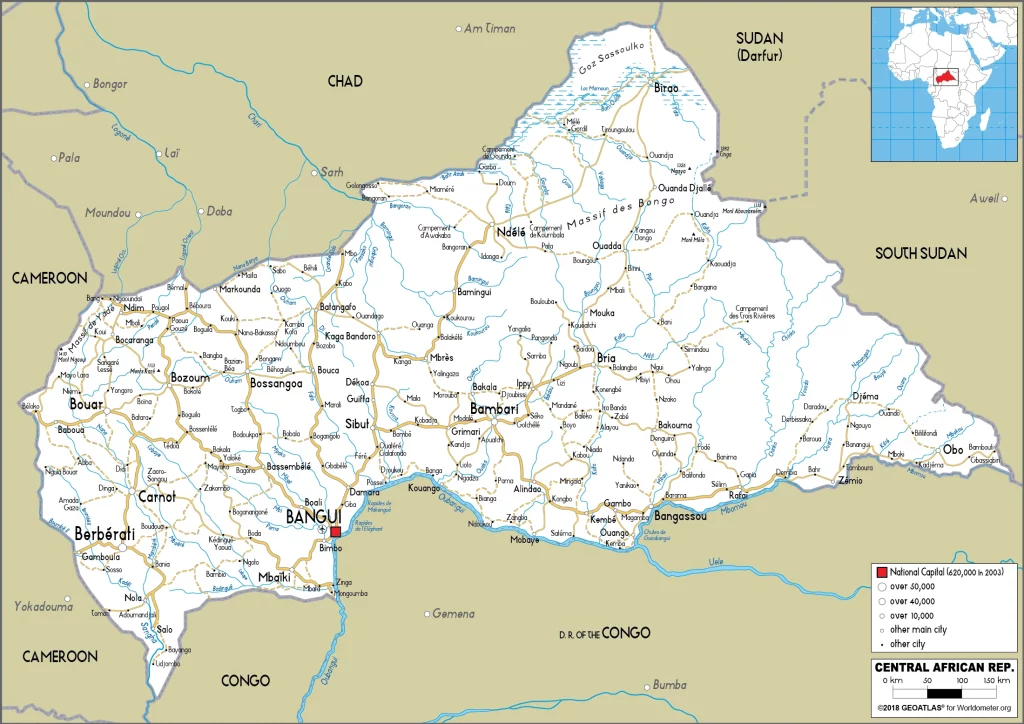
Central African Republic Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Central African Republic, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Central African Republic, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Bangui, bordering countries like Cameroon, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, Sudan, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google mapsthe Central African Republic, Bangui Google maps, Driving Directionsthe Central African Republic, Printable Road Map.

Aboutthe Central African Republic in a nutshell
- Emperor Bokassas eccentric rule from 1965 to 1979 was followed by military dictatorship until democracy was restored in 1993.
- Conventional short form of the name: none
- The conventional long form of the name:the Central African Republic
- Local long form: Republique Centrafricaine
- Local short form: none
- Former name(s): Ubangi-Shari, Central African Empire
- Etymology: self-descriptive name specifying the countrys location on the continent; Africa is derived from the Roman designation of the area corresponding to present-day Tunisia Africa terra, which meant Land of the Afri (the tribe resident in that area), but which eventually came to mean the entire continent.
- The legal system inthe Central African Republic: civil law system based on the French model.
- Climate: The south is equatorial; the north is hot and dry. Rain occurs all year round, with heaviest falls between July and October.
- The national symbols are elephant; national colors: blue, white, green, yellow, red.
- Internet TLD: .cf
Background
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a perennially weak state that sits at the crossroads of ethnic and linguistic groups in the center of the African continent. Among the last areas of sub-Saharan Africa to be drawn into the world economy, its introduction into trade networks around the early 1700s fostered significant competition among its population. The local population sought to benefit from the lucrative Atlantic, trans-Saharan, and Indian Ocean trade in enslaved people and ivory. Slave raids aided by representatives from the local populations fostered hatred between ethnic groups that remains today. The territory was established as a French colony named Ubangui-Shari in 1903. France modeled its colony administration after the Belgian Congo, subcontracting the territory to private companies that collected rubber and ivory.
