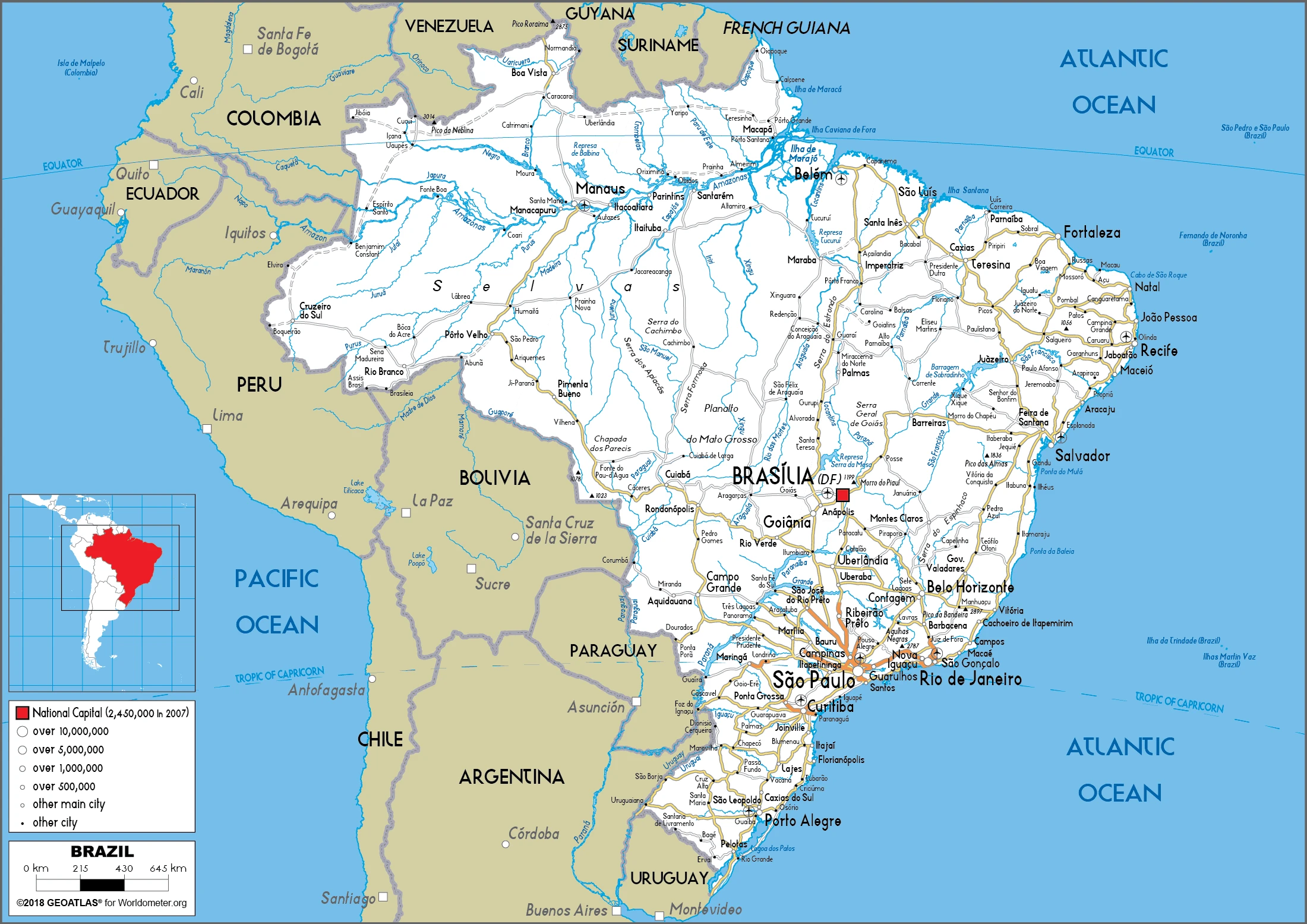
Brazil Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Brazil, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Brazil, South America (13 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Brasilia, bordering countries like Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this South American state.
Quick links: Google Maps Brazil, Brasilia Google maps, Driving Directions Brazil, Printable Road Map.

