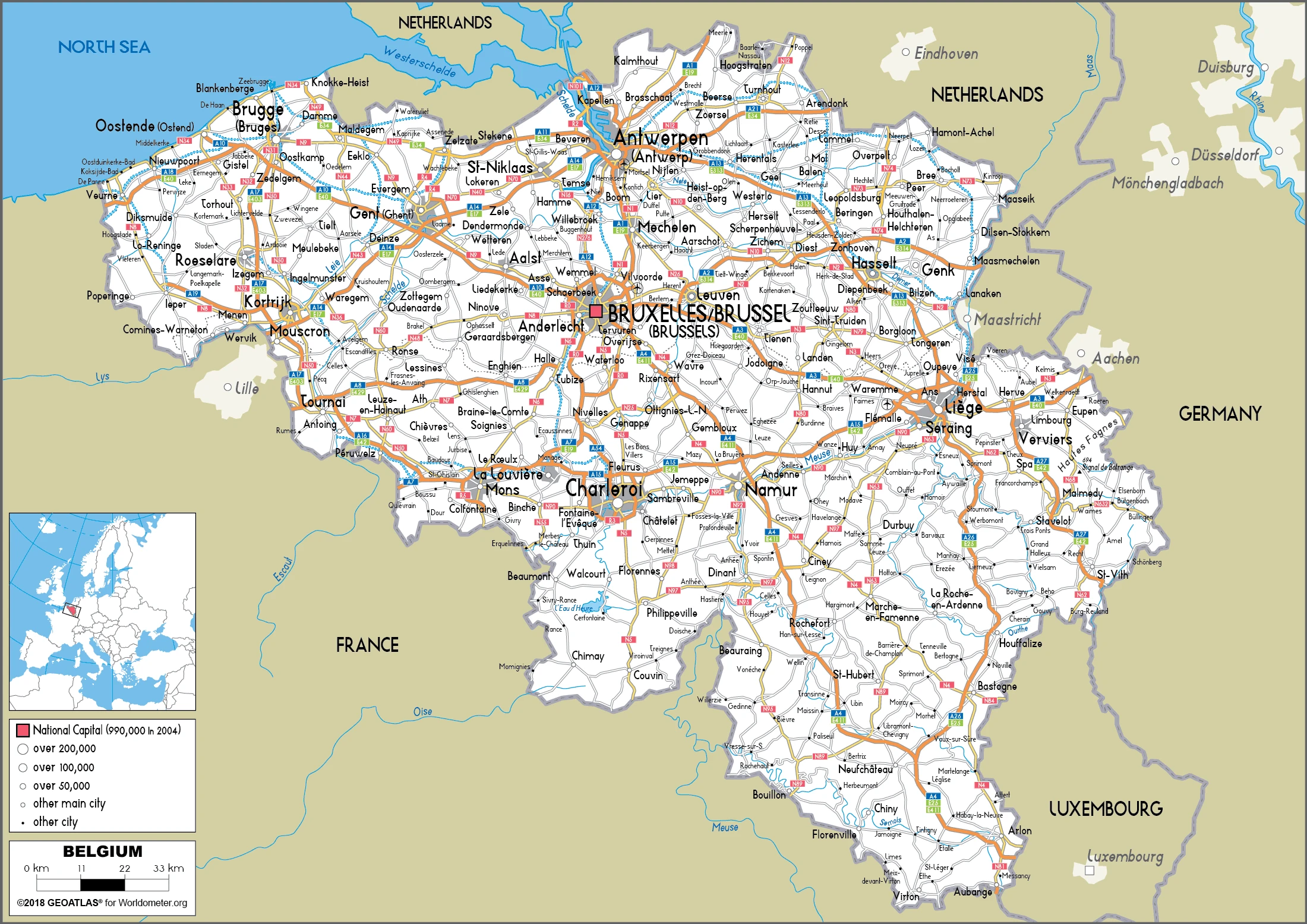
Belgium Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Belgium, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Belgium, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Brussels, bordering countries like France, Germany, Luxembourg, Netherlands, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Belgium, Brussels Google maps, Driving Directions Belgium, Printable Road Map.

About Belgium in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Belgium
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Belgium
- Local long form: Royaume de Belgique (French) / Koninkrijk Belgie (Dutch) / Koenigreich Belgien (German)
- Local short form: Belgique / Belgie / Belgien
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the name derives from the Belgae. This ancient Celtic tribal confederation inhabited an area between the English Channel and the west bank of the Rhine in the first centuries B.C.
- The legal system in Belgium: civil law system based on the French Civil Code.
