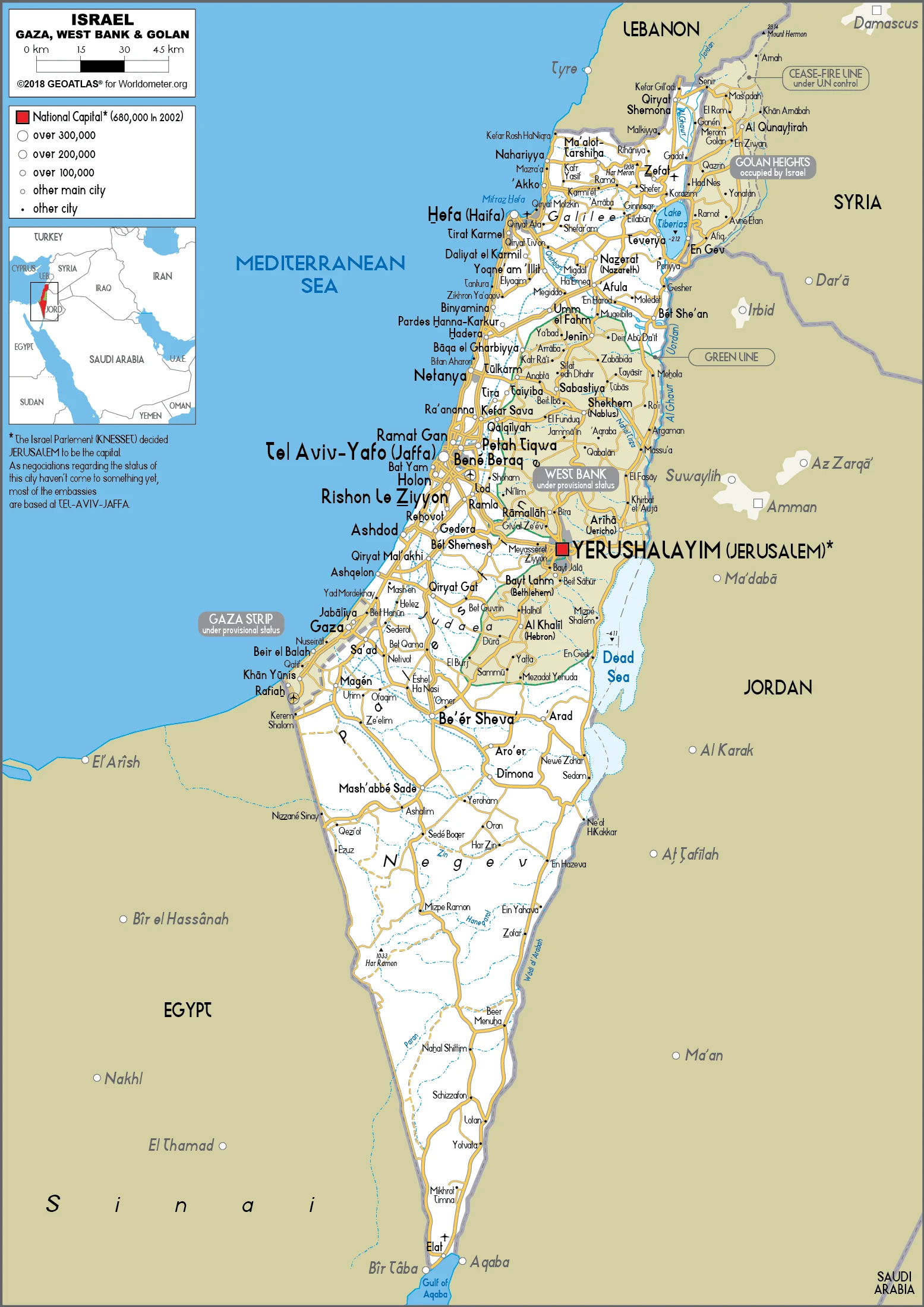
Israel Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Israel, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Israel, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Jerusalem, bordering countries like Egypt, Gaza Strip, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, West Bank, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Israel, Jerusalem Google maps, Driving Directions Israel, Printable Road Map.

About Israel in a nutshell
- All Jews worldwide have the right to Israeli citizenship.