About Brazil in a nutshell
- Since 1900, a third of Brazils indigenous Amerindian groups have become extinct due to disease, starvation, or the forceful taking of land by miners, loggers, and settlers.
- Conventional short form of the name: Brazil
- The conventional long form of the name: Federative Republic of Brazil
- Local long form: Republica Federativa do Brasil
- Local short form: Brasil
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the country name derives from the brazilwood tree that used to grow plentifully along the coast of Brazil and that was used to produce a deep red dye.
- The legal system in Brazil: civil law.
- Climate: Brazils share of the Amazon Basin has a model tropical equatorial climate, with high temperatures and rainfall all year round. The Brazilian plateau has far greater seasonal variation. The dry northeast suffers frequent droughts, though coastal regions are occasionally flooded by bouts of torrential rain. The south has hot summers and cool winters.
- The national symbols are Southern Cross constellation; national colors: green, yellow, blue.
- Internet TLD: .br
After the Portuguese admiral Pedro Alvarez Cabral discovered and took possession of what was then thought to be an unknown island off the coast of modern-day Brazil in 1500 AD, Portuguese has been spoken in the country, which occupies almost half the continent and is the only one in the New World to do so. The old cities of Ouro Preto, Olinda, Salvador, Sáo Luis, Diamantina, and Goiás, monuments of Brazil’s golden age, are universal treasures of humanity, as are the ruins of the Jesuit mission of Sáo Miguel das Missoes and the pilgrimage church of Bőm Jesus do Congonhas. Finds in a cave in the Serra da Capivara National Park are the oldest traces of man’s presence in South America, dating back some 50 000 years. At the same time, the modern capital, Brasilia, designed on an engineering table, only appeared on maps in 1960.
The World Natural Heritage sites include almost every habitat type in the continent-sized country: the national parks of the planet’s largest tropical rainforest, the dry savannah of the Brazilian highlands, the protected areas of the cerrado, the subtropical rainforest around the Igua^u rainforest, the remaining patches of Atlantic rainforest along the coast, the most extensive wetland on Earth, the areas of the Pantanal that extend into Bolivia, and the protected islands of the Atlantic Ocean.
Background
Following more than three centuries under Portuguese rule, Brazil gained its independence in 1822, maintaining a monarchical system of government until the abolition of slavery in 1888 and the subsequent proclamation of a republic by the military in 1889. Brazilian coffee exporters politically dominated the country until populist leader Getulio VARGAS rose to power in 1930. By far the largest and most populous country in South America, Brazil underwent more than a half-century of populist and military government until 1985, when the military regime peacefully ceded power to civilian rulers.
Brazil continues to pursue industrial and agricultural growth and development of its interior. Having successfully weathered a period of global financial difficulty in the late 20th century, Brazil was seen as one of the world’s strongest emerging markets and a contributor to global growth. The awarding of the 2014 FIFA World Cup and 2016 Summer Olympic Games, the first-ever to be held in South America, was seen as symbolic of the country’s rise. However, from about 2013 to 2016, Brazil was plagued by a sagging economy, high unemployment, and high inflation, only emerging from the recession in 2017.
Former President Dilma ROUSSEFF (2011-2016) was removed from office in 2016 by Congress to commit impeachable acts against Brazil’s budgetary laws. Her vice president, Michel TEMER, served the remainder of her second term. In October 2018, Jair BOLSONARO won the presidency with 55 percent of the vote and assumed office on January 1, 2019.
Geography
Rainforest grows around the massive Amazon River and its delta, covering almost half of Brazils total land area. Apart from the basin of the River Plate to the south, the rest of the country consists of high lands. The mountainous east is part-forested and part-desert. The coastal plain in the southeast has swampy areas. The Atlantic coastline is 1240 miles (2000 km) long.
Covering almost half of South America, Brazil is the site of the worlds largest and ecologically most important rainforest. The country has immense natural and economic resources.
This state is located in Eastern South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, under the coordinates of 10 00 S, 55 00 W, covering an area of 8,515,770 sq km with a coastline of 7,491 km. Brazil is slightly smaller than the US.
Brazil has 16,145 km of land boundaries in total and bordering with (10 nations): Argentina 1263 km, Bolivia 3403 km, Colombia 1790 km, French Guiana 649 km, Guyana 1308 km, Paraguay 1371 km, Peru 2659 km, Suriname 515 km, Uruguay 1050 km, Venezuela 2137 km.
