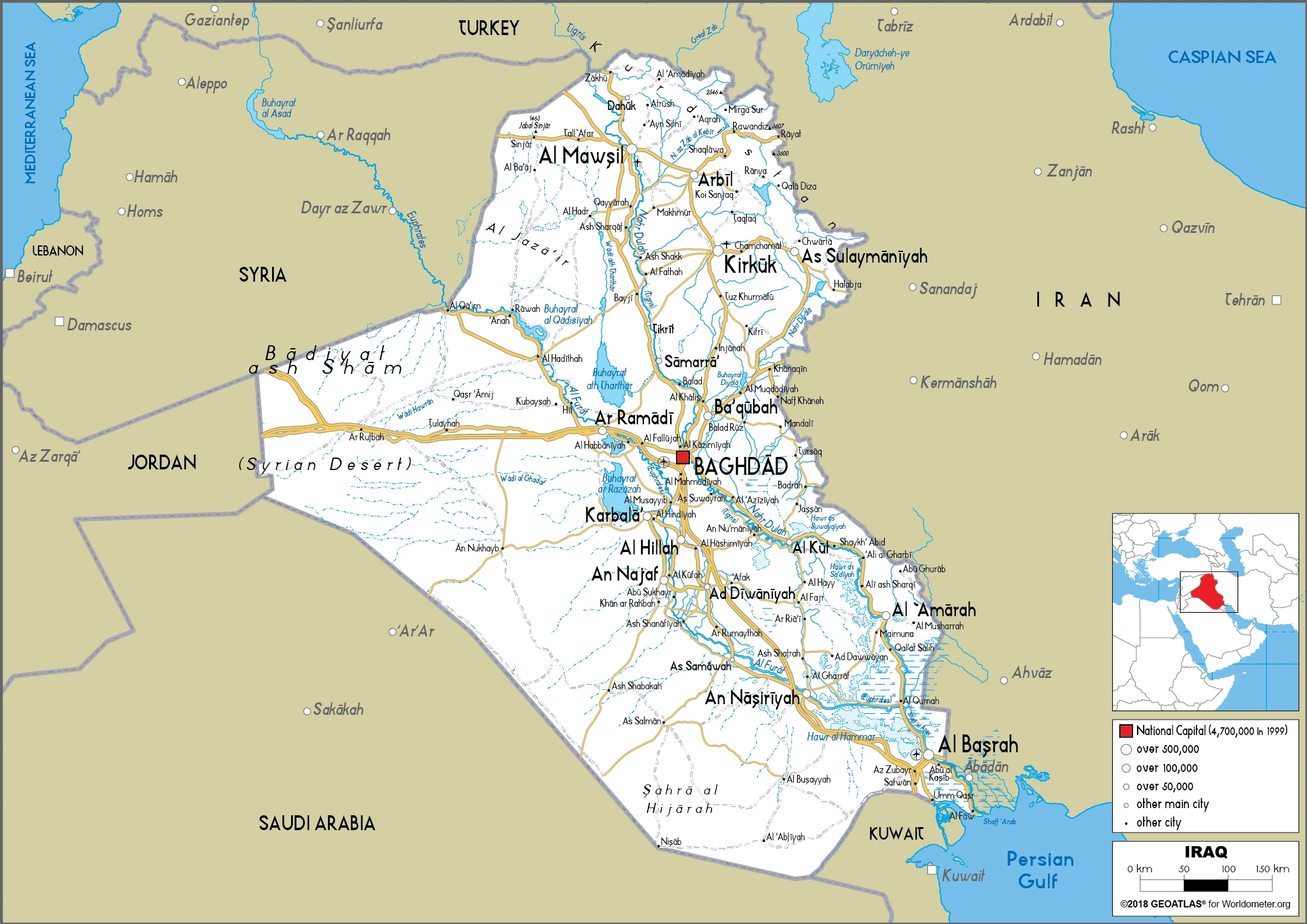
Iraq Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Iraq, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Iraq, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Baghdad, bordering countries like Iran, Jordan, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Iraq, Baghdad Google maps, Driving Directions Iraq, Printable Road Map.

About Iraq in a nutshell
- As Mesopotamia, Iraq was the site where the Sumerians established the worlds first civilization.
- Conventional short form of the name: Iraq
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Iraq
- Local long form: Jumhuriyat al-Iraq / Komar-i Eraq
- Local short form: Al Iraq / Eraq
- Former name(s): Mesopotamia, Mandatory Iraq, Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq
- Etymology: the name probably derives from Uruk (Biblical Erech), the ancient Sumerian and Babylonian city on the Euphrates River.
- The legal system in Iraq: mixed legal system of civil and Islamic law.
- Climate: Southern deserts have hot, dry summers and mild winters. North has dry summers, but winters can be harsh in the mountains. Rainfall is low.
