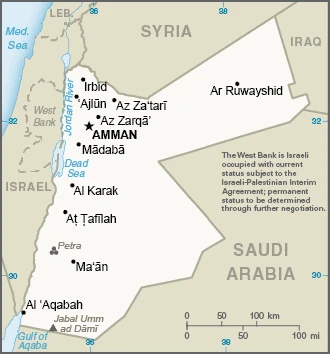
The Kingdom of Jordan lies east of Israel and borders the Palestinian West Bank. Usually pro-Western in outlook, Jordan fears the rise of Islamists in Syria and Iraq.
This state is located in the Middle East, northwest of Saudi Arabia, between Israel (to the West) and Iraq, under the coordinates of 31 00 N, 36 00 E, covering an area of 89,342 sq km with a coastline of 26 km. Jordan is About three-quarters the size of Pennsylvania, slightly smaller than Indiana.
Jordan has 1,744 km of land boundaries and borders with (5 nations): Iraq 179 km, Israel 307 km, Saudi Arabia 731 km, Syria 379 km, West Bank 148 km.
The dominant topographical feature is the arid, mainly desert plateau, a tremendous north-south geological rift along the West. It includes the Jordan river valley, the dead sea, and the Jordanian highlands, with Jabal Umm ad Dami 1,854 m as the highest point of Jordan, while the Dead Sea -431 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 812 m throughout the country. With a total of 89,342 sq km, Jordan has 88,802 sq km of land and 540 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Dead Sea (shared with Israel and West Bank) – 1,020 sq km (saltwater lake). The significant watersheds for Jordan are the Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf), Tigris, and Euphrates (918,044 sq km).
Strategic location at the head of the Gulf of Aqaba and as the Arab country that shares the longest border with Israel and the occupied West Bank. The Dead Sea, the lowest point in Asia and the second saltiest body of water in the world (after Lac Assal in Djibouti), lie on Jordan’s western border with Israel and the West Bank; Jordan is almost landlocked but does have a 26 km southwestern coastline with a single port, Al Aqabah (Aqaba).
The climate in Jordan is primarily an arid desert, rainy season in the West (November to April).
When you visit Jordan, the natural hazards are droughts, periodic earthquakes, flash floods.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Jordan: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Jordanian people: limited natural freshwater resources; declining water table; salinity; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; biodiversity and ecosystem damage/loss.
Google Maps Jordan
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Amman found under the coordinates 31 57 N, 35 56 E, applying the time zone UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Friday in March; ends last Friday in October.
Amman is the capital of Jordan. It is located in north-central Jordan, on the east bank of the Yarmouk River, and close to the Dead Sea. Amman flourished under its first two dynasties, the Umayyads and Abbasids, but Amman became a center for learning and culture during the time of Caliph Mamun.
Jordan became independent on 25 May 1946 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 25 May (1946).
Administrative divisions: 12 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah); Ajlun, Al Aqabah, Al Balqa, Al Karak, Al Mafraq, Al Asimah (Amman), At Tafilah, Az Zarqa, Irbid, Jarash, Maan, Madaba.
People and society
Jordanians are mainly Muslim with a strong national identity but with Bedouin roots. The monarchys power base lies among the rural tribes, providing the army’s backbone. Protests since 2011 have elicited gradual political reform, with more extraordinary powers for parliament. Jordan ceded its claim to the West Bank to the aspiring Palestinian state in 1988. Palestinian refugees make up over a third of the population. The recent influx of over 600,000 Syrian refugees.
The population in Jordan is 10,909,567 (July 2021 estimate). Note: increased estimate reflects revised assumptions about the net migration rate due to the increased flow of Syrian refugees, with an average of 0.82% (2021 estimate) change. That means Jordan is the No. 85 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 23.5 years median age (23.9 years for males and 23.9 years for women), Jordan ranks No. 175 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Jordanian(s) (noun) or Jordanian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Jordanian 69.3%, Syrian 13.3%, Palestinian 6.7%, Egyptian 6.7%, Iraqi 1.4%, other 2.6% (includes Armenian, Circassian) (2015 estimate). Note: data represent population by self-identified nationality.
