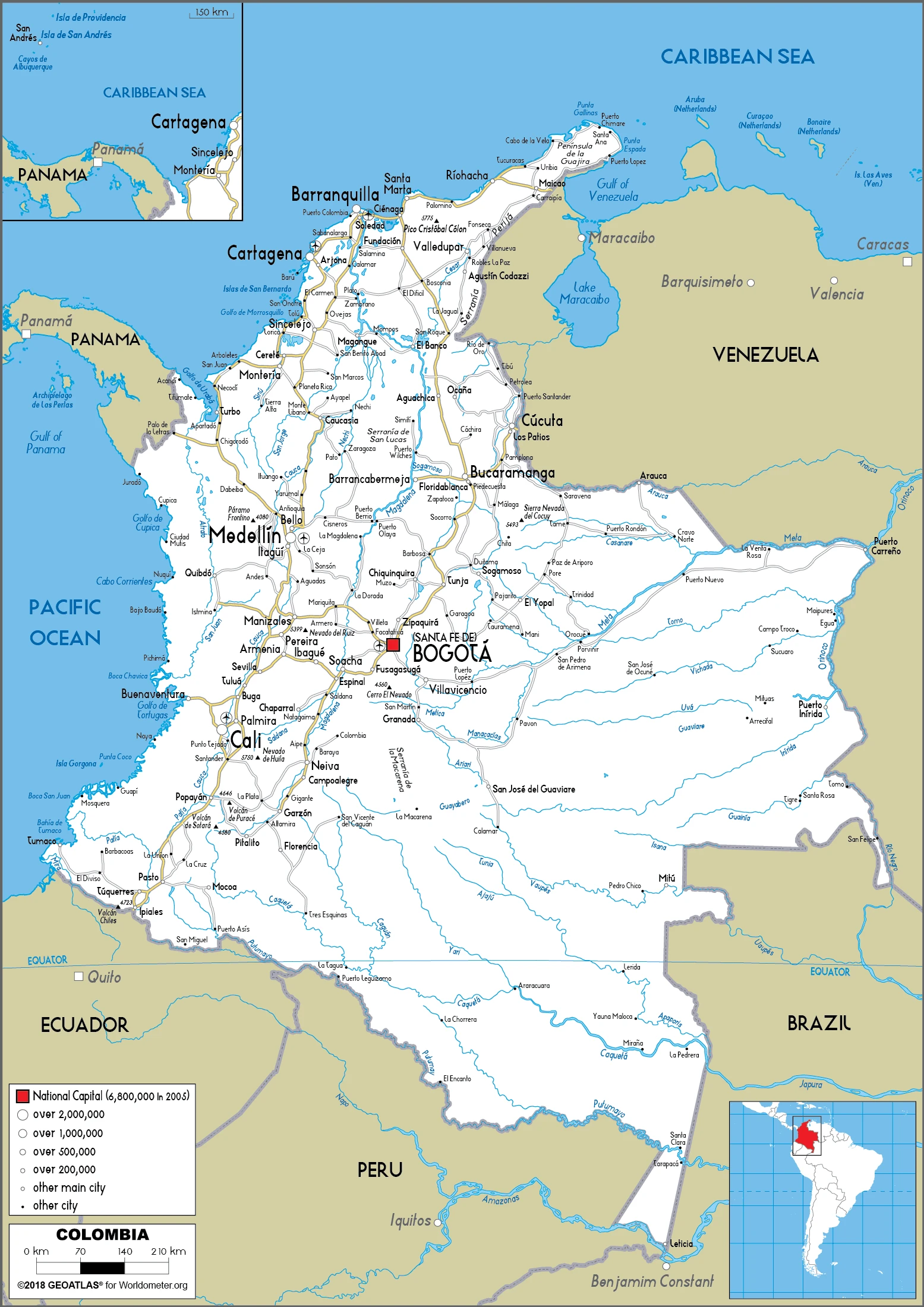
Colombia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Colombia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Colombia, South America (13 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Bogota, bordering countries like Brazil, Ecuador, Panama, Peru, Venezuela, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this South American state.
Quick links: Google Maps Colombia, Bogota Google maps, Driving Directions Colombia, Printable Road Map.

About Colombia in a nutshell
- Colombia is the world’s main source of emeralds.
- Conventional short form of the name: Colombia
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Colombia
- Local long form: Republica de Colombia
- Local short form: Colombia
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the country is named after explorer Christopher COLUMBUS.
- The legal system in Colombia: civil law system influenced by the Spanish and French civil codes.
- Climate: Coastal plains are hot and wet. The highlands are much cooler. The equatorial east has two wet seasons.
- The national symbols are Andean condor; national colors: yellow, blue, red.
