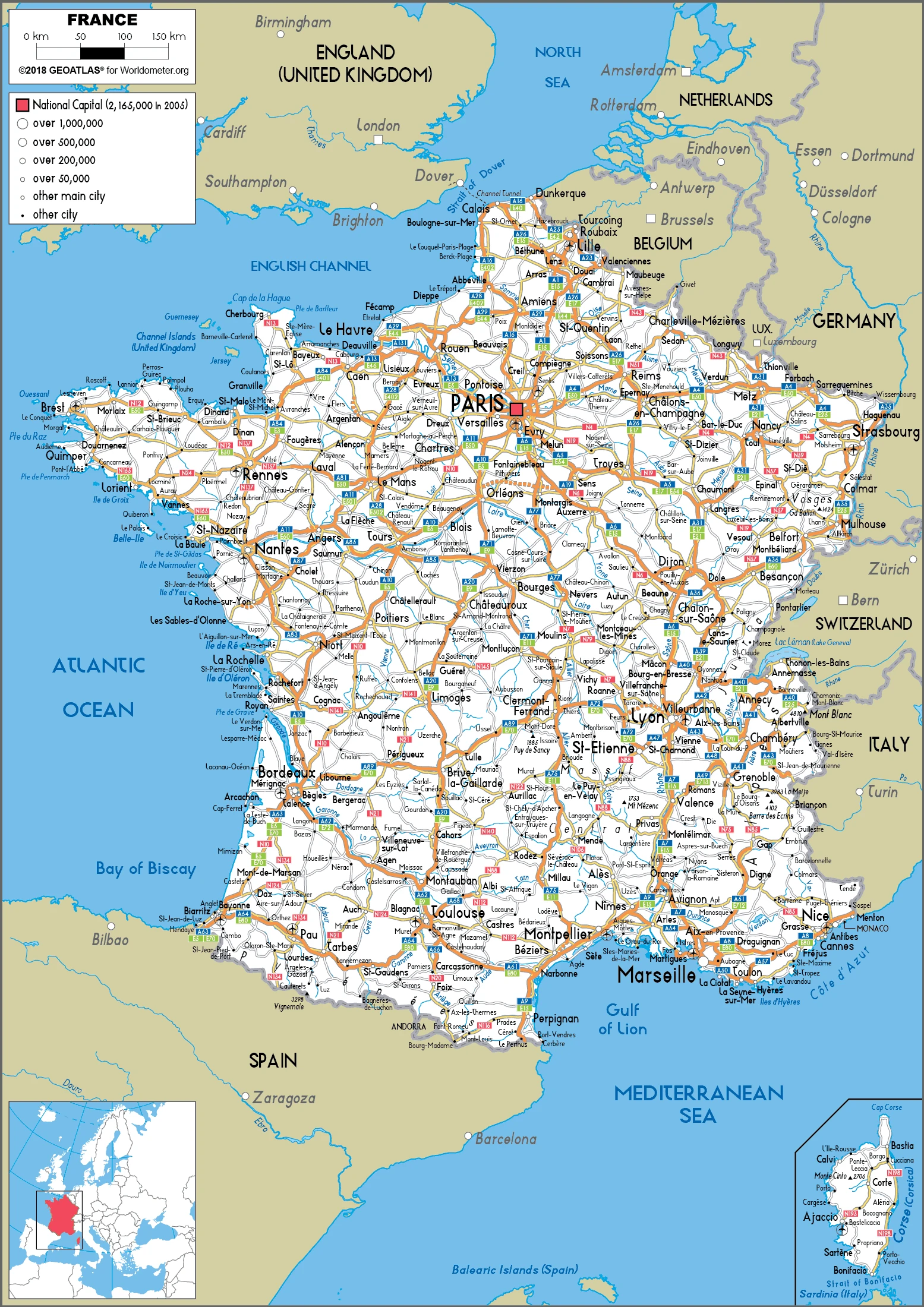
France Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like France, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to France and Metropolitan France in Europe. Still, you also may find French Guiana, South America, Guadeloupe, Central America and the Caribbean, Martinique, Central America and the Caribbean, Mayotte, Africa, Reunion information, showing their location, country facts, details about the capital city of France, Paris, and its bordering countries like Andorra, Belgium, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Monaco, Spain, Switzerland, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European country.
