Chile Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Chile, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Chile, South America (13 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Santiago, bordering countries like Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this South American state.
Quick links: Google Maps Chile, Santiago Google maps, Driving Directions Chile, Printable Road Map.

About Chile in a nutshell
- Chiles Atacama Desert is the driest place on Earth, making it the perfect location for hi-tech space observatories.
- Conventional short form of the name: Chile
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Chile
- Local long form: Republica de Chile
- Local short form: Chile
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: derivation of the name is unclear, but it may come from the Mapuche word chilli meaning limit of the earth or from the Quechua chiri meaning cold.
- The legal system in Chile: civil law system influenced by several West European civil legal systems; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional Tribunal.
- Climate: Arid in the north. Hot, dry summers and mild winters in the center. Higher Andean peaks have glaciers and year-round snow. Very wet and stormy
- The national symbols are huemul (mountain deer), Andean condor; national colors: red, white, blue.
- Internet TLD: .cl
Background
Before the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, the Inca ruled northern Chile for nearly a century while an indigenous people, the Mapuche, inhabited central and southern Chile. Although Chile declared its independence in 1810, it did not achieve a decisive victory over the Spanish until 1818. In the War of the Pacific (1879-83), Chile defeated Peru and Bolivia to win its present northern regions. In the 1880s, the Chilean central government gained control over the central and southern regions inhabited by the Mapuche. After a series of elected governments, the three-year-old Marxist government of Salvador ALLENDE was overthrown in 1973 by a military coup led by General Augusto PINOCHET. He ruled until a democratically-elected president was inaugurated in 1990. Economic reforms, maintained consistently since the 1980s, contributed to steady growth, reduced poverty rates by over half, and helped secure the country’s commitment to democratic and representative government. Chile has increasingly assumed regional and international leadership roles befitting its stable, democratic nation.
Geography
Fertile valleys in the center between the coast and the Andes. The Atacama Desert in the north. Deep-sea channels, lakes, and fjords in the south.
Chile extends in a ribbon down the west coast of South America. It returned to elected civilian rule in 1989 after a referendum forced out military dictator General Pinochet.
This state is located in Southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru, under the coordinates of 30 00 S, 71 00 W, covering an area of 756,102 sq km with a coastline of 6,435 km. Chile is Slightly smaller than twice the size of Montana.
Chile has 7,801 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (3 nations): Argentina 6691 km, Bolivia 942 km, Peru 168 km.
Low coastal mountains, fertile central valley, the rugged Andes in the east, with Nevado Ojos del Salado 6,893 m (highest volcano in the world) as the highest point of Chile, while Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 1,871 m throughout the country. With a total of 756,102 sq km, Chile has 743,812 sq km of land and 12,290 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lago General Carrera (shared with Argentina) – 2,240 sq km; Lago OHiggins (shared with Argentina) – 1,010 sq km; Lago Llanquihue – 800 sq km; Lago Fagnano (shared with Argentina) – 590 sq km (a freshwater lake), N/A (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: N/A. The significant watersheds for Chile are N/A.
The longest north-south trending country in the world, extending across 39 degrees of latitude; strategic location relative to sea lanes between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage).
The climate in Chile is as follows: Temperate, desert in the north, the Mediterranean in the central region, cool and damp in the south.
When you visit Chile, the natural hazards shall be considered: Severe earthquakes; active volcanism; tsunamis volcanism: significant volcanic activity due to more than three-dozen active volcanoes along the Andes mountains; lascar (5,592 m), which last erupted in 2007, is the most active volcano in the northern Chilean Andes; llama (3,125 m) in central Chile, which last erupted in 2009, is another of the country’s most active; chastens 2008 eruption forced significant evacuations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Cerro Hudson, Calbuco, Copahue, Guallatiri, Ilullaillaco, Nevados de Chillan, Puyehue, San Pedro, and Villarrica.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Chile: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Chilean people: air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage; noise pollution; improper garbage disposal; soil degradation; widespread deforestation and mining threaten the environment; wildlife conservation.
Google Maps Chile
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Santiago found under the coordinates 33 27 S, 70 40 W, applying the time zone UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in August; ends second Sunday in May.
Santiago, Chile, is known for its beautiful and intriguing vistas. But when it comes to the local cuisine, this vibrant destination is known for something else entirely: empanadas – savory pastries made with white dough stuffed with meat, cheese, or vegetables.
Chile became independent on 18 September 1810 (from Spain), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 18 September (1810).
