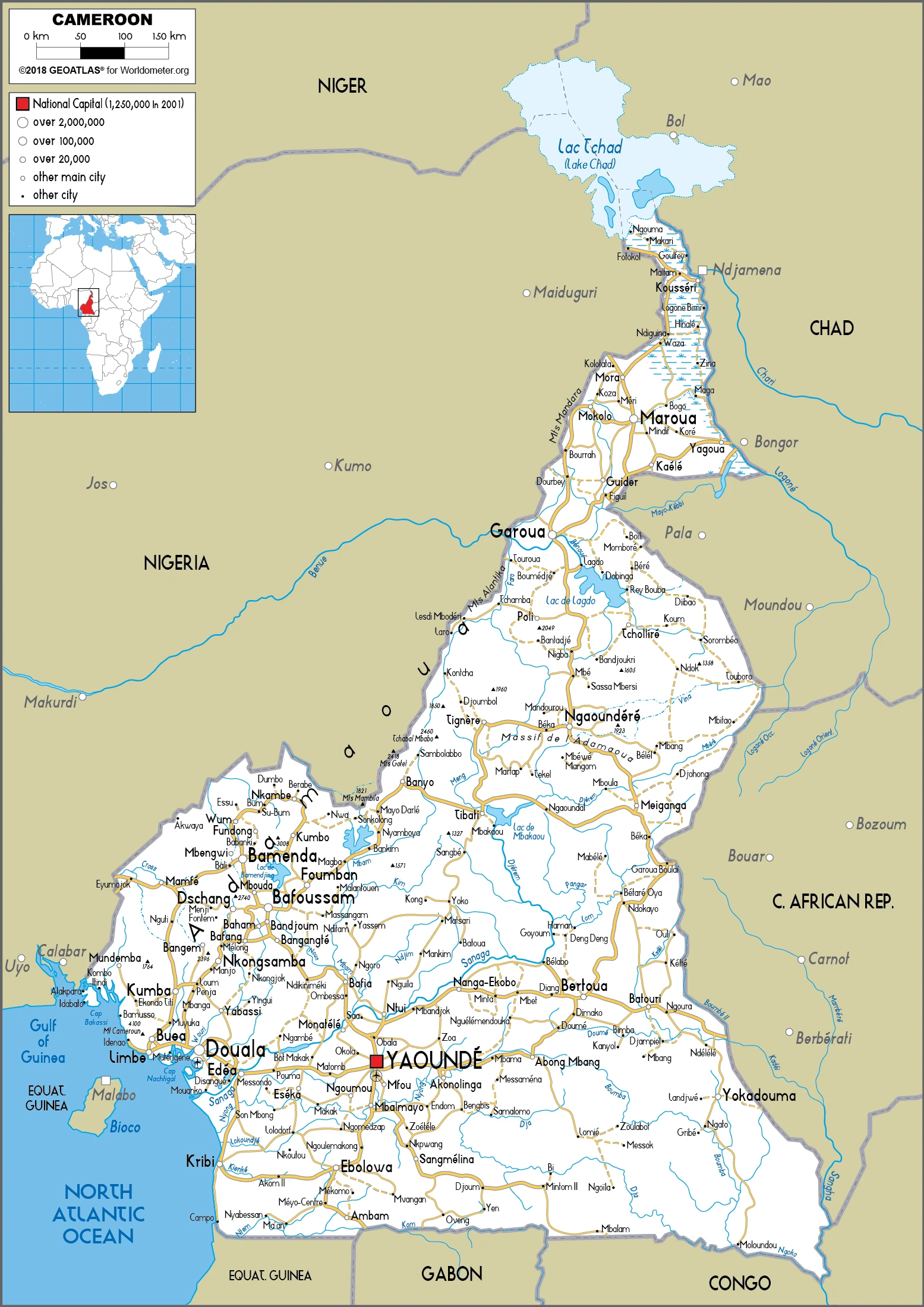
Cameroon Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Cameroon, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Cameroon, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Yaounde, bordering countries like Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Nigeria, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google Maps Cameroon, Yaounde Google maps, Driving Directions Cameroon, Printable Road Map.

About Cameroon in a nutshell
- Cameroons name derives from the Portuguese word camares, after the shrimp fished by the early European explorers.