- Climate: Maritime with Gulf Stream influences. Mild temperatures, with heavy cloud cover and rain. More rainfall and weather fluctuations at the coast.
- The national symbols are a golden rampant lion, while the national colors are red, black, and yellow.
- Internet TLD: .be
Belgium is a tiny country squeezed between Holland, France, and Germany. The nation is diverse because of its location at the crossroad of Europe’s Germanic north and Latin south. Belgium has two major ethnic regions: Dutch-speaking Flanders and French-speaking Wallonia. Two historic cities in Belgium offer visitors a glimpse into Belgian culture and history. With tourist destinations as unique as the medieval cities of Bruges and Ghent, it would be worth your time to visit this country. Both of these Belgian cities offer collections of medieval art and architecture. These include some northern Renaissance’s most outstanding paintings in their museums and churches. Though each has a distinct character, visiting them is still worth it: you can easily do so on day trips. You will want to stay overnight if you want to explore the city more thoroughly.
Belgium is bisected by the river Meuse, with the Flemish Plain to the north and the low, rounded hills of the Ardennes to the south. Its World Heritage sites are mainly linked to the country’s Flemish-Walloon history. The Neolithic flint quarries near Spiennes are Europe’s most significant ancient mining district. The medieval bell towers of Flanders and northern France were built between the 11th and 17th centuries. Notre-Dame Cathedral in Tournai is one of the most beautiful churches of the French Gothic period. The religious communities of the Flemish beguinages, consisting of houses, churches, outbuildings, and green spaces, were inhabited by spinsters and widows from the 13th century onwards. The historic old town of Bruges was once the commercial gateway to the continent and the birthplace of the Flemish primitive school of painting. The public buildings and guild houses surrounding Brussels’ main square, the Grand Place, were primarily built in the 17th century, while Victor Horta’s Art Nouveau buildings are a relic of the 20th century. In Antwerp, the House of Plantin-Moretus was the home of Christophe Plantin, the most remarkable printer and publisher in the Low German Countries in the second half of the 16th century. The construction of the Canal du Centre, the lock system of the Canal du Centre, which bridges a difference in the level of around 90 meters, was one of the crowning achievements of European engineering in the 19th century.
Belgium holds the world record for the country with the most extended period without a government.
Background
Belgium became independent from the Netherlands in 1830. Germany occupied it during World Wars I and II. The country prospered in the past half-century as a modern, technologically advanced European state and member of NATO and the EU. In recent years, political divisions between the Dutch-speaking Flemish of the north and the French-speaking Walloons of the south have led to constitutional amendments granting these regions formal recognition and autonomy. The capital city of Brussels is home to numerous international organizations, including the EU and NATO.
Geography
Low-lying coastal plain covers two-thirds of the country. Land becomes hilly and forested in the southeast (Ardennes).
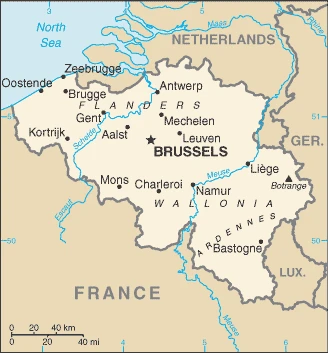
Belgium lies in northwestern Europe. Its history has been marked by tensions between the majority Dutch-speaking (Flemish) and minority French-speaking (Walloon) communities.
This state is located in Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between France and the Netherlands, under the coordinates of 50 50 N, 4 00 E, covering an area of 30 528 sq km with a coastline of 66.5 km. Belgium is About the size of Maryland.
Belgium has 1,297 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (4 nations): France 556 km, Germany 133 km, Luxembourg 130 km, Netherlands 478 km.
Flat coastal plains in northwest, central rolling hills, rugged mountains of Ardennes Forest in the southeast, with Botrange 694 m as the highest point of Belgium, while the North Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 181 m throughout the country. With a total of 30 528 sq km, Belgium has 30 278 sq km of land and 250 sq km of water surface area.
The significant watersheds for Belgium are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Seine 78,919 sq km), Rhine-Maas (198,735 sq km).
Crossroads of Western Europe; most West European capitals are within 1,000 km of Brussels, the European Union, and the NATO seat.
The climate in Belgium is as follows: Temperate, mild winters, cool summers, rainy, humid, cloudy.
When you visit Belgium, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flooding is a threat along rivers and in areas of reclaimed coastal land, protected from the sea by concrete dikes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Belgium: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Belgian people: intense pressures from human activities: urbanization, dense transportation network, industry, extensive animal breeding, and crop cultivation; air and water pollution also have repercussions for neighboring countries.