Quick links: Google Maps France, Paris Google maps, Driving Directions France, Printable Road Map.

About France in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: France
- The conventional long form of the name: French Republic
- Local long form: Republique francaise
- Local short form: France
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: name derives from Latin Francia, meaning Land of the Franks; the Franks were a group of Germanic tribes located along the middle and lower Rhine River in the 3rd century A.D. who merged with Gallic-Roman populations in succeeding centuries and to whom they passed on their name.
- The legal system in France: civil law; review of administrative but not legislative acts.
- Climate: Three main climates: temperate and damp northwest; continental east; and Mediterranean south.
- The national symbols are the Gallic rooster, fleur-de-lis, Marianne (female personification), and national colors: blue, white, and red.
- Internet TLD: metropolitan France: .fr, French Guiana: .gf, Guadeloupe: .gp, Martinique: .mq, Mayotte: .yt, Reunion: .re
The scenery in France is so diverse that no other country offers a comparable experience in such a small area. Travelers to France can head to Paris and experience one of the best cities or drive through green hills along the Loire River before going on to bask in the sun of Provence and the French Riviera.
France considered the gateway to Europe because of its favorable geographical location, is washed by the waves of three seas. Six times larger and six times more populous than our country, it has a varied landscape of lowlands, rolling hills, extinct volcanic cones, old rugged mountains, and glaciers carved by young chains. Here you will find everything a tourist could ever dream of: Mediterranean coastline with the Riviera, the superb ski slopes and peaks of the Alps at 3,000-4,000 meters – including the continent’s highest point, Mont Blanc at 4,807 meters, rivers and canals perfect for water sports, rolling hills, world-famous wines, and cheeses – not to mention the Champagne and Cognac that have made the names of France’s friendly landscapes known the world over.
Among the historical and cultural monuments of more than a millennium and a half the past, there are 31 World Heritage sites: prehistoric cave paintings, Romanesque monuments, medieval towns and Renaissance castles, Gothic cathedrals and palaces, castles and fortifications, and the incredible natural treasures of the national parks of the Pyrenees and Corsica. And of course Paris. The French capital, founded by the Celts, is a world apart: a center of art and fashion and home to the UNESCO headquarters. Paris is not only the capital of France but also the cultural capital of Europe and the world. And in terms of its technological development, it is the home of the world’s first photograph and the first motion picture, Piccard’s first deep-sea submarine, Captain Cousteau’s “voyage of conquest,” and the headquarters of the ESA, the European Space Agency.
France is the most popular tourist destination globally, with over 80 million visitors.
Background
France today is one of the most modern countries in the world and is a leader among European nations. It plays an influential global role as a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, NATO, the G-7, the G-20, the EU, and other multilateral organizations. France rejoined NATO’s integrated military command structure in 2009, reversing DE GAULLEs 1966 decision to withdraw French forces from NATO. Since 1958, it has constructed a hybrid presidential-parliamentary governing system resistant to the instabilities experienced in earlier, more purely parliamentary administrations. In recent decades, its reconciliation and cooperation with Germany have proved central to the economic integration of Europe, including the introduction of a common currency, the euro, in January 1999. In the early 21st century, five French overseas entities – French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion – became French regions and became part of France proper.
Geography
Broad plain covers the northern half of the country. High mountain ranges in the east and southwest, with a mountainous plateau in the center.
Stretching across western Europe, from the English Channel (la Manche) to the Mediterranean Sea, France was Europes first modern republic and is still a leading industrial power.
Metropolitan France is located in Western Europe, bordering the Bay of Biscay and the English Channel, between Belgium and Spain, southeast of the UK, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Italy and Spain, under the coordinates of 46 00 N, 2 00 E. France covers an area of 643,801 sq km, 551,500 sq km (Metropolitan France) with a coastline of 4,853 km, 3,427 km (Metropolitan France). France is Slightly more than four times the size of Georgia and slightly less than the size of Texas.