- Conventional short form of the name: Cameroon
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Cameroon
- Local long form: Republique du Cameroun / Republic of Cameroon
- Local short form: Cameroun / Cameroon
- Former name(s): Kamerun, French Cameroon, British Cameroon, Federal Republic of Cameroon, United Republic of Cameroon
- Etymology: in the 15th century, Portuguese explorers named the area near the mouth of the Wouri River the Rio dos Camaroes (River of Prawns) after the abundant shrimp in the water; over time the designation became Cameroon in English; this is the only instance where a country is named after a crustacean.
- The legal system in Cameroon: mixed legal system of English common law, French civil law, and customary law.
- Climate: South is equatorial, with plentiful rainfall, declining inland. Far north is beset by drought.
- The national symbols are lion; national colors: green, red, yellow.
- Internet TLD: .cm
Background
Much of the area of present-day Cameroon was ruled by powerful chiefdoms before becoming a German colony in 1884 known as Kamerun. After World War I, the territory was divided between France and the UK as League of Nations mandates. French Cameroon became independent in 1960 as the Republic of Cameroon. The southern portion of neighboring British Cameroon voted to merge with the new country to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. In 1972, a new constitution replaced the federation with a unitary state, the United Republic of Cameroon. The country has generally enjoyed stability, which has enabled the development of agriculture, roads, railways, and the petroleum industry. Despite slow movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Paul BIYA.
Geography
Over half the land is forested: equatorial rainforest in the north, evergreen forest, and wooded savanna in the south. Mountains in the west.
Situated in the corner of the Gulf of Guinea, Cameroon was effectively a one-party state for 30 years. Multiparty elections, since 1992 regularly return that same party to power.
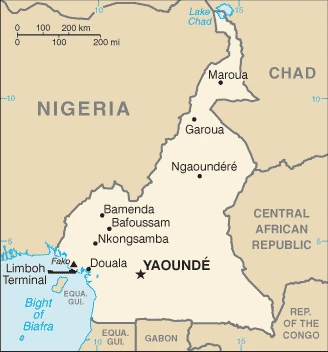
This state is located in Central Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial Guinea and Nigeria, under the coordinates of 6 00 N, 12 00 E, covering an area of 475,440 sq km with a coastline of 402 km. Cameroon is Slightly larger than California, about four times the size of Pennsylvania.
Cameroon has 5,018 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (6 nations): The Central African Republic 901 km, Chad 1116 km, Republic of the Congo 494 km, Equatorial Guinea 183 km, Gabon 349 km, Nigeria 1975 km.
Diverse, with coastal plain in southwest, dissected plateau in center, mountains in the west, plains in the north, with Fako on mont Cameroun 4,045 m as the highest point of Cameroon, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 667 m throughout the country. With a total of 475,440 sq km, Cameroon has 472,710 sq km of land and 2,730 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Chad (endorheic lake shared with Niger, Nigeria, and Chad) – 10,360-25,900 sq km (a freshwater lake), The significant watersheds for Cameroon are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Congo (3,730,881 sq km), Niger (2,261,741 sq km) Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km).
Sometimes referred to as the hinge of Africa because of its central location on the continent and its position at the west-south juncture of the Gulf of Guinea; throughout the country, there are areas of thermal springs and indications of current or prior volcanic activity; Mount Cameroon, the highest mountain in Sub-Saharan West Africa, is an active volcano.
The climate in Cameroon is as follows: Varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in north.
When you visit Cameroon, the natural hazards shall be considered: Volcanic activity with periodic releases of poisonous gases from Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun volcanoes volcanism: mt. Cameroon (4,095 m), which last erupted in 2000, is the most frequently active volcano in west Africa; lakes in Oku volcanic field have released fatal gas levels on occasion, killing some 1,700 people in 1986.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Cameroon: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, malaria, dengue fever, schistosomiasis, rabies, meningococcal meningitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Cameroonian people: waterborne diseases are prevalent; deforestation and overgrazing result in erosion, desertification, and reduced quality of pastureland; poaching; overfishing; overhunting.
Google Maps Cameroon
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Yaounde found under the coordinates 3 52 N, 11 31 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Cameroon, formerly known as French Cameroon, has been Nigeria’s country since the latter’s independence in 1960. The capital of Cameroon is Yaoundé, and it is easy to see why – it is a charming city with many attractions and has a densely populated city center. Today, Yaoundé is one of the most important economic centers in West Africa.
Cameroon became independent on 1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship), and its national holiday is State Unification Day (National Day), 20 May (1972).
Administrative divisions: 10 regions (regions, singular – region); Adamaoua, Centre, East (Est), Far North (Extreme-Nord), Littoral, North (Nord), North-West (Nord-Ouest), West (Ouest), South (Sud), South-West (Sud-Ouest).