Google Maps Belgium
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Brussels found under the coordinates 50 50 N, 4 20 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Brussels is a major European city and one of the three capital cities of Europe. It is located in the Brussels-Capital Region and Belgium’s de facto capital. Brussels is home to many international organizations and NATO, but it is best known for two other things: its beer and chocolate.
Belgium became independent on 4 October 1830 (a provisional government declared independence from the Netherlands); 21 July 1831 (King LEOPOLD I ascended to the throne), and its national holiday is Belgian National Day (ascension to the throne of King LEOPOLD I), 21 July (1831).
Administrative divisions: 3 regions (French: regions, singular – region; Dutch: gewesten, singular – gewest); Brussels-Capital Region, also known as Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest (Dutch), Region de Bruxelles-Capitale (French long form), Bruxelles-Capitale (French short form); Flemish Region (Flanders), also known as Vlaams Gewest (Dutch long form), Vlaanderen (Dutch short form), Region Flamande (French long form), Flandre (French short form); Walloon Region (Wallonia), also known as Region Wallone (French long form), Wallonie (French short form), Waals Gewest (Dutch long form), Wallonie (Dutch short form) note: as a result of the 1993 constitutional revision that furthered devolution into a federal state, there are now three levels of government (federal, regional, and linguistic community) with a complex division of responsibilities; the 2012 sixth state reform transferred additional competencies from the federal state to the regions and linguistic communities.
People and society
Since 1970, Flemish regions have become more prosperous than the minority Walloons, overturning traditional roles and increasing friction. Belgium moved to a federal system in 1980 to contain tensions, but recent fractious politics have raised doubts over the union’s survival. The Flemish separatist N-VA heads the Flanders government and since 2010 has been the largest party at the federal level. Brussels hosts vital EU institutions.
The population in Belgium is 11,778,842 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.59% (2021 estimate) change. That means Belgium is the No. 80 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 41.6 years median age (40.4 years for males and 40.4 years for women), Belgium ranks No. 44 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Belgian(s) (noun) or Belgian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Belgian 75.2%, Italian 4.1%, Moroccan 3.7%, French 2.4%, Turkish 2%, Dutch 2%, other 10.6% (2012 estimate).
They speak Dutch (official language) 60%, French (official language) 40%, German (official language) less than 1% languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant and other Christian 2.5%, Muslim 5%, Jewish 0.4%, Buddhist 0.3%, atheist 9.2%, none 32.6% (2009 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Belgium: Most of the population is concentrated in the northern two-thirds of the country. The southeast is more thinly populated. Considered to have one of the highest population densities in the world. Approximately 97% live in urban areas. In Belgium, we are talking about 98.1% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 2.096 million, Brussels (capital city), 1.048 million, Antwerp (2021).
Industry
Many industrial exports, including steel, glassware, cut diamonds, and textiles. High levels of public debt. Bureaucracy is more enormous than the European average.
Belgium’s central geographic location and highly developed transport network have helped develop a well-diversified economy, with a broad mix of transport, services, manufacturing, and high tech. Service and high-tech industries are concentrated in the northern Flanders region, while the southern region of Wallonia is home to industries like coal and steel manufacturing. Belgium is utterly reliant on foreign sources of fossil fuels, and the planned closure of its seven nuclear plants by 2025 should increase its dependence on foreign energy. Its role as a regional logistical hub makes its economy vulnerable to shifts in foreign demand, particularly with EU trading partners. Roughly three-quarters of Belgium’s trade is with other EU countries. The port of Zeebrugge conducts almost half its trade with the United Kingdom alone, leaving Belgiums economy vulnerable to the outcome of negotiations on the UK’s exit from the EU. Belgium’s GDP grew by 1.7% in 2017. The budget deficit was 1.5% of GDP.
Unemployment stood at 7.3%. However, the unemployment rate is lower in Flanders than in Wallonia, 4.4% compared to 9.4%, because of industrial differences between the regions. The economy largely recovered from the March 2016 terrorist attacks that mainly impacted the Brussels region tourist and hospitality industry. Prime Minister Charles Michels, the center-right government, has pledged to further reduce the deficit in response to EU pressure to decrease Belgium’s high public debt of about 104% of GDP. Still, such efforts would also dampen economic growth. In addition to restrained public spending, low wage growth and higher inflation promise to curtail a more robust recovery in private consumption.
The government has pledged to pursue a reform program to improve Belgium’s competitiveness, including changes to labor market rules and welfare benefits. These changes have generally made Belgian wages more