- Internet TLD: .co
Background
Colombia was one of the three countries that emerged after the dissolution of Gran Colombia in 1830 (the others are Ecuador and Venezuela). A decades-long conflict between government forces, paramilitaries, and antigovernment insurgent groups heavily funded by the drug trade, principally the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), escalated during the 1990s. More than 31,000 former United Self Defense Forces of Colombia (AUC) paramilitaries were demobilized by the end of 2006, and the AUC as a formal organization ceased to operate. In the wake of the paramilitary demobilization, illegal armed groups arose, whose members included some former paramilitaries.
After four years of formal peace negotiations, the Colombian government signed a final peace accord with the FARC in November 2016, subsequently ratified by the Colombian Congress. The accord calls for members of the FARC to demobilize, disarm, and reincorporate into society and politics. The accord also committed the Colombian government to create three new institutions to form a comprehensive system for truth, justice, reparation, and non-repetition, to include a truth commission, a particular unit to coordinate the search for those who disappeared during the conflict, and a Special Jurisdiction for Peace to administer justice for conflict-related crimes.
The Colombian government has stepped up efforts to expand its presence into every one of its administrative departments. Despite decades of internal conflict and drug-related security challenges, Colombia maintains relatively strong democratic institutions characterized by peaceful, transparent elections and the protection of civil liberties.
Geography
The densely forested and almost uninhabited east is separated from the western coastal plains by the Andes, which divide into three ranges (cordilleras) with intervening valleys.
Lying in northwest South America, Colombia has coastlines on the Caribbean and the Pacific. It is primarily noted for its coffee, emeralds, gold, and cocaine trafficking.
This state is located in Northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Panama and Venezuela, and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Ecuador and Panama, under the coordinates of 4 00 N, 72 00 W, covering an area of 1,138,910 sq km with a coastline of 3,208 km. Colombia is Slightly less than twice the size of Texas.
Colombia has 6,672 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (5 nations): Brazil 1790 km, Ecuador 708 km, Panama 339 km, Peru 1494 km, Venezuela 2341 km.
Flat coastal lowlands, central highlands, high Andes Mountains, eastern lowland plains (llanos), with Pico Cristobal colon 5,730 m as the highest point of Colombia, while Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 593 m throughout the country. With a total of 1,138,910 sq km, Colombia has 1,038,700 sq km of land and 100,210 sq km water surface area.
The principal rivers are the Rio Negro river source (shared with Venezuela and Brazil m) – 2,250 km, Orinoco (shared with Venezuela s) – 2,101 km. The significant watersheds for Colombia are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km) Orinoco (953,675 sq km).
Only South American countries with coastlines on the North Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
The climate in Colombia is as follows: Tropical along the coast and eastern plains, more relaxed in highlands.
When you visit Colombia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Highlands subject to volcanic eruptions; occasional earthquakes; periodic droughts volcanism: Galeras (4,276 m) is one of Colombia’s most active volcanoes, having erupted in 2009 and 2010 causing significant evacuations; it has been deemed a decade volcano by the international association of volcanology and chemistry of the interior of the earth, worthy of study due to its tumultuous history and proximity to human populations; Nevado del Ruiz (5,321 m), 129 km (80 mi) west of Bogota, erupted in 1985 producing lahars (mudflows) that killed 23,000 people; the volcano last erupted in 1991; additionally, after 500 years of dormancy, Nevado del Huila reawakened in 2007 and has experienced frequent eruptions since then; other historically active volcanoes include cumbal, Dona Juana, Nevado del Tolima, and Purace.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Colombia: degree of risk: high (2020), bacterial diarrhea, dengue fever, malaria, and yellow fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Colombian people: deforestation resulting from timber exploitation in the jungles of the Amazon and the region of Chocó; illicit drug crops grown by peasants in the national parks; soil erosion; soil and water quality damage from overuse of pesticides; air pollution, especially in Bogota, from vehicle emissions.
Google Maps Colombia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Bogota found under the coordinates 4 36 N, 74 05 W, applying the time zone UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital of Colombia, Bogota, is one of the most beautiful cities in South America. Though it’s not as developed as other big cities in Colombia, it still attracts travelers from all over the world with its mountainous backdrop and cobblestone streets.
Colombia became independent on 20 July 1810 (from Spain), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 20 July (1810).
Administrative divisions: 32 departments (departamentos, singular – departamento) and 1 capital district (distrito capital); Amazonas, Antioquia, Arauca, Atlantico, Bogota, Bolivar, Boyaca, Caldas, Caqueta, Casanare, Cauca, Cesar, Choco, Cordoba, Cundinamarca, Guainia, Guaviare, Huila, La Guajira, Magdalena, Meta, Narino, Norte de Santander, Putumayo, Quindio, Risaralda, Archipielago de San Andres, Providencia y Santa Catalina (colloquially San Andres y Providencia), Santander, Sucre, Tolima, Valle del Cauca, Vaupes, Vichada.
People and society
Most Colombians are of mixed blood. Blacks and Amerindians have minor political representation. Civil conflict since the 1960s has killed over 220,000 people and displaced more than five million. The fighting is deeply entwined with the narcotics trade. Violent crime is common.