Administrative divisions: 16 regions (regiones, singular – region); Aysen, Antofagasta, Araucania, Arica y Parinacota, Atacama, Biobio, Coquimbo, Libertador General Bernardo OHiggins, Los Lagos, Los Rios, Magallanes y de la Antartica Chilena (Magallanes and Chilean Antarctica), Maule, Nuble, Region Metropolitana (Santiago), Tarapaca, Valparaiso, note: the US does not recognize any claims to Antarctica.
People and society
Most people are mestizo (mixed SpanishAmerindian descent) and are highly urbanized. General Pinochets dictatorship was brutally repressive, but the business and middle classes prospered. Over a third of the population live in Santiago, many in enormous slums. There are three main indigenous groups, including the Rapa Nui of Easter Island.
The population in Chile is 18,307,925 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.68% (2021 estimate) change. That means Chile is the No. 66 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 35.5 years median age (34.3 years for males and 34.3 years for women), Chile ranks No. 83 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Chilean(s) (noun) or Chilean (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White and non-Indigenous 88.9%, Mapuche 9.1%, Aymara 0.7%, other indigenous groups 1% (includes Rapa Nui, Likan Antai, Quechua, Colla, Diaguita, Kawesqar, Yagan or Yamana), unspecified 0.3% (2012 estimate).
They speak Spanish 99.5% (official language), English 10.2%, indigenous 1% (includes Mapudungun, Aymara, Quechua, Rapa Nui), other 2.3%, unspecified 0.2%; languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 66.7%, Evangelical or Protestant 16.4%, Jehovahs Witness 1%, other 3.4%, none 11.5%, unspecified 1.1% (2012 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Chile: 90% of the population is located in the middle third of the country around the capital of Santiago. The far north (anchored by the Atacama desert) and the extreme south are relatively underpopulated. In Chile, we are talking about 87.8% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 6.812 million, Santiago (capital city), 992,000 Valparaiso, 892,000 Concepcion (2021).
Industry
Worlds biggest copper producer. Growth in foreign investment due to political stability. Exports include wine, fishmeal, fruits, and salmon. Severe earthquake damage in 2010.
Chile has a market-oriented economy characterized by a high level of foreign trade and a reputation for strong financial institutions and sound policy. It has given it the most robust sovereign bond rating in South America. Exports of goods and services account for approximately one-third of GDP, with commodities making up some 60% of total exports. Copper is Chiles top export and provides 20% of government revenue. From 2003 through 2013, real growth averaged almost 5% per year, despite a slight contraction in 2009 that resulted from the global financial crisis. Growth slowed to an estimated 1.4% in 2017. A continued drop in copper prices prompted Chile to experience its third consecutive year of slow growth. Chile deepened its longstanding commitment to trade liberalization by signing a free trade agreement with the US, effective 1 January 2004. Chile has 26 trade agreements covering 60 countries, including the EU, Mercosur, China, India, South Korea, and Mexico.
In May 2010, Chile signed the OECD Convention, becoming the first South American country to join the OECD. In October 2015, Chile signed the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade agreement, which was finalized as the Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and signed at a ceremony in Chile in March 2018. The Chilean government has generally followed a countercyclical fiscal policy. It accumulates surpluses in sovereign wealth funds during periods of high copper prices and economic growth and generally allows deficit spending only during periods of low copper prices and growth.
As of 31 October 2016, those sovereign wealth funds – kept mostly outside the country and separate from Central Bank reserves – amounted to more than $23.5 billion. Chile used these funds to finance fiscal stimulus packages during the 2009 economic downturn. In 2014, then-President Michelle BACHELET introduced tax reforms to deliver her campaign promise to fight inequality and provide education and health care access. The reforms are expected to generate additional tax revenues equal to 3% of Chiles’s GDP, primarily by increasing corporate tax rates to OECD averages.
Chile is rich in the following natural resources: Copper, timber, iron ore, nitrates, precious metals, molybdenum, hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are copper, lithium, other minerals, foodstuffs, fish processing, iron and steel, wood and wood products, transport equipment, cement, textiles.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in copper, wood pulp, fish fillets, pitted fruits, wine (2019), partnering with these nations: China 32%, United States 14%, Japan 9%, South Korea 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $79.8 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Chile’s position of 46.
Land use in Chile: 21.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 57% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1.7% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 21.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.6% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 18.8% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 11,100 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Chile are grapes, apples, wheat, sugar beet, milk, potatoes, tomatoes, maize, poultry, pork.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, crude petroleum, cars, broadcasting equipment, delivery trucks (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 24%, United States 20%, Brazil 8%, Germany 5%, Argentina 5% (2019) in a sum value of $66.43 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $80.17 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $85.11 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Chile 50.