- The national symbols are golden eagle; national colors: red, white, black.
- Internet TLD: .iq
The embrace of the Tigris and the Euphrates once was home to the oldest civilizations on Earth. Since the conflicts of the last two decades – the Iranian war, the Gulf War, and the outbreak of the Iraqi war that turned into a civil war to overthrow Saddam Hussein – tourism has been suspended, and the priceless treasures of the Baghdad National Museum have disappeared. What remains of Mesopotamia’s Sumerian, Assyrian, Babylonian and Arabic monuments after the devastating wars are now on UNESCO’s World Heritage List. Rising on the banks of the Tigris, the city-state of Assur became the first capital of the Assyrian Empire in the third millennium B.C. and a commercial and religious center of international importance. It has been a World Heritage Site in Danger since 2003: the planned construction of a reservoir would flood the ruins. The fortified fortress of Hatra, the first Arab kingdom to resist the Roman siege for 80 years in the 2nd century, with its temples combining Hellenic and Roman architecture with oriental ornamentation, is a testimony to the greatness of this early civilization.
Background
Formerly part of the Ottoman Empire, Iraq was occupied by the United Kingdom during World War I and was declared a League of Nations mandate under U.K. administration in 1920. Iraq attained its independence as a kingdom in 1932. It was proclaimed a republic in 1958 after a coup overthrew the monarchy, but a series of strongmen ruled the country until 2003. The last was SADDAM Husayn from 1979 to 2003. Territorial disputes with Iran led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war (1980-88). In August 1990, Iraq seized Kuwait but was expelled by US-led UN coalition forces during the Gulf War of January-February 1991. After Iraq’s expulsion, the U.N. Security Council (UNSC) required Iraq to scrap all weapons of mass destruction and long-range missiles and allow U.N. verification inspections. Continued Iraqi noncompliance with UNSC resolutions led to the Second Gulf War in March 2003 and US-led forces’ ouster of the SADDAM Husayn regime. In October 2005, Iraqis approved a constitution in a national referendum and, under this document, elected a 275-member Council of Representatives (COR) in December 2005.
The COR approved most cabinet ministers in May 2006, marking the transition to Iraq’s first constitutional government in nearly a half-century. Iraq held elections for provincial councils in all governorates in January 2009 and April 2013 and postponed the next provincial elections, initially planned for April 2017, until 2019. Iraq had held three national legislative elections since 2005, most recently in May 2018, when 329 legislators were elected to the COR. Adil ABD AL-MAHDI assumed the premiership in October 2018 as a consensus and independent candidate – the first prime minister who is not an active member of a significant political bloc. However, widespread protests that began in October 2019 demanding more employment opportunities and an end to corruption prompted ABD AL-MAHDI to announce his resignation on 20 November 2019. Between 2014 and 2017, Iraq was engaged in a military campaign against the Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS) to recapture territory lost in the western and northern portion of the country. Iraqi and allied forces recaptured Mosul, the country’s second-largest city, in 2017 and drove ISIS out of its other urban strongholds. In December 2017, then-Prime Minister Haydar al-ABADI publicly declared victory against ISIS while continuing operations against the group’s residual presence in rural areas. Also, in late 2017, ABADI responded to an independence referendum held by the Kurdistan Regional Government by ordering Iraqi forces to take control of disputed territories across central and northern Iraq that were previously occupied and governed by Kurdish forces.
Geography
Mainly desert. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers water fertile regions and create the southern marshland. Mountains along the northeast border.
Oil-rich Iraq is situated in the central Middle East. The last five decades have been dominated by dictatorship, war, and civil strife. A US-led Coalition ousted Saddam Hussein in 2003.
This state is located in the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait, under the coordinates of 33 00 N, 44 00 E, covering an area of 438,317 sq km with a coastline of 58 km. Iraq is Slightly more than three times the size of New York state.
Iraq has 3,809 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (6 nations): Iran 1599 km, Jordan 179 km, Kuwait 254 km, Saudi Arabia 811 km, Syria 599 km, Turkey 367 km.
Mostly broad plains, reedy marshes along Iranian border in south with large flooded areas, mountains along borders with Iran and Turkey, with Cheekha dar (Kurdish for black tent) 3,611 m as the highest point of Iraq, while Persian Gulf 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 312 m throughout the country. With a total of 438,317 sq km, Iraq has 437,367 sq km of land and 950 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Hammar – 1,940 sq km (a freshwater lake), N/A (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Euphrates river mouth (shared with Turkeys, Syria, and Iran) – 3,596 km, Tigris river mouth (shared with Turkeys, Syria, and Iran) – 1,950 km, the Tigris and Euphrates join to form the Shatt al Arab. The significant watersheds for Iraq are the Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf), Tigris, and Euphrates (918,044 sq km).