- Conventional short form of the name: Israel
- The conventional long form of the name: State of Israel
- Local long form: Medinat Yisrael
- Local short form: Yisrael
- Etymology: named after the ancient Kingdom of Israel; according to Biblical tradition, the Jewish patriarch Jacob received the name Israel (He who struggles with God) after he wrestled an entire night with an angel of the Lord; Jacobs 12 sons became the ancestors of the Israelites, also known as the Twelve Tribes of Israel, who formed the Kingdom of Israel.
- The legal system in Israel: mixed legal system of English common law, British Mandate regulations, and Jewish, Christian, and Muslim religious laws.
- Climate: Summers are hot and dry. Wet season, MarchNovember, is mild.
- The national symbols are Star of David (Magen David), menorah (seven-branched lampstand); national colors: blue, white.
- Internet TLD: .il
The Jordan River runs parallel to the eastern shore of the Mediterranean; the fertile valley of Palestine ends in the Dead Sea, the most profound depression on the planet, 400 meters below sea level. After World War II, the State of Israel was established in Palestine. Since the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel has ruled the Golan Heights, the west bank of the Jordan River, and the Gaza Strip, conquered from Egypt. The Judean Desert and the Negev cover almost two-thirds of Israel’s territory. The settlement of Palestine began around 1800 BC when Abraham led his nomads from Mesopotamia to the land of Canaan. By 1023 BC, the first Israelite kingdom was established, and in 950 BC, King Solomon had the first temple built in Jerusalem. Babylonian conquerors and then the Roman Empire in 63 BC began to shape the history of Palestine and Judea. Revolts and oppressions, crusades, then the Ottoman Empire, and finally, in the mid-19th century, Palestine became a British protectorate.
Israel’s World Heritage Sites represent almost all periods of the last 3,000 years. The Phoenicians founded the fortified port city of Acre, and the Crusaders and the Turks have influenced its buildings. The rocky promontory of Masada, rising in the Judean desert overlooking the Dead Sea, is a symbol of the ancient kingdom of Israel, a symbol of the struggle against the Romans. The Iron Age burial cities of Meggido, Hazor, and Beer Sheba in the Bible, the Nabatean trading cities along the desert incense route in the Negev, and the modern ‘White Quarter’ of Tel Aviv, Israel’s capital, founded in the early 20th century and designed by European architects, are also universal treasures of humanity.
Background
Israel has emerged as a regional economic and military powerhouse, leveraging its booming high-tech sector, massive defense industry, and concerns about Iran to foster partnerships worldwide, even with some of its former foes. The State of Israel was declared in 1948 after Britain withdrew from its mandate of Palestine. The UN proposed partitioning the area into Arab and Jewish states, and Arab armies that rejected the UN plan were defeated. Israel was admitted as a member of the UN in 1949 and saw rapid population growth, primarily due to migration from Europe and the Middle East, over the following years. Israel fought wars against its Arab neighbors in 1967 and 1973, followed by peace treaties with Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994. Israel took control of the West Bank and Gaza Strip in the 1967 war and subsequently administered those territories through military authorities. Israel and Palestinian officials signed several interim agreements in the 1990s that created an interim period of Palestinian self-rule in the West Bank and Gaza.
Israel withdrew from Gaza in 2005. While the most recent formal efforts to negotiate final status issues occurred in 2013-2014, the US continues to advance peace. Immigration to Israel continues, with more than20,000 new immigrants, predominantly Jewish, in 2020. The Israeli economy has undergone a dramatic transformation in the last 25 years, led by cutting-edge, high-tech sectors. Offshore gas discoveries in the Mediterranean, most notably in the Tamar and Leviathan gas fields, place Israel at the center of a potential regional natural gas market. However, longer-term structural issues such as low labor force participation among minority populations, low workforce productivity, high costs for housing and consumer staples, and a lack of competition remain a concern for many Israelis and an essential consideration for Israeli politicians.
Former Prime Minister Benjamin NETANYAHU dominated Israel’s political landscape from 2009 to June 2021, becoming Israel’s longest-serving prime minister before he was unseated by Naftali BENNETT, after Israel’s fourth election in two years. BENNETT formed the most ideologically diverse coalition in Israel’s history, including an Arab-Israeli party. Under the terms of the coalition agreement, BENNETT would remain as prime minister until August 2023, then Alternate Prime Minister and Foreign Minister Yair LAPID would succeed him. Israel signed normalization agreements brokered by the US with Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, and Morocco in late 2020 and with Sudan in early 2021.