France has 3,956 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (8 nations): Andorra 55 km, Belgium 556 km, Germany 418 km, Italy 476 km, Luxembourg 69 km, Monaco 6 km, Spain 646 km, Switzerland 525 km.
- French Guiana: Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Brazil and Suriname. GPS: 4 00 N, 53 00 W.
- Guadeloupe: the Caribbean islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico. GPS: 16 15 N, 61 35 W.
- Martinique: the Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago. GPS: 14 40 N, 61 00 W.
- Mayotte: Southern Indian Ocean, an island in the Mozambique Channel, about halfway between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique. GPS: 12 50 S, 45 10 E.
- Reunion: Southern Africa, an island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar. GPS: -21 06 S, 55 31 E.
Metropolitan France: mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in the north and west. The remainder is mountainous, especially the Pyrenees in the south and the Alps in the east. Mont Blanc 4,810 is the highest point of France, while Rhone River delta -2 m is the lowest point, causing a mean elevation of 375 m throughout the country. With a total of 643,801 sq km (Metropolitan France: 551,500 sq km), France has 640,427 sq km (Metropolitan France: 549,970 sq km) of land and 3,374 sq km and 1,530 sq km (Metropolitan France) water surface area.
- French Guiana: low-lying coastal plains rising to hills and small mountains.
- Guadeloupe: Basse-Terre is volcanic in origin with interior mountains. Grande-Terre is a low limestone formation. Most of the seven other islands are volcanic in origin.
- Martinique: mountainous with indented coastline, a dormant volcano.
- Mayotte: generally undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks.
- Reunion: mostly rugged and mountainous, fertile lowlands along the coast.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Geneva (shared with Switzerland) – 580 sq km (a freshwater lake), while the major rivers are: Rhine (shared with Switzerland, Germany, and the Netherlands) – 1,233 km, Loire – 1,012 km. The significant watersheds for France are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Loire (115,282 sq km), Seine 78,919 sq km), Rhine-Maas (198,735 sq km), (Adriatic Sea) Po (76,997 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea) Rhone (100,543 sq km).
The largest West European nation; most major French rivers – the Meuse, Seine, Loire, Charente, Dordogne, and Garonne – flow northward or westward into the Atlantic Ocean, only the Rhone flows southward into the Mediterranean Sea.
The climate in Metropolitan France is as follows: generally cool winters and mild summers, but mild winters and hot summers along the Mediterranean, occasional strong, cold, dry, north-to-northwesterly wind known as the mistral.
- French Guiana: tropical, hot, humid, slight seasonal temperature variation.
- Guadeloupe and Martinique: subtropical tempered by trade winds, moderately high humidity, rainy season (June to October), vulnerable to devastating cyclones (hurricanes) every eight years.
- Martinique: Tropical, hot, and humid all year round, with a relatively calm and dry season from January to mid-April and a hot, humid, and rainy season from mid-June to mid-November.
- Mayotte: tropical, marine, hot, humid, rainy season during northeastern monsoon (November to May). The dry season is cooler (May to November).
- Reunion: tropical, but temperature moderates with elevation, cool and dry (May to November), hot and rainy (November to April).
When you visit France, the natural hazards shall be considered: Metropolitan France: flooding, avalanches, midwinter windstorms, drought, and forest fires in the south near the Mediterranean.
Overseas departments: hurricanes (cyclones), flooding. Volcanism: Montagne Pelee (1,394 m) on the island of Martinique in the Caribbean is the most active volcano of the Lesser Antilles Arc; it last erupted in 1932. A catastrophic eruption in may 1902 destroyed the city of St. Pierre, killing an estimated 30,000 people. La Soufriere (1,467 m) on the island of Guadeloupe in the Caribbean last erupted from July 1976 to March 1977. These volcanoes are part of the volcanic island arc of the Lesser Antilles that extends from Saba in the north to Grenada in the south.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting France: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the French people: some forest damage from acid rain; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from urban wastes, and agricultural runoff.