Mostly flat to rolling lowlands in the north, some plains, hills, mountains, and narrow coastal belt, with Pico da Neblina 2,994 m as the highest point of Brazil, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 320 m throughout the country. With 8,515,770 sq km, Brazil has 8,358,140 sq km of land and 157,630 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lagoa dos Patos – 10,140 sq km (a freshwater lake), Lagoa Mirim (shared with Uruguay) – 2,970 sq km (a saltwater lake). The major rivers are the Amazon river mouth (shared with Peru s) – 6,400 km, Rio de la Plata/Parana river source (shared with Paraguay, Argentina, and Uruguay) – 4,880 km, Tocantins – 3,650 km, Sao Francisco – 3,180 km, Paraguay river source (shared with Argentina and Paraguay m) – 2,549 km, Rio Negro (shared with Colombia and Venezuela) – 2,250 km, Uruguay river source (shared with Argentina and Uruguay m) – 1,610 km. The significant watersheds for Brazil are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km), Orinoco (953,675 sq km), Paraná (2,582,704 sq km), S?o Francisco (617,814 sq km), Tocantins (764,213 sq km).
The largest country in South America and the Southern Hemisphere; it shares common boundaries with every South American country except Chile and Ecuador; most of the Pantanal, the world’s largest tropical wetland, extends through the west-central part of the country; shares Iguazu Falls, the worlds most extensive waterfalls system, with Argentina.
The climate in Brazil is primarily tropical but temperate in the south.
When you visit Brazil, the natural hazards shall be considered: Droughts in the northeast, floods, and occasional frost in the south.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Brazil: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A, dengue fever and malaria, and schistosomiasis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Brazilian people: deforestation in the Amazon Basin destroys the habitat and endangers a multitude of plant and animal species indigenous to the area; illegal wildlife trade; illegal poaching; air and water pollution in Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo, and several other large cities; land degradation and water pollution caused by improper mining activities; wetland degradation; severe oil spills.
Google Maps Brazil
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Brasilia found under the coordinates 15 47 S, 47 55 W, applying the time zone UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Brasilia is the federal capital of Brazil and is also the most populous city in Brazil. Inaugurated in 1960, Brasilia became the new national capital on April 21, 1960. The concept of this planned city was drawn by French architect Léon Brédif, whose design was developed by engineers Raoul Moreira da Silva and Lúcio Costa.
Brazil became independent on September 7, 1822 (from Portugal), and its national holiday is Independence Day, September 7 (1822).
Administrative divisions: 26 states (estados, singular – estado) and 1 federal district (distrito federal); Acre, Alagoas, Amapa, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceara, Distrito Federal, Espirito Santo, Goias, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Para, Paraiba, Parana, Pernambuco, Piaui, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondonia, Roraima, Santa Catarina, Sao Paulo, Sergipe, Tocantins.
People and society
The diverse population includes Amerindians, black people of African descent, European immigrants, and mixed races. Amerindians suffer prejudice from most other groups. Shantytowns in the cities attract poor migrants from the northeast. Urban Crime, violent land disputes, and unchecked development in Amazonia tarnish Brazils image as a modern nation. Catholicism and the family unit remain strong.
The population in Brazil is 213,445,417 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.65% (2021 estimate) change. That means Brazil is the No. 7 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 33.2 years median age (32.3 years for males and 32.3 years for women), Brazil ranks No. 101 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Brazilian(s) (noun) or Brazilian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White 47.7%, Mulatto (mixed White and Black) 43.1%, Black 7.6%, Asian 1.1%, Indigenous 0.4% (2010 estimate).
They speak Portuguese (official language and most widely spoken language) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 64.6%, other Catholic 0.4%, Protestant 22.2% (includes Adventist 6.5%, Assembly of God 2.0%, Christian Congregation of Brazil 1.2%, Universal Kingdom of God 1.0%, other Protestant 11.5%), other Christian 0.7%, Spiritist 2.2%, other 1.4%, none 8%, unspecified 0.4% (2010 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Brazil: The vast majority of people live along, or relatively near, the Atlantic coast in the east. The population core is in the southeast, anchored by Sao Paolo, Brasilia, and Rio de Janeiro. In Brazil, we are talking about 87.3% (2021) of the total population is living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 22.237 million, Sao Paulo, 13.544 million, Rio De Janeiro, 6.140 million, Belo Horizonte, 4.728 million, Brasilia (capital city), 4.175 million, Recife, 4.161 million, Porto Alegre (2021).