Geography
Coastal plain. Desert in the south. In the east lie the Great Rift Valley and the Dead Sea, the lowest point on the Earths land surface.
In the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Britain, the Irish Republic governs about 85% of the island of Ireland, with the remainder (Northern Ireland) being part of the UK.
This state is located in the Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and Lebanon, under the coordinates of 31 30 N, 34 45 E, covering an area of 21,937 sq km with a coastline of 273 km. Israel is Slightly more significant than New Jersey.
Israel has 1,068 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (6 nations): Egypt 208 km, Gaza Strip 59 km, Jordan 327 km (20 km are within the Dead Sea), Lebanon 81 km, Syria 83 km, West Bank 330 km.
Negev desert in the south, low coastal plain, central mountains, Jordan rift valley, with Mitspe Shlagim 2,224 m; as the highest point of Israel, while the Dead Sea -431 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 508 m throughout the country. With 21,937 sq km, Israel has 21,497 sq km of land and 440 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Dead Sea (shared with Jordan and West Bank) – 1,020 sq km (saltwater lake).
Lake Tiberias (Sea of Galilee) is an important freshwater source; the Dead Sea is the second saltiest body of water in the world (after Lake Assal in Djibouti).
The climate in Israel is as follows: Temperate, hot, and dry in southern and eastern desert areas.
When you visit Israel, the natural hazards shall be considered: Sandstorms may occur during spring and summer, droughts, periodic earthquakes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Israel: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Israeli people: limited arable land and limited natural fresh water resources; desertification; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; groundwater pollution from industrial and domestic waste, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides.
Google Maps Israel
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Jerusalem found under the coordinates 31 46 N, 35 14 E, applying the time zone UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, Friday before the last Sunday in March; ends the last Sunday in October.
The capital of Israel is Jerusalem. It’s the most ancient city in the world, and it’s where Judaism, Islam, and Christianity all believe that their respective prophets lived. The city has been fought over by many different countries and empires throughout history, with its status changing more than once. Today and for a few hundred years at least, it is considered the capital of Israel.
Israel became independent on 14 May 1948 (following League of Nations mandate under British administration), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 14 May (1948);.
Administrative divisions: 6 districts (mehozot, singular – mehoz); Central, Haifa, Jerusalem, Northern, Southern, Tel Aviv.
People and society
Large numbers of Jews settled in Palestine before Israel was founded in 1948. After World War II, there was a massive increase in immigration. Sephardi Jews from the Middle East and the Mediterranean are now in the majority, but Ashkenazi Jews from central Europe dominate business and politics. Palestinians in Gaza and Jericho gained limited autonomy in 1994, but Israeli Palestinian talks on a two-state solution, backed by most of the world, have repeatedly foundered.
The population in Israel is 8,787,045 (includes populations of the Golan Heights or Golan Sub-District and East Jerusalem, which Israel annexed in 1967) (July 2021 estimate). Note: approximately 227,100 Israeli settlers live in East Jerusalem (2019); following the March 2019 US recognition of the Golan Heights as being part of Israel, we no longer include the Israeli settler population of the Golan Heights (estimated at 23,400 in 2019) in its overall Israeli settler total, with an average of 1.45% (2021 estimate) change. That means Israel is the No. 98 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 30.4 years median age (29.8 years for males and 29.8 years for women), Israel ranks No. 121 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Israeli(s) (noun) or Israeli (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Jewish 74.1% (of which Israel-born 78.1%, Europe/America/Oceania-born 15.2%, Africa-born 4.3%, Asia-born 2.4%), Arab 21%, other 4.9% (2019 estimate).
They speak Hebrew (official language), Arabic (special status under Israeli law), English (most commonly used foreign language) languages and practice the following religions: Jewish 74.1%, Muslim 17.9%, Christian 1.9%, Druze 1.6%, other 4.5% (2019 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Israel: Population concentrated in and around Tel-Aviv and around the Sea of Galilee. The south remains sparsely populated, except the shore of the Gulf of Aqaba. In Israel, we are talking about 92.7% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 4.264 million, Tel Aviv-Yafo, 1.155 million, Haifa, 944,000 Jerusalem (capital city) (2021).
