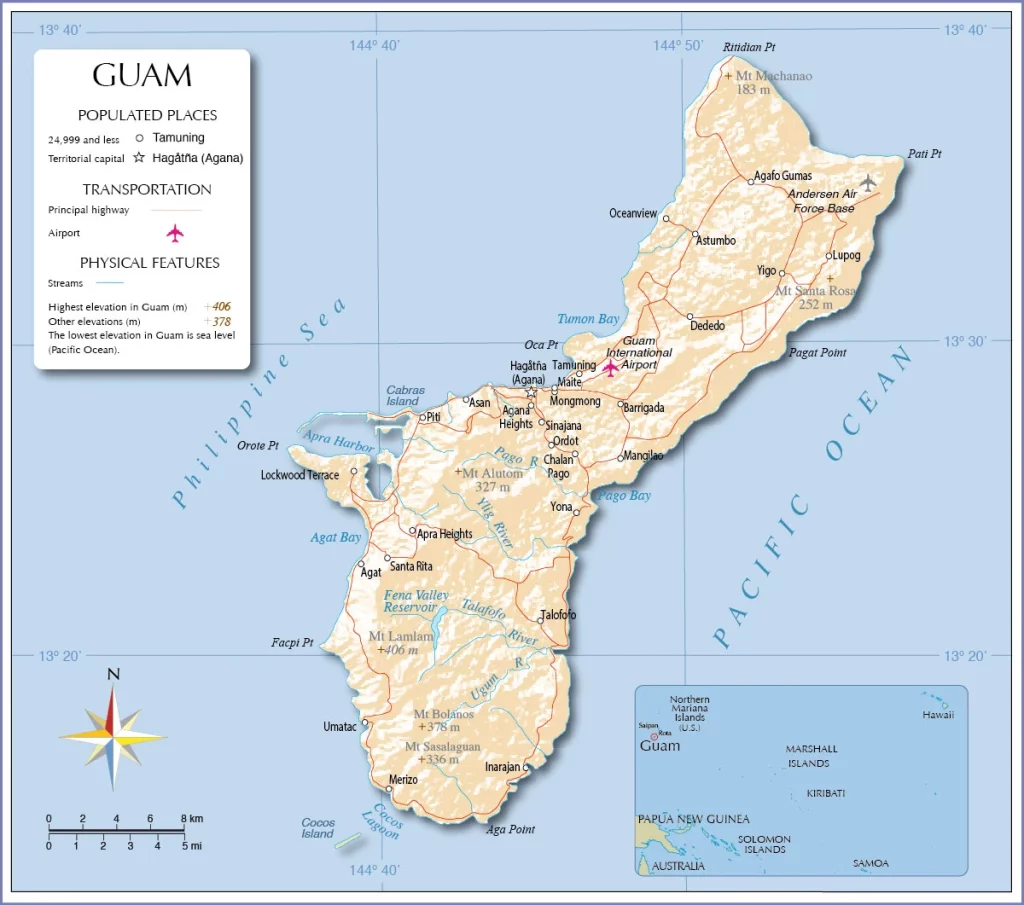
Guam Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Guam, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Guam, Oceania (27 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Hagatna (Agana), and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Oceanian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Guam, Hagatna (Agana) Google maps, Driving Directions Guam, Printable Road Map.

About Guam in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Guam
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Local long form: none
- Local short form: Guahan
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the native Chamorro name for the island Guahan (meaning we have or ours) was changed to Guam in the 1898 Treaty of Paris, whereby Spain relinquished Guam, Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines to the US.
- The legal system in Guam: common law modeled on US system; US federal laws apply.
- Climate: Tropical marine, generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds, dry season (January to June), rainy season (July to December), little seasonal temperature variation.
- The national symbols are coconut tree; national colors: deep blue, red.
- Internet TLD: .gu
Background
Guam was settled by Austronesian people around 1500 B.C. These people became the indigenous Chamorro and were influenced by later migrations, including the Micronesians in the first millennium A.D. and island Southeast Asians around 900. Society was stratified with higher classes living along the coast and lower classes living inland. Spanish explorer Ferdinand MAGELLAN was the first European to see Guam in 1521, and Spain claimed the island in 1565 as it served as a refueling stop for ships between Mexico and the Philippines. Spain formally colonized Guam in 1668. Spain’s brutal repression of Chamorro, along with new diseases and intermittent warfare, reduced the indigenous population from more than 100,000 to less than 5,000 by the 1700s. Spain tried to repopulate the island by forcing people from nearby islands to settle on Guam and preventing them from escaping.
Guam became a hub for whalers and traders in the western Pacific in the early 1800s. During the 1898 Spanish-American War, the U.S. Navy occupied Guam and set up a military administration. The U.S. Navy opposed local control of government despite repeated petitions by Chamorro. Japan invaded Guam in 1941 and instituted a repressive regime. During the U.S. recapture of Guam in 1944, the island’s two largest villages were destroyed. After World War II, political pressure from local Chamorro leaders led to Guam being established as an unincorporated organized territory in 1950 with U.S. citizenship granted to all Chamorro. In a referendum in 1982, more than 75% of voters chose closer relations with the U.S. over independence. However, no change in status was made because of disagreements on the future right of Chamorro’s self-determination. The U.S. military holds about 29% of Guam’s land and stations several thousand troops. The installations are some of the most strategically important U.S. bases in the Pacific. They also constitute the island’s most important source of income and economic stability.