People and society
Around 230 ethnic groups; no single group is dominant. The Bamileke is the largest, though it has never held political power. North-south tensions are diminished by ethnic diversity. There is more rivalry between majority French and minority English-speakers.
The population in Cameroon is 28,524,175 (July 2021 estimate). Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected, with an average of 2.77% (2021 estimate) change. That means Cameroon is the No. 51 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 18.5 years median age (18.2 years for males and 18.2 years for women), Cameroon ranks No. 209 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Cameroonian(s) (noun) or Cameroonian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Bamileke-Bamu 24.3%, Beti/Bassa, Mbam 21.6%, Biu-Mandara 14.6%, Arab-Choa/Hausa/Kanuri 11%, Adamawa-Ubangi, 9.8%, Grassfields 7.7%, Kako, Meka/Pygmy 3.3%, Cotier/Ngoe/Oroko 2.7%, Southwestern Bantu 0.7%, foreign/another ethnic group 4.5% (2018 estimate).
They speak 24 major African language groups, English (official language), French (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 38.3%, Protestant 25.5%, other Christian 6.9%, Muslim 24.4%, animist 2.2%, other 0.5%, none 2.2% (2018 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Cameroon: Population concentrated in the west and north, with the country’s interior sparsely populated as shown in this population distribution map. In Cameroon, we are talking about 58.1% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 4.164 million, Yaounde (capital city), 3.793 million, Douala (2021).
Industry
Oil reserves. Very diversified agricultural economy timber, cocoa, bananas, coffee. Fuel smuggling from Nigeria undermines refinery profits. Corruption. Port for Chad and CAR.
Cameroon’s market-based, diversified economy features oil and gas, timber, aluminum, agriculture, mining, and the service sector. Oil remains Cameroon’s main export commodity, and despite falling global oil prices, it still accounts for nearly 40% of exports. Cameroon’s economy suffers from factors that often impact underdeveloped countries, such as stagnant per capita income, relatively inequitable distribution of income, a top-heavy civil service, endemic corruption, continuing inefficiencies of an extensive parastatal system in key sectors, and a generally unfavorable climate for business enterprise.
Since 1990, the government has embarked on various IMF and World Bank programs designed to spur business investment, increase efficiency in agriculture, improve trade, and recapitalize the nation’s banks. The IMF presses for economic reforms, including increased budget transparency, privatization, and poverty reduction programs. The Government of Cameroon provides subsidies for electricity, food, and fuel that have strained the federal budget and diverted funds from education, healthcare, and infrastructure projects, as low oil prices have led to lower revenues., Cameroon devotes significant resources to several large infrastructure projects under construction, including a deep seaport in Kribi and the Lom Pangar Hydropower Project. Cameroon’s energy sector continues to diversify, recently opening a natural gas-powered electricity generating plant. Cameroon continues to seek foreign investment to improve its inadequate infrastructure, create jobs, and improve its economic footprint, but its unfavorable business environment remains a significant deterrent.
Cameroon is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, bauxite, iron ore, timber, hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are petroleum production and refining, aluminum production, food processing, light consumer goods, textiles, lumber, ship repair.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in crude petroleum, cocoa beans, lumber, gold, natural gas, bananas (2019), partnering with these nations: China 17%, Netherlands 14%, Italy 9%, United Arab Emirates 8%, India 7%, United States 6%, Belgium 6%, Spain 5%, France 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $7.73 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Cameroon’s position of 107.
Land use in Cameroon: 41.7% (2018 estimate) forest, 37.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 13.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 20.6% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 3.3% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 4.2% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 290 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Cameroon are cassava, plantains, maize, oil palm fruit, taro, sugar cane, sorghum, tomatoes, bananas, vegetables.
The country typically needs to import: crude petroleum, scrap vessels, rice, special purpose ships, packaged medicines (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 28%, Nigeria 15%, France 9%, Belgium 6% (2019) in a sum value of $9.09 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $8.42 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Cameroon 111.
Cameroon Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Cameroon, Central Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial Guinea and Nigeria. We published some basic information about its capital Yaounde and the Cameroonian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Cameroon and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Cameroon below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Cameroon
Did you know about Cameroon?
Cameroon is a country in Central Africa fighting for independence from France and Britain since the colonial era, in the late nineteenth century. The French and British colonizers annexed most of the territory, ruling it as a united colony. Cameroonians, who had fought for their independence during these wars, felt betrayed when they learned about this new development.
After virtually visiting Cameroon, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Nigeria.
If you liked our Google map and Cameroon information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.