Industry
High-tech industries, modern infrastructure, and educated workforce, but hampered by conflict and boycotts.
Israel has a technologically advanced free market economy. Cut diamonds, high-technology equipment, and pharmaceuticals are among its leading exports. Its major imports include crude oil, grains, raw materials, and military equipment. Israel usually posts sizable trade deficits, offset by tourism and other service exports and significant foreign investment inflows. Since March 2020, economic growth has slowed compared to recent historical averages. Still, Israel’s slump has been less severe than other Middle Eastern countries because of its swift vaccine roll-out and diversified economic base. Between 2016 and 2019, growth averaged 3.6% per year, led by exports. Israel’s new government is hoping to pass the country’s first budget in two years, which, combined with prudent fiscal policy and global solid trade ties, would enable Israel to recover from the economic challenges caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Natural gas fields discovered off Israel’s coast since 2009 have brightened Israel’s energy security outlook. The Tamar and Leviathan fields were some of the world’s largest offshore natural gas finds in the last decade. In 2020, Israel began exporting gas to Egypt and Jordan.
Income inequality and high housing and commodity prices continue to concern many Israelis. Israel’s income inequality and poverty rates are among the highest OECD countries. There is a broad perception among the public that a small number of tycoons have a cartel-like grip over the major parts of the economy. Government officials have called for reforms to boost the housing supply and increase competition in the banking sector to address these public grievances. Despite calls for reforms, the restricted housing supply continues to impact younger Israelis seeking to purchase homes. Tariffs and non-tariff barriers, coupled with guaranteed prices and customs tariffs for farmers, kept food prices high. Private consumption is expected to drive growth through 2021, with consumers benefitting from low inflation and a strong currency.
Israel faces structural issues in the long term, including low labor participation rates for its fastest growing social segments – the ultraorthodox and Arab-Israeli communities. Also, Israel’s progressive, globally competitive, knowledge-based technology sector employs only about 8% of the workforce, with the rest mainly employed in manufacturing and services – sectors that face downward wage pressures from global competition. Expenditures on educational institutions remain low compared to most other OECD countries with similar GDP per capita.
Israel is rich in the following natural resources: Timber, potash, copper ore, natural gas, phosphate rock, magnesium bromide, clays, sand.
The main industrial sectors are typically high-technology products (including aviation, communications, computer-aided design and manufactures, medical electronics, fiber optics), wood and paper products, potash and phosphates, food, beverages, and tobacco, caustic soda, cement, pharmaceuticals, construction, metal products, chemical products, plastics, cut diamonds, textiles, footwear.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in diamonds, packaged medicines, medical instruments, integrated circuits, refined petroleum (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 26%, China 9%, United Kingdom 7% (2020). The export trade resulted in $113.87 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Israel’s position of 38.
Land use in Israel: 7.1% (2018 estimate) forest, 69.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 13.7% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 23.8% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 3.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 6.3% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 2,250 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Israel are milk, potatoes, poultry, tomatoes, carrots, turnips, tangerines/mandarins, green chilies/peppers, eggs, vegetables.
The country typically needs to import: diamonds, cars, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 12%, China 11%, Germany 7.5%, Switzerland 7%, Turkey 6% (2020) in a sum value of $96.53 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $108.26 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $107.74 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Israel 41.
Israel Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Israel, the Middle East, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and Lebanon. We published some basic information about its capital Jerusalem, and the Israeli nation.
Are you interested in visiting Israel and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Israel below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Israel
Did you know about Israel?
Israel was founded in 1948 as a homeland for Jewish people. The nation was initially established to provide a safe haven for Jews and their culture, but it quickly became a strong center of democracy and peace. Israel is home to many cultural, religious, and historical sites that interest those who visit the country. It is one of the oldest nationalities globally and has a diverse history that includes biblical accounts, Arab invasions, two world wars, Holocausts, and much more.
After virtually visiting Israel, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Egypt, Gaza Strip, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, West Bank.
If you liked our Google map and Israel information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.