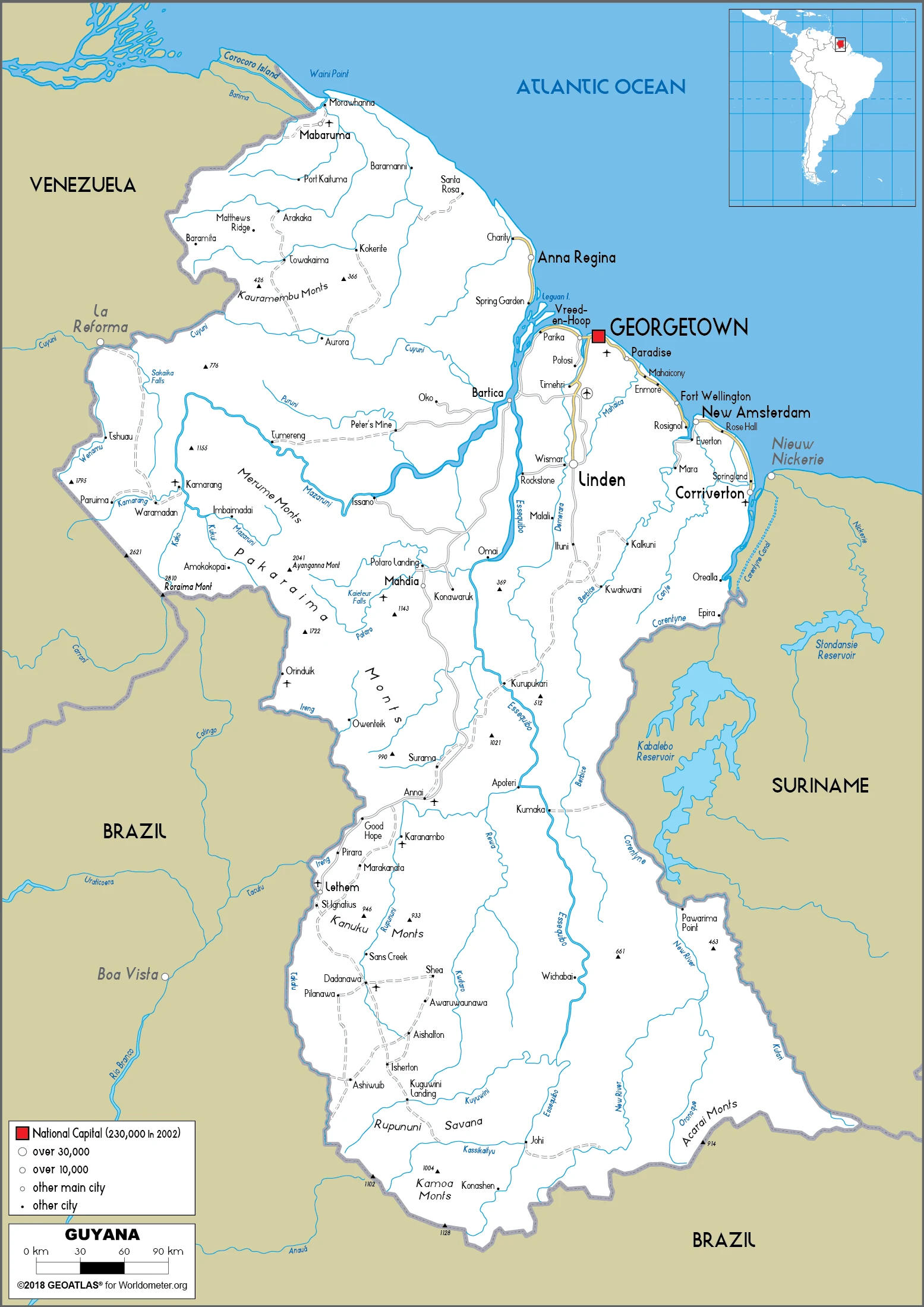
Guyana Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Guyana, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Guyana, South America (13 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Georgetown, bordering countries like Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this South American state.
Quick links: Google Maps Guyana, Georgetown Google maps, Driving Directions Guyana, Printable Road Map.

About Guyana in a nutshell
- Guyana means “land of many waters,” reflecting its dense network of rivers.
- Conventional short form of the name: Guyana
- The conventional long form of the name: Cooperative Republic of Guyana
- Former name(s): British Guiana
- Etymology: the name is derived from Guiana, the original name for the region that included British Guiana, Dutch Guiana, and French Guiana; ultimately the word is derived from an indigenous Amerindian language and means Land of Many Waters (referring to the areas multitude of rivers and streams).