Geography
Guam is an island in the Pacific Ocean part of the United States. With a total landmass of approximately 23 square miles, it’s one of the world’s smallest countries. With a population of around 165,000 people, Guam has changed hands throughout history and has been controlled by Spain, Germany, and Japan, among others.
This state is located in Oceania, an island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines, under the coordinates of 13 28 N, 144 47 E, covering an area of 544 sq km with a coastline of 125.5 km. Guam is Three times the size of Washington, DC.
Volcanic origin, surrounded by coral reefs, relatively flat coralline limestone plateau (source of most freshwater), with steep coastal cliffs and narrow coastal plains in the north, low hills in the center, mountains in the south, with Mount Lamlam 406 m as the highest point of Guam, while Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point. With 544 sq km, Guam has 544 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
The largest and southernmost island in the Mariana Islands archipelago and the largest island in Micronesia; strategic location in western North Pacific Ocean.
The climate in Guam is as follows: Tropical marine, generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds, dry season (January to June), rainy season (July to December), slight seasonal temperature variation.
When you visit Guam, the natural hazards shall be considered: Frequent squalls during the rainy season; relatively rare but potentially destructive typhoons (June to December).
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Guam: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Guamanian people: freshwater scarcity, reef damage; inadequate sewage treatment; the extermination of native bird populations by the rapid proliferation of the brown tree snake, an exotic, invasive species.
Google Maps Guam
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Hagatna (Agana) found under the coordinates 13 28 N, 144 44 E, applying the time zone UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital of Guam, Hagatna, is the main city on the island. For many years it was called Agana and was home to many Spanish missionaries. It became a village in 1671 and was included in the Municipality of Guam on September 12, 1878, by Governor Graciano Lopez Jaena.
Guam became independent on none (territory of the U.S.), and its national holiday is Discovery Day (or Magellan Day), the first Monday in March (1521).
Administrative divisions: none (territory of the U.S.).
People and society
The population in Guam is 168,801 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.18% (2021 estimate) change. That means Guam is the No. 185 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 29.4 years median age (28.7 years for males and 28.7 years for women), Guam ranks No. 130 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Guamanian(s) (US citizens) (noun) or Guamanian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Chamorro 37.3%, Filipino 26.3%, White 7.1%, Chuukese 7%, Korean 2.2%, other Pacific Islander 2%, other Asian 2%, Chinese 1.6%, Palauan 1.6%, Japanese 1.5%, Pohnpeian 1.4%, mixed 9.4%, other 0.6% (2010 estimate).
They speak English 43.6%, Filipino 21.2%, Chamorro 17.8%, other Pacific island languages 10%, Asian languages 6.3%, other 1.1% (2010 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Christian (predominantly Roman Catholic) 94.2%, folk religions 1.5%, Buddhist 1.1%, other 1.6%, unaffiliated 1.7% (2020 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Guam: No large cities exist on the island, though large villages (municipalities) attract much of the population. The largest of these is Dededo. In Guam, we are talking about 95% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 147,000 Hagatna (capital city) (2018).
Industry
U.S. national defense spending is the primary driver of Guam’s economy, followed closely by tourism and other services. Guam serves as a forward U.S. base for the Western Pacific and thousands of American military personnel. Total federal spending (defense and non-defense) amounted to $1.988 billion in 2016, or 34.2 of Guam’s GDP. Of that total, federal grants and cover-over payments amounted to $3444.1 million in 2016, or 35.8% of Guam’s total revenues for the fiscal year. In 2016, Guam’s economy grew by 0.3%. Guam’s economy has been stable over the last decade despite a slow growth. National defense spending cushions the island’s economy against fluctuations in tourism. Service exports, mainly spent by foreign tourists in Guam, amounted to over $1 billion for the first time in 2016, or 17.8% of GDP.
Guam is rich in natural resources: Aquatic wildlife (supporting tourism) fishing (largely undeveloped).
The main industrial sectors are typically national defense, tourism, construction, transshipment services, concrete products, printing and publishing, food processing, textiles.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in scrap iron, electric batteries, gas turbines, scrap copper, beauty products (2019), partnering with these nations: South Korea 31%, Hong Kong 27%, Taiwan 18%, Philippines 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.124 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2016 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Guam’s position of 176.
Land use in Guam: 47.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 18.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 33.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 16.7% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 14.8% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 2 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Guam are fruits, copra, vegetables, eggs, pork, poultry, beef.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, trunks/cases, cars, insulated wire, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: Singapore 33%, Japan 21%, South Korea 18%, Hong Kong 9%, Malaysia 6% (2019) in a sum value of $2.964 billion (2016 estimate) $3.054 billion (2015 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Guam 160.
Guam Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Guam, Oceania, an island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines. We published some basic information about its capital Hagatna (Agana), and the Guamanian nation.
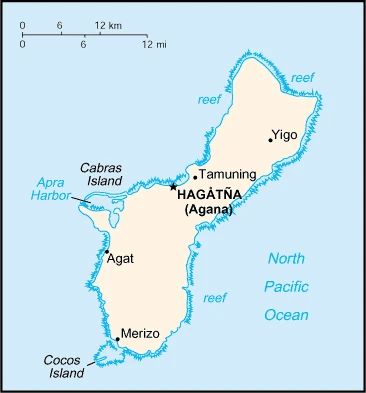
Are you interested in visiting Guam and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Guam below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Guam
Did you know about Guam?
Guam is part of the United States and is the smallest island in Micronesia. Even though it is small, Guam has a lot to offer. Guam is home to beautiful beaches, rich culture, and excellent cuisine.
After virtually visiting Guam, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and Guam information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.