They speak Arabic (official language), English (widely understood among upper and middle classes) languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 97.1% (official; predominantly Sunni), Christian 2.1% (majority Greek Orthodox, but some Greek and Roman Catholics, Syrian Orthodox, Coptic Orthodox, Armenian Orthodox, and Protestant denominations), Buddhist 0.4%, Hindu 0.1%, Jewish <0.1%, folk <0.1%, other <0.1%, unaffiliated <0.1% (2020 estimate). We can conclude the following about the population in Jordan: Population heavily concentrated in the West, and particularly the northwest, in and around the capital of Amman. A sizeable but smaller population is located southwest along the shore of the Gulf of Aqaba. In Jordan, we are talking about 91.6% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 2.182 million, Amman (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Lack of water. Exports garments, potash, fertilizers, and phosphates. Tourism hit by regional instability.
Jordan’s economy is among the smallest in the Middle East, with insufficient water, oil, and other natural resources, underlying the government’s heavy reliance on foreign assistance. Other economic challenges for the government include chronic high rates of unemployment and underemployment, budget and current account deficits, government debt., During the first decade of the 2000s, King ABDALLAH implemented significant economic reforms, such as expanding foreign trade and privatizing state-owned companies that attracted foreign investment and contributed to the average annual economic growth of 8% for 2004 through 2008. The global economic slowdown and regional turmoil contributed to slower growth from 2010 to 2017 – with growth averaging about 2.5% per year – and hurt export-oriented sectors, construction/real estate, and tourism.
Since the onset of the civil war in Syria and the resulting refugee crisis, one of Jordan’s most pressing socioeconomic challenges has been managing the influx of approximately 660,000 UN-registered refugees, more than 80% of whom live in Jordan’s urban areas. Jordan’s official census estimated the refugee number at 1.3 million Syrians as early as 2016. Jordan is nearly wholly dependent on imported energy, primarily natural gas, and energy consistently makes up 25-30% of Jordan’s imports. To diversify its energy mix, Jordan has secured several contracts for liquefied and pipeline natural gas, developed several major renewables projects, and is currently exploring nuclear power generation and exploitation of abundant oil shale reserves. In August 2016, Jordan and the IMF agreed to a $723 million Extended Fund Facility that aims to build on the three-year, $2.1 billion IMF program that ended in August 2015, intending to help Jordan correct budgetary and balance of payments imbalances.
Jordan is rich in the following natural resources: Phosphates, potash, shale oil.
The main industrial sectors are tourism, information technology, clothing, fertilizer, potash, phosphate mining, pharmaceuticals, petroleum refining, cement, inorganic chemicals, light manufacturing.
The country’s export sectors are robust in fertilizers, calcium phosphates, packaged medicines, clothing and apparel, phosphoric acid (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 21%, Saudi Arabia 13%, India 8%, Iraq 7%, United Arab Emirates 5%, China 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $16.29 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global export rank, values resulted in Jordan’s position of 89.
Land use in Jordan: 1.1% (2018 estimate) forest, 87.5% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 11.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 8.4% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 964 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Jordan are tomatoes, poultry, olives, milk, potatoes, cucumbers, vegetables, watermelons, green chilies/peppers, peaches/nectarines.
The country typically needs to import: cars, refined petroleum, natural gas, crude petroleum, clothing, and apparel (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 17%, Saudi Arabia 15%, United States 6%, United Arab Emirates 6%, Egypt 5%, India 5% (2019) in a sum value of $22.04 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $22.92 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Jordan 79.
Jordan Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Jordan, the Middle East, the northwest of Saudi Arabia, between Israel (to the West) and Iraq. We published some basic information about its capital Amman, and the Jordanian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Jordan and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Jordan below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Jordan
Did you know about Jordan?
Jordan is located in the Middle East, and it has been a part of many different empires. The most well-known era for Jordan was part of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman Empire consisted of primarily Muslim countries ruled by a mighty empire. When World War I broke out, the Ottoman Empire lost its power, and Jordan became a colony.
After virtually visiting Jordan, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Iraq, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Syria, West Bank.
If you liked our Google map and Jordan information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.