- The legal system in Guyana: common law system, based on the English model, with some Roman-Dutch civil law influence.
- Climate: Tropical. Coast cooled by sea breezes. Lowlands are hot, wet, and humid. Highlands are a little cooler.
- The national symbols are Canje pheasant (hoatzin), jaguar, Victoria Regia water lily; national colors: red, yellow, green, black, white.
- Internet TLD: .gy
Background
Originally a Dutch colony in the 17th century, by 1815, Guyana had become a British possession. The abolition of slavery led to the settlement of urban areas by formerly enslaved people and the importation of indentured servants from India to work the sugar plantations. The resulting ethnocultural divide has persisted and has led to turbulent politics. Guyana achieved independence from the UK in 1966, and since then, it has been ruled mostly by socialist-oriented governments.
In 1992, Cheddi JAGAN was elected president in the country’s first free and fair election since independence. After his death five years later, his wife, Janet JAGAN, became president but resigned in 1999 due to poor health. Her successor, Bharrat JAGDEO, was elected in 2001 and 2006. Early elections held in May 2015 resulted in the first change in the governing party and the replacement of President Donald RAMOTAR by current President David GRANGER. After a December 2018 no-confidence vote against the GRANGER government, national elections will be held before the scheduled spring 2020.
Geography
Mainly artificial coast, reclaimed by dikes and dams from swamps and tidal marshes. Forests cover 85% of the interior, rising to savanna uplands and mountains.
On the northeast coast of South America, Guyana is the continent’s only English-speaking country. Independent since 1966, it had close ties with the anglophone Caribbean.
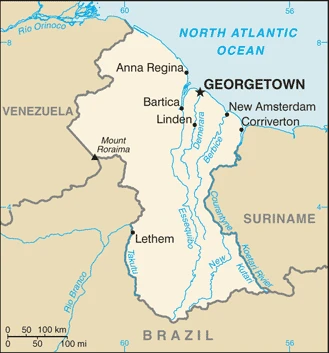
This state is located in Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela, under the coordinates of 5 00 N, 59 00 W, covering an area of 214,969 sq km with a coastline of 459 km. Guyana is Slightly smaller than Idaho, almost twice the size of Tennessee.
Guyana has 2,933 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (3 nations): Brazil 1308 km, Suriname 836 km, Venezuela 789 km.
Mostly rolling highlands, low coastal plain, savanna in south, with Laberintos del Norte on Mount Roraima 2,775 m as the highest point of Guyana, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 207 m throughout the country. With a total of 214,969 sq km, Guyana has 196,849 sq km of land and 18,120 sq km water surface area.
The principal rivers are Orinoco (shared with Colombia and Venezuela) – 2,101 km. The significant watersheds for Guyana are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km) Orinoco (953,675 sq km).
The third-smallest country in South America after Suriname and Uruguay; substantial portions of its western and eastern territories are claimed by Venezuela and Suriname respectively; contains some of the largest unspoiled rainforests on the continent.
The climate in Guyana is as follows: Tropical, hot, humid, moderated by northeast trade winds, two rainy seasons (May to August, November to January).
When you visit Guyana, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flash flood threat during rainy seasons.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Guyana: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, dengue fever, and malaria.
Current environmental issues affecting the Guyanese people: water pollution from sewage and agricultural and industrial chemicals; deforestation.
Google Maps Guyana
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Georgetown found under the coordinates 6 48 N, 58 09 W, applying the time zone UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Guyana, the capital of Guyana, and Georgetown is the largest city in Guyana. The city is situated on Sandy Point Bay on the north side of the Essequibo River, forming the border between Guyana and Venezuela. Georgetown has often been described as one of South America’s most culturally rich cities, dating back to colonial days.
Guyana became independent on 26 May 1966 (from the UK), and its national holiday is Republic Day, 23 February (1970).
Administrative divisions: 10 regions; Barima-Waini, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Demerara-Mahaica, East Berbice-Corentyne, Essequibo Islands-West Demerara, Mahaica-Berbice, Pomeroon-Supenaam, Potaro-Siparuni, Upper Demerara-Berbice, Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo.
People and society
Guyana is a complex multiracial society. Tension exists between the Afro-Guyanese, descended from enslaved people, and the Indo-Guyanese, descendants of laborers brought over after slavery was abolished. Politics is highly polarized around this split and has often spilled over into violence on the streets. Amerindian subsistence farmers are the poorest people in society and have little representation.