Google Maps France
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Paris found under the coordinates 48 52 N, 2 20 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Paris is a beautiful city in France with a long and illustrious history. During the 19th century, Paris grew to become one of the most culturally diverse cities in Europe. Today, it is home to numerous museums and historical landmarks that have been carefully preserved. One of these landmarks is the Arc de Triomphe de lÉtoile which was built during Napoléon Bonapartes regime as a triumphal arch celebrating his military victories.
France became independent on no official date of independence: 486 (Frankish tribes unified under Merovingian kingship); 10 August 843 (Western Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire); 14 July 1789 (French monarchy overthrown); 22 September 1792 (the First French Republic founded); 4 October 1958 (the Fifth French Republic established), and its national holiday is Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790).
Administrative divisions: 18 regions (regions, singular – region); Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes, Bourgogne-Franche-Comte (Burgundy-Free County), Bretagne (Brittany), Centre-Val de Loire (Center-Loire Valley), Corse (Corsica), Grand Est (Grand East), Guadeloupe, Guyane (French Guiana), Hauts-de-France (Upper France), Ile-de-France, Martinique, Mayotte, Normandie (Normandy), Nouvelle-Aquitaine (New Aquitaine), Occitanie (Occitania), Pays de la Loire (Lands of the Loire), Provence-Alpes-Côte dAzur, Reunion, note: France is divided into 13 metropolitan regions (including the collectivity of Corse or Corsica) and 5 overseas regions (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion) and is subdivided into 96 metropolitan departments and 5 overseas departments (which are the same as the overseas regions).
People and society
National solid identity coexists with pronounced regional differences, including local languages. Immigration laws have been tightened since the 1970s, but ethnic minorities growing up in city suburbs feel increasingly alienated. Wearing the veil is banned in public. New equality laws are under debate.
The population in France is 68,084,217 (July 2021 estimate). Note: the above figure is for metropolitan France and five overseas regions; the metropolitan France population is 62,814,233, with an average of 0.33% (2021 estimate) change. That means France is the No. 21 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 41.7 years median age (40 years for males and 40 years for women), France ranks No. 43 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Frenchman (men), Frenchwoman (women) (noun), or French (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Celtic and Latin with Teutonic, Slavic, North African, Indochinese, Basque minorities. Note: overseas departments: Black, White, Mulatto, East Indian, Chinese, Amerindian.
They speak French (official language) 100%, declining regional dialects and languages (Provencal, Breton, Alsatian, Corsican, Catalan, Basque, Flemish, Occitan, Picard); languages and practice the following religions: Christian (overwhelmingly Roman Catholic) 63-66%, Muslim 7-9%, Buddhist 0.5-0.75%, Jewish 0.5-0.75%, other 0.5-1.0%, none 23-28% (2015 estimate) note: France maintains a tradition of secularism and has not officially collected data on religious affiliation since the 1872 national census, which complicates assessments of Frances religious composition; an 1872 law prohibiting state authorities from collecting data on individuals ethnicity or religious beliefs was reaffirmed by a 1978 law emphasizing the prohibition of the collection or exploitation of personal data revealing an individuals race, ethnicity, or political, philosophical, or religious opinions; a 1905 law codified Frances separation of church and state.
We can conclude the following about the population in France: Much of the population is concentrated in the north and southeast. Although many urban agglomerations throughout the country, Paris is the largest city, with Lyon ranked a distant second. In France, we are talking about 81.2% (2021) of the total population living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 11.079 million, Paris (capital city), 1.734 million, Lyon, 1.614 million, Marseille-Aix-En-Provence, 1.068 million, Lille, 1.037 million, Toulouse, 980,000 Bordeaux (2021).
Industry
Chemicals, electronics, heavy engineering, cars, and aircraft typify a diversified and robust export sector. World leader in cosmetics, perfumes, and quality wines. Modernized agriculture.