Although France banned the domestic slave trade in CAR in the 1910s, the private companies continued to exploit the population through forced labor. The colony of Ubangi-Shari gained independence from France as the Central African Republic in August 1960. Still, the death of independence leader Barthelemy BOGANDA six months prior led to an immediate struggle for power. CARs political history has since been marred by a series of coups, the first of which brought Jean-Bedel BOKASSA to power in 1966. Bokassa’s regime was characterized by widespread corruption and intolerance of opposition, which manifested in the disappearances of many who challenged BOKASSAs rule. To prolong his mandate, he named himself emperor in 1976 and changed the country’s name to the Central African Empire. His regime’s economic mismanagement culminated in widespread student protests in early 1979 that were violently suppressed by security forces. BOKASSA, rumored to have participated in the killing of some young students after the protests, fell out of favor with the international community and was overthrown in a French-backed coup in 1979.
After BOKASSAs departure, the country’s name became the Central African Republic. CARs fifth coup in March 2013 unseated President Francois BOZIZE after a mainly Muslim rebel coalition named the Seleka seized the capital and forced BOZIZE, who himself had taken power in a coup in 2003, to flee the country. Widespread abuses by the Seleka spurred the formation of mainly Christian self-defense groups called themselves the anti-Balaka, which has also committed human rights abuses against Muslim populations in retaliation. Since the rise of the self-defense groups, conflict in CAR has become increasingly ethnoreligious-based, although focused on identity instead of religious ideology. Elections organized by a transitional government in early 2016 installed independent candidate Faustin-Archange TOUADERA as president. He was reelected in December 2020. A peace agreement signed in February 2019 between the government and the main armed factions has had little effect, and armed groups remain in control of large swaths of the country’s territory.
Geography
Comprises a low plateau covered by scrub or savanna. North is arid. Equatorial rainforests in the south. The Ubangi River forms the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
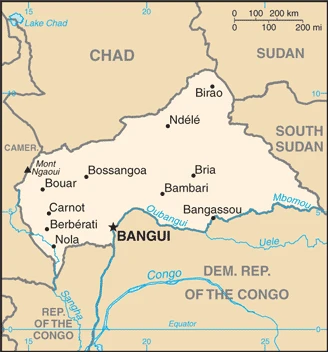
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country lying between the basins of the Chad and Congo Rivers. Politics suffers frequent interruption by coups and rebellions.
This state is located in Central Africa, north of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, under the coordinates of 7 00 N, 21 00 E, covering an area of 622,984 sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). The Central African Republic is slightly smaller than Texas, about four times the size of Georgia.
The central African Republic has 5,920 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (6 nations): Cameroon 901 km, Chad 1556 km, the Democratic Republic of the Congo 1747 km, Republic of the Congo 487 km, South Sudan 1055 km, Sudan 174 km.
Vast, flat to rolling plateau, scattered hills in northeast and southwest, with Mont Ngaoui 1,410 m as the highest point of the Central African Republic, while Oubangui River 335 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 635 m throughout the country. With a total of 622,984 sq km, the Central African Republic has 622,984 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
The principal river is the Ubangi river source (shared with the Democratic Republic of Congo and Congo) – 2,270 km. The significant watersheds for the Central African Republic are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), (Mediterranean Sea), Nile (3,254,853 sq km), Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km).
Landlocked; almost the precise center of Africa.
The climate in the Central African Republic is as follows: Tropical, hot, dry winters, mild to hot, wet summers.
When you visit the Central African Republic, the natural hazards shall be considered: Hot, dry, dusty harmattan winds affect northern areas; floods are common.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Central African Republic: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, typhoid fever, malaria, and dengue fever, schistosomiasis, rabies, meningococcal meningitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Central African people: water pollution; tap water is not potable; poaching and mismanagement have diminished the country’s reputation as one of the last great wildlife refuges; desertification; deforestation; soil erosion.
Google mapsthe Central African Republic
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Bangui found under the coordinates 4 22 N, 18 35 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Bangui is a city in the Central African Republic and the capital of the nation’s third-largest province. It is situated on the Ubangi River in the southeastern corner of that country, near its border with Chad.
The central African Republic became independent on 13 August 1960 (from France), and its national holiday is Republic Day, 1 December (1958).
Administrative divisions: 14 prefectures (prefectures, singular – prefecture), 2 economic prefectures (prefectures economiques, singular – prefecture economique), and 1 commune**; Bamingui-Bangoran, Bangui*, Basse-Kotto, Haute-Kotto, Haut-Mbomou, Kemo, Lobaye, Mambere-Kadei, Mbomou, Nana-Grebizi, Nana-Mambere, Ombella-Mpoko, Ouaka, Ouham, Ouham-Pende, Sangha-Mbaere, Vakaga.
People and society
The Baya and Banda are the largest ethnic groups. Still, the lingua franca is Sango, a trading creole spoken by the minorities in the south who have traditionally provided most political leaders. Less than 2% of the population lives in the north. Recent rebellions by northern militias have displaced thousands of people.