Industry
Dominant regional economy. Massive potential for growth based on abundant natural resources. A leading exporter of coffee, sugar, soybeans, and orange juice. Social tension threatens stability. Infrastructure needs investment. A downturn in 2014.
Brazil is the eighth-largest economy in the world but is recovering from a recession in 2015 and 2016 that ranks as the worst in the country’s history. In 2017, Brazil’s GDP grew 1%, inflation fell to historic lows of 2.9%, and the Central Bank lowered benchmark interest rates from 13.75% in 2016 to 7%. The economy has been negatively affected by multiple corruption scandals involving private companies and government officials, including the impeachment and conviction of Former President Dilma ROUSSEFF in August 2016. Sanctions against the firms involved some of the largest in Brazil have limited their business opportunities, producing a ripple effect on associated businesses and contractors but creating opportunities for foreign companies to step into what had been a closed market.
The successive TEMER administration has implemented fiscal and structural reforms to restore credibility to government finances. Congress approved legislation in December 2016 to cap public spending. Government spending growth had pushed public debt to 73.7% of GDP at the end of 2017, up from over 50% in 2012. To raise revenues, the government also boosted infrastructure projects, such as oil and natural gas auctions.
Other economic reforms proposed in 2016 aim to reduce barriers to foreign investment and improve labor conditions. Policies to strengthen Brazil’s workforce and the industrial sector, such as local content requirements, have boosted employment but at investment expense. Brazil is a member of the Common Market of the South (Mercosur), a trade bloc that includes Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay – Venezuela’s membership in the organization was suspended In August 2017. After the Asian and Russian financial crises, Mercosur adopted a protectionist stance to guard against exposure to volatile foreign markets. It is currently negotiating Free Trade Agreements with the European Union and Canada.
Brazil is rich in natural resources: Alumina, bauxite, beryllium, gold, iron ore, manganese, nickel, niobium, phosphates, platinum, tantalum, tin, rare earth elements, uranium, petroleum, hydropower, timber.
The main industrial sectors are typically textiles, shoes, chemicals, cement, lumber, iron ore, tin, steel, aircraft, motor vehicles and parts, and other machinery and equipment.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in soybeans, crude petroleum, iron, corn, and wood pulp products (2019), partnering with these nations: China 28%, United States 13% (2019). The export trade resulted in $239.18 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Brazil’s position of 27.
Land use in Brazil: 61.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 5.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 8.6% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 32.9% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 23.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 54,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Brazil are sugar cane, soybeans, maize, milk, cassava, oranges, poultry, rice, beef, and cotton.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, vehicle parts, crude petroleum, integrated circuits, pesticides (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 21%, the United States 18%, Germany 6%, Argentina 6% (2019) in a sum value of $227.44 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $269.02 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $267.52 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Brazil 27.
Brazil Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Brazil, Eastern South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. We published some basic information about its capital Brasilia, and the Brazilian nation.
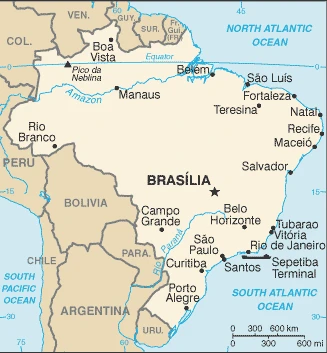
Are you interested in visiting Brazil and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Brazil below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Brazil
Did you know about Brazil?
Brazil has many varied landscapes, with jungles, mountains, and beaches. Brazilians speak Portuguese (mostly), but many Brazilians also speak English.
No one can deny that Brazil is a fascinating country. The Brazilian culture, people, and language are all unique. That is why it is essential to understand the basics of this country before you explore it.
After virtually visiting Brazil, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela.
If you liked our Google map and Brazil information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.