The French economy is diversified across all sectors. The government has partially or fully privatized many large companies, including Air France, France Telecom, Renault, and Thales. However, the government maintains a strong presence in some sectors, particularly power, public transport, and defense industries. France is the most visited country globally, with 89 million foreign tourists in 2017. Frances leaders remain committed to a capitalism in which they maintain social equity using laws, tax policies, and social spending that mitigate economic inequality. Frances’s real GDP grew by 1.9% in 2017, up from 1.2% before. The unemployment rate (including overseas territories) increased from 7.8% in 2008 to 10.2% in 2015 before falling to 9.0% in 2017. Youth unemployment in metropolitan France decreased from 24.6% in 2014 to 20.6% in 2017.
Frances’s public finances have historically been strained by high spending and low growth. In 2017, the budget deficit improved to 2.7% of GDP, complying with the EU-mandated 3% deficit target. Meanwhile, Frances’s public debt rose from 89.5% of GDP in 2012 to 97% in 2017. Since entering office in May 2017, President Emmanuel MACRON launched a series of economic reforms to improve competitiveness and boost economic growth. President MACRON campaigned on reforming Frances’s labor code. In late 2017, a range of reforms was implemented to increase flexibility in the labor market by making it easier for firms to hire and fire and simplifying negotiations between employers and employees. In addition to labor reforms, President MACRON’s 2018 budget cuts public spending, taxes, and social security contributions to spur private investment and increase purchasing power. The government plans to gradually reduce the corporate tax rate for businesses from 33.3% to 25% by 2022.
France is rich in the following natural resources: Metropolitan France: coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, antimony, arsenic, potash, feldspar, fluorspar, gypsum, timber, arable land, and fish.
The main industrial sectors are machinery, chemicals, automobiles, metallurgy, aircraft, electronics, textiles, food processing, and tourism.
The country’s export sectors are robust in aircraft, packaged medicines, cars and vehicle parts, gas turbines, and wine (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 14%, United States 8%, Italy 7%, Spain 7%, Belgium 7%, the United Kingdom 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $746.91 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in France’s position of 5.
Land use in France: 29.2% (2018 estimate) forest, 18.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 33.4% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 52.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 17.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 26,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of France are wheat, sugar beet, milk, barley, maize, potatoes, grapes, rapeseed, pork, and apples.
The country typically needs to import: cars, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, and aircraft machinery (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 18%, Belgium 9%, Italy 9%, Spain 7%, China 7%, Netherlands 6%, the United Kingdom 5% (2019) in a sum value of $803.66 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $919.63 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $947.31 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in France 4.
France Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about France, Metropolitan France: Western Europe, bordering the Bay of Biscay and the English Channel, between Belgium and Spain, southeast of the UK, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and between Italy and Spain.
- French Guiana: Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Brazil and Suriname.
- Guadeloupe: the Caribbean islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico.
- Martinique: the Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago.
- Mayotte: Southern Indian Ocean, an island in the Mozambique Channel, about halfway between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique.
- Reunion: Southern Africa, an island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar.
We published some basic information about its capital Paris, and the French nation.
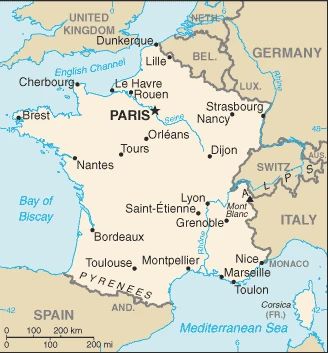
Are you interested in visiting France and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of France below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of France
Did you know about France?
France is a European country with a rich history stretching over 2,000 years. France is well known for its gourmet meals. France’s cuisine has evolved over the centuries and utilized local farmers and seasonal ingredients to create varied dishes. French cuisine can be found worldwide, from Michelin-starred restaurants to street food stalls serving baguettes, croissants, or crêpes.
After virtually visiting France, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Andorra, Belgium, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Monaco, Spain, and Switzerland.
If you liked our Google map and France information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.