The population in Colombia is 50,355,650 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.04% (2021 estimate) change. That means Colombia is the No. 29 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 31.2 years median age (30.2 years for males and 30.2 years for women), Colombia ranks No. 115 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Colombian(s) (noun) or Colombian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Mestizo and White 87.6%, Afro-Colombian (includes Mulatto, Raizel, and Palenquero) 6.8%, Amerindian 4.3%, unspecified 1.4% (2018 estimate).
They speak Spanish (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 79%, Protestant 14% (includes Pentecostal 6%, mainline Protestant 2%, other 6%), other 2%, unspecified 5% (2014 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Colombia: The majority of people live in the north and west, where agricultural opportunities and natural resources are found. The vast grasslands of the llanos to the south and east, which make up approximately 60% of the country, are sparsely populated. In Colombia, we are talking about 81.7% (2021) of the total population is living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 11.167 million, Bogota (capital city), 4.034 million, Medellin, 2.810 million, Cali, 2.299 million, Barranquilla, 1.349 million, Bucaramanga, 1.071 million, Cartagena (2021).
Industry
A Healthy and diversified export sector includes coffee and coal. Considerable growth potential, but narcotics-related violence and corruption deter foreign investors.
Colombia heavily depends on energy and mining exports, making it vulnerable to fluctuations in commodity prices. Colombia is Latin America’s fourth-largest oil producer and the world’s fourth-largest coal producer, third-largest coffee exporter, and second-largest cut flowers exporter. Colombia’s economic development is hampered by inadequate infrastructure, poverty, narcotrafficking, and an uncertain security situation, in addition to dependence on primary commodities (goods that have little value-added from processing or labor inputs). Colombia’s economy slowed in 2017 because of falling world market prices for oil and lower domestic oil production due to insurgent attacks on pipeline infrastructure.
Although real GDP growth averaged 4.7% during the past decade, it fell to an estimated 1.8% in 2017. Declining oil prices also have contributed to reduced government revenues. In 2016, oil revenue dropped below 4% of the federal budget, and likely remained below 4% in 2017. A Western credit rating agency in December 2017 downgraded Colombia’s sovereign credit rating to BBB because of weaker-than-expected growth and increasing external debt. Colombia has struggled to address local referendums against foreign investment, which has slowed its expansion, especially in oil and mining.
Colombia’s FDI declined by 3% to $10.2 billion between January and September 2017. Colombia has signed or is negotiating Free Trade Agreements (FTA) with more than a dozen countries; the US-Colombia FTA went into effect in May 2012. Colombia is a founding member of the Pacific Alliance, a regional trade block formed in 2012 by Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Peru to promote regional trade and economic integration. The Colombian government took steps in 2017 to address several bilateral trade irritants with the US, including those on truck scrappage, distilled spirits, pharmaceuticals, ethanol imports, and labor rights. Colombia hopes to accede to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
Colombia is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, coal, iron ore, nickel, gold, copper, emeralds, hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are textiles, food processing, oil, clothing and footwear, beverages, chemicals, cement, gold, coal, emeralds.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in crude petroleum, coal, refined petroleum, coffee, gold (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 31%, China 11%, Panama 6%, Ecuador 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $39.14 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Colombia’s position of 65.
Land use in Colombia: 54.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 8.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1.4% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 37.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1.6% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 34.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 10,900 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Colombia are sugar cane, milk, oil palm fruit, potatoes, rice, bananas, cassava leaves, plantains, poultry, maize.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cars, broadcasting equipment, packaged medicines, corn (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 27%, China 20%, Mexico 7%, Brazil 6% (2019) in a sum value of $51.56 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $65.83 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $64.56 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Colombia 58.
Colombia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Colombia, Northern South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Panama and Venezuela, and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between Ecuador and Panama. We published some basic information about its capital Bogota, and the Colombian nation.
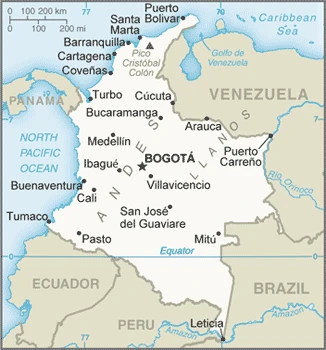
Are you interested in visiting Colombia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Colombia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Colombia
Did you know about Colombia?
Colombia is one of the most beautiful countries in Latin America. It is located in the northwest part of South America and has 1,141,748 square kilometers. Colombia is diverse with climatic zones, fertile soils, mountain ranges, and plains. Colombian culture is known for its music, literature, sports, dance, and cuisine. Colombian food is typically very hearty and includes many plantains, beans, rice, potatoes, and maize.
After virtually visiting Colombia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Brazil, Ecuador, Panama, Peru, Venezuela.
If you liked our Google map and Colombia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.