Strategic location on Shatt al Arab waterway and at the head of the Persian Gulf.
The climate in Iraq is as follows: Mostly desert, mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers, northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding in central and southern Iraq.
When you visit Iraq, the natural hazards are dust storms, sandstorms, floods.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Iraq: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Iraqi people: government water control projects drained most of the inhabited marsh areas east of An Nasiriyah by drying up or diverting the feeder streams and rivers; a once sizable population of Marsh Arabs, who inhabited these areas for thousands of years, has been displaced; furthermore, the destruction of the natural habitat poses severe threats to the areas wildlife populations; inadequate supplies of potable water; soil degradation (salination) and erosion; desertification; military and industrial infrastructure has released heavy metals and other hazardous substances into the air, soil, and groundwater; significant sources of environmental damage are effluents from oil refineries, factory, and sewage discharges into rivers, fertilizer and chemical contamination of the soil, and industrial air pollution in urban areas.
Google Maps Iraq
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Baghdad found under the coordinates 33 20 N, 44 24 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Baghdad, or The City of Peace, is Iraq’s capital and most populous city. It was founded in 762 BC by the Assyrian king Sargon II as a new capital for the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Baghdad is a city that has seen many ups and downs throughout its history, but in recent years it has experienced a drastic transformation. Baghdad’s development over the last decade has been nothing short of remarkable.
Iraq became independent on 3 October 1932 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration);, and its national holiday is Independence Day, 3 October (1932); Republic Day, 14 July (1958).
Administrative divisions: 18 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah (Arabic); parezgakan, singular – parezga (Kurdish)) and 1 region*; Al Anbar; Al Basrah; Al Muthanna; Al Qadisiyah (Ad Diwaniyah); An Najaf; Arbil (Erbil) (Arabic), Hewler (Kurdish); As Sulaymaniyah (Arabic), Slemani (Kurdish); Babil; Baghdad; Dahuk (Arabic), Dihok (Kurdish); Dhi Qar; Diyala; Karbala; Kirkuk; Kurdistan Regional Government; Maysan; Ninawa; Salah ad-Din; Wasit.
People and society
Carved out of remnants of the Ottoman Empire, Iraq is home to Arab Muslims (mainly Shia, some Sunni), northern Kurds (persecuted under Saddam), and smaller minorities. Since Saddams removal, sectarian violence has overshadowed efforts to build democracy. U.S. forces withdrew in 2011. By 2014 Islamic State jihadists controlled part of the country. After years of war and sanctions, poverty is widespread.
The population in Iraq is 39,650,145 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 2.06% (2021 estimate) change. That means Iraq is the No. 36 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 21.2 years median age (20.8 years for males and 20.8 years for women), Iraq ranks No. 185 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Iraqi(s) (noun) or Iraqi (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Arab 75-80%, Kurdish 15-20%, other 5% (includes Turkmen, Yezidi, Shabak, Kakai, Bedouin, Romani, Assyrian, Circassian, Sabaean-Mandaean, Persian),. Note: data is a 1987 government estimate; no more recent reliable numbers are available.
They speak Arabic (official language), Kurdish (official language), Turkmen (a Turkish dialect), Syriac (Neo-Aramaic), and Armenian are official in areas where native speakers of these languages constitute a majority of the population languages and practice the following religions: Muslim (official) 95-98% (Shia 64-69%, Sunni 29-34%), Christian 1% (includes Catholic, Orthodox, Protestant, Assyrian Church of the East), other 1-4% (2015 estimate) note: while there has been voluntary relocation of many Christian families to northern Iraq, the overall Christian population has decreased at least 50% and perhaps as high as 90% since the fall of the SADDAM Husayn regime in 2003, according to U.S. Embassy estimates, with many fleeing to Syria, Jordan, and Lebanon.
We can conclude the following about the population in Iraq: Population is concentrated in the north, center, and eastern parts of the country, with many of the larger urban agglomerations found along with extensive parts of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Much of the western and southern areas are either lightly populated or uninhabited. In Iraq, we are talking about 71.1% (2021) of the total population is living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 7.323 million, Baghdad (capital city), 1.683 million, Mosul, 1.382 million, Basra, 1.031 million, Kirkuk, 901,000 Najaf, 861,000 Erbil (2021).
Industry
The economy and infrastructure have been destroyed. Given stability and aid for reconstruction, hopes of recovery would rest on massive oil reserves.