The population in the Central African Republic is 5,357,984 (July 2021 estimate). Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected, with an average of 1.79% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Central African Republic is the No. 120 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 20 years median age (19.7 years for males and 19.7 years for women), the Central African Republic ranks No. 194 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Central African(s) (noun) or Central African (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Baya 28.8%, Banda 22.9%, Mandjia 9.9%, Sara 7.9%, MBaka-Bantu 7.9%, Arab-Fulani (Peul) 6%, Mbum 6%, Ngbanki 5.5%, Zande-Nzakara 3%, other Central African Republic ethnic groups 2%, non-Central African Republic ethnic groups .1% (2003 estimate).
They speak French (official language), Sangho (lingua franca and national language), tribal languages and practice the following religions: Christian 89%, Muslim 9%, folk religion 1%, unaffiliated 1% (2020 estimate) note: animistic beliefs and practices strongly influence the Christian majority.
We can conclude the following about the population in the Central African Republic: The majority of residents live in the western and central areas of the country, especially in and around the capital of Bangui, as shown in this population distribution map. In the Central African Republic, we are talking about 42.6% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 910,000 Bangui (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Dominated by subsistence farming. Exports include diamonds, cotton, timber, and coffee. Aid is needed to support refugees. Instability and poor infrastructure hinder progress.
Together with forestry and mining, subsistence agriculture remains the backbone of the Central African Republic (CAR) economy, with about 60% of the population living in outlying areas. Although statistics are unreliable in conflict-prone countries, the agricultural sector generates more than half of the estimated GDP. Timber and diamonds account for most export earnings, followed by cotton. Significant constraints to economic development include the CARs landlocked geography, poor transportation system, largely unskilled workforce, and legacy of misdirected macroeconomic policies. Factional fighting between the government and its opponents remains a drag on economic revitalization. The income distribution is highly unequal, and grants from the international community can only partially meet humanitarian needs.
CAR shares a common currency with the Central African Monetary Union. The currency is pegged to the Euro., Since 2009, the IMF has worked closely with the government to institute reforms to improve budget transparency, but other problems remain. In the run-up to the 2011 election, the government’s additional spending worsened CARs fiscal situation. In 2012, the World Bank approved $125 million in funding for transport infrastructure and regional trade, focused on the route between CAR’s capital and the port of Douala in Cameroon. In July 2016, the IMF approved a three-year extended credit facility valued at $116 million; in mid-2017, the IMF completed a review of CARs fiscal performance and broadly approved the government’s management, although issues with revenue collection, weak government capacity, and transparency remain.
The World Bank in late 2016 approved a $20 million grant to restore essential fiscal management, improve transparency, and assist with economic recovery., Participation in the Kimberley Process, a commitment to remove conflict diamonds from the global supply chain, led to a partially lifted ban on diamond exports from CAR in 2015. Still, persistent insecurity is likely to constrain real GDP growth.
The central African Republic is rich in the following natural resources: Diamonds, uranium, timber, gold, oil, hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are typically gold and diamond mining, logging, brewing, sugar refining.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in lumber, gold, diamonds, sea vessels, cocoa paste (2019), partnering with these nations: China 41%, United Arab Emirates 19%, France 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $113.7 million. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2017 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in the Central African Republic’s position of 209.
Land use inthe Central African Republic: 36.2% (2018 estimate) forest, 55.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 8.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 5.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 10 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the Central African Republic are cassava, yams, groundnuts, taro, bananas, sugar cane, beef, maize, plantains, milk.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, packaged medicines, natural gas, broadcasting equipment, second-hand clothing (2019), partnering with the following nations: India 18%, France 12%, United States 11%, China 9%, Netherlands 7%, Belgium 7%, Malta 6% (2019) in a sum value of $393.1 million (2017 estimate) $342.2 million (2016 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in the Central African Republic 208.
Central African Republic Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the Central African Republic, Central Africa, north of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. We published some basic information about its capital Bangui, and the Central African nation.
Are you interested in visiting the Central African Republic and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Central African Republic below to overview the route network.
Printable map ofthe Central African Republic
Did you know aboutthe Central African Republic?
The Central African Republic (CAR) is one of the poorest countries in the world and has been suffering from chronic political instability since its independence. As a result, the CAR has seen many military coups, periods of violent conflict, and two major civil wars.
The country has never had any significant mineral resources, so it is dependent on aid for economic growth and government funding.
After virtually visiting the Central African Republic, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Cameroon, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, Sudan.
If you liked our Google map and the Central African Republic information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.