Chile Driving Directions
You learned about Chile, Southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Argentina and Peru in this post. We published some basic information about its capital Santiago, and the Chilean nation.
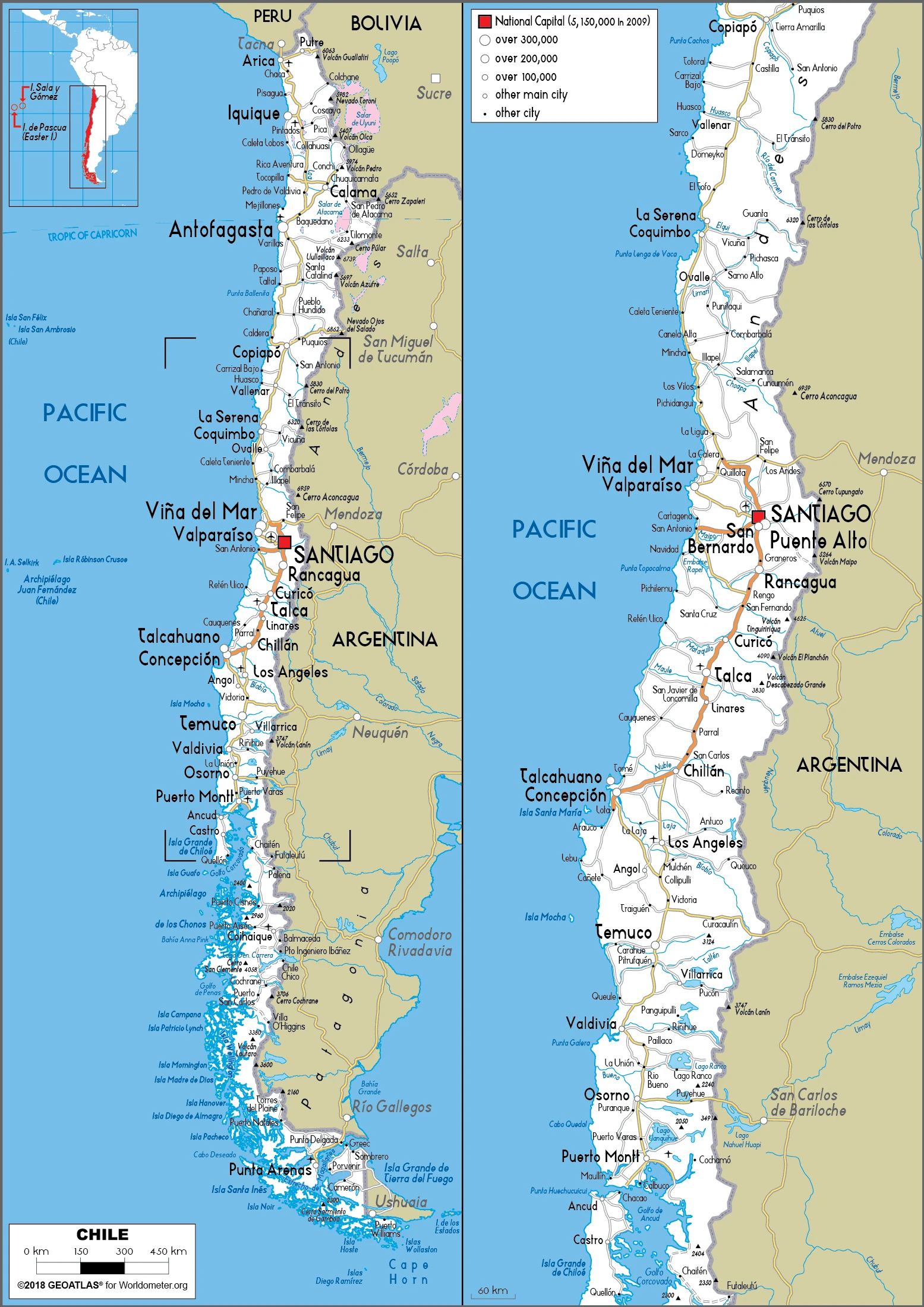
Are you interested in visiting Chile and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Chile below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Chile
Did you know about Chile?
Chile is one of the most stable and prosperous countries in Latin America.
Chileans are proud of the landscape and beauty of their country. The Pacific coastal climate favors the growth of wheat, grapes, apples, and other crops, which contribute to Chile’s large agricultural sector.
Chile has many different tourist attractions, from the mountains to the ocean. For example, there’s the Atacama desert with its fantastic night sky and Patagonia with its volcanos and glaciers.
After virtually visiting Chile, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Argentina, Bolivia, Peru.
If you liked our Google map and Chile information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.