Iraq’s GDP growth slowed to 1.1% in 2017, a marked decline compared to the previous two years as domestic consumption and investment fell because of civil violence and a sluggish oil market. The Iraqi government received its third tranche of funding from its 2016 Stand-By Arrangement (SBA) with the IMF in August 2017, intended to stabilize its finances by encouraging improved fiscal management, needed economic reform, and expenditure reduction. Additionally, in late 2017 Iraq received more than $1.4 billion in financing from international lenders, part of which was generated by issuing a $1 billion bond for reconstruction and rehabilitation in areas liberated from ISIL. Investment and key sector diversification are crucial components to Iraq’s long-term economic development. They require a strengthened business climate with enhanced legal and regulatory oversight to bolster private-sector engagement. The overall standard of living depends on global oil prices, the central government passage of major policy reforms, a stable security environment post-ISIS, and the resolution of civil discord with the Kurdish Regional Government (KRG)., The oil sector dominates Iraq’s largely state-run economy, which provides roughly 85% of government revenue and 80% of foreign exchange earnings. It is a significant determinant of the economy’s fortunes.
Iraq’s contracts with major oil companies have the potential to expand oil exports and revenues further, but Iraq will need to make significant upgrades to its oil processing, pipeline, and export infrastructure to enable these deals to reach their economic potential., In 2017, Iraqi oil exports from northern fields were disrupted following a KRG referendum, resulting in the Iraqi government reasserting federal control over disputed oil fields and energy infrastructure in Kirkuk. The Iraqi government and the KRG dispute the role of federal and regional authorities in the development and export of natural resources. In 2007, the KRG passed an oil law to develop IKR oil and gas reserves independent of the Federal Government. The KRG has signed about 50 contracts with foreign energy companies to develop its reserves, some of which lie in territories taken by Baghdad in October 2017. The KRG can unilaterally export oil from the fields it retains control of through its pipeline to Turkey, which Baghdad claims is illegal. In the absence of a national hydrocarbons law, the two sides have entered into five provisional oil- and revenue-sharing deals since 2009, all of which collapsed. Iraq is making slow progress in enacting laws and developing the institutions needed to implement economic policy. Political reforms are still needed to assuage investors’ concerns regarding the uncertain business climate.
The Government of Iraq is eager to attract additional foreign direct investment. Still, it faces several obstacles, including a tenuous political system and security and societal stability concerns. Rampant corruption, outdated infrastructure, insufficient essential services, skilled labor shortages, and antiquated commercial laws stifle investment and continue to constrain the growth of private, nonoil sectors. Under the Iraqi constitution, some competencies relevant to the overall investment climate are either shared by the federal government and the regions or are devolved entirely to local governments. Investment in the IKR operates within the framework of the Kurdistan Region Investment Law (Law 4 of 2006) and the Kurdistan Board of Investment, designed to provide incentives to help economic development in areas under the KRG. Inflation has remained under control since 2006. However, Iraqi leaders remain hard-pressed to translate macroeconomic gains into an improved standard of living for the Iraqi populace. Unemployment remains a problem throughout the country despite a bloated public sector. Overregulation has made it difficult for Iraqi citizens and foreign investors to start new businesses. Corruption and lack of economic reforms – such as restructuring banks and developing the private sector have inhibited the growth of the private sector.
Iraq is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, phosphates, sulfur.
The main industrial sectors are typically petroleum, chemicals, textiles, leather, construction materials, food processing, fertilizer, metal fabrication/processing.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in crude petroleum, refined petroleum, gold, dates, petroleum coke (2019), partnering with these nations: China 26%, India 24%, South Korea 9%, United States 8%, Italy 6%, Greece 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $50.61 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Iraq’s position of 56.
Land use in Iraq: 1.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 80% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 8.4% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 18.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.5% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 9.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 35,250 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Iraq are wheat, barley, dates, tomatoes, rice, maize, grapes, potatoes, rice, watermelons.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, cars, jewelry, cigarettes (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United Arab Emirates 28%, Turkey 21%, China 19% (2019) in a sum value of $54.72 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $72.28 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $56.88 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Iraq 55.
Iraq Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Iraq, the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait. We published some basic information about its capital Baghdad, and the Iraqi nation.
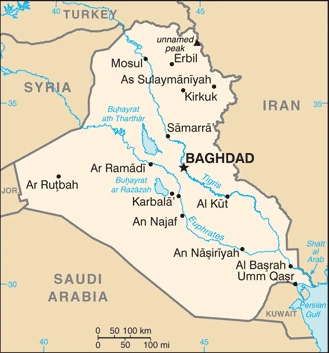
Are you interested in visiting Iraq and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Iraq below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Iraq
Did you know about Iraq?
The United States military invaded Iraq in 2003, installing a new government and taking control of the country. The Middle Eastern country was an oil-rich nation not unlike Kuwait, but it posed a threat to the U.S. because of its connections to Islamic terrorism.
After virtually visiting Iraq, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Iran, Jordan, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey.
If you liked our Google map and Iraq information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.