The population in Guyana is 787,971 (July 2021 estimate). Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected, with an average of 0.19% (2021 estimate) change. That means Guyana is the No. 166 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 27.5 years median age (27.2 years for males and 27.2 years for women), Guyana ranks No. 146 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Guyanese (also singular and plural) (noun) or Guyanese (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: East Indian 39.8%, African descent 29.3%, mixed 19.9%, Amerindian 10.5%, other 0.5% (includes Portuguese, Chinese, White) (2012 estimate).
They speak English (official language), Guyanese Creole, Amerindian languages (including Caribbean and Arawak languages), Indian languages (including Caribbean Hindustani, a dialect of Hindi), Chinese (2014 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 34.8% (Pentecostal 22.8%, Seventh Day Adventist 5.4%, Anglican 5.2%, Methodist 1.4%), Hindu 24.8%, Roman Catholic 7.1%, Muslim 6.8%, Jehovahs Witness 1.3%, Rastafarian 0.5%, other Christian 20.8%, other 0.9%, none 3.1% (2012 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Guyana: Population is heavily concentrated in the northeast in and around Georgetown, with noticeable concentrations along the Berbice River to the east. The remainder of the country is sparsely populated. In Guyana, we are talking about 26.9% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 110,000 Georgetown (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Diverse exports: gold, sugar, fish, bauxite, rice, timber, diamonds. Debt relief granted. Narcotics transit zone.
In recent years, the Guyanese economy exhibited moderate economic growth mainly based on agriculture and extractive industries. The economy is heavily dependent upon the export of six commodities – sugar, gold, bauxite, shrimp, timber, and rice – which represent nearly 60% of the country’s GDP and are highly susceptible to adverse weather conditions and fluctuations in commodity prices. Guyana closed or consolidated several sugar estates in 2017, reducing sugar production to a forecasted 147,000 tons in 2018, less than half of 2017 production. In recent years, much of Guyana’s growth has come from a surge in gold production. With a record-breaking 700,000 ounces of gold produced in 2016, Guyana’s gold production has offset the economic effects of declining sugar production. In January 2018, an estimated 3.2 billion barrels of oil were found offshore, and Guyana is scheduled to become a petroleum producer by March 2020.
Guyana’s entrance into the Caricom Single Market and Economy in January 2006 broadened the country’s export market, primarily in the raw materials sector. Guyana has experienced positive growth almost every year over the past decade. Inflation has been kept under control. Recent years have seen the government’s debt stock reduced significantly – with external debt now less than half of what it was in the early 1990s. Despite these improvements, the government is still juggling a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. In March 2007, the Inter-American Development Bank, Guyana’s principal donor, canceled Guyanas nearly $470 million debt, equivalent to 21% of GDP, which along with other Highly Indebted Poor Country debt forgiveness, brought the debt-to-GDP ratio down from 183% in 2006 to 52% in 2017. Guyana had become heavily indebted due to the inward-looking, state-led development model pursued in the 1970s and 1980s. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient infrastructure.
Guyana is rich in the following natural resources: Bauxite, gold, diamonds, hardwood timber, shrimp, fish.
The main industrial sectors are typically bauxite, sugar, rice milling, timber, textiles, gold mining.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in ships, gold, shipping containers, excavation machinery, aluminum ores, rice (2019), partnering with these nations: Trinidad and Tobago 31%, Canada 11%, Portugal 11%, Ghana 8%, Norway 6%, United Arab Emirates 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.8 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Guyana’s position of 157.
Land use in Guyana: 77.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 14.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 8.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 6.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1,430 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Guyana are rice, sugar cane, coconuts, pumpkins, squash, gourds, milk, eggplants, green chilies/peppers, poultry.
The country typically needs to import: ships, refined petroleum, excavation machinery, shipping containers, aircraft (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 26%, Trinidad and Tobago 16%, Singapore 18%, Liberia 11%, China 5%, Norway 5% (2019) in a sum value of $4 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $3.12 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Guyana 151.
Guyana Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Guyana, Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela. We published some basic information about its capital Georgetown, and the Guyanese nation.
Are you interested in visiting Guyana and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Guyana below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Guyana
Did you know about Guyana?
It was discovered by Amerigo Vespucci in 1499 and was a colony of the Netherlands since 1623. Guyana is also known as Guiana, which is its official name. The country shares borders with Brazil, Suriname, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
After virtually visiting Guyana, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela.
If you liked our Google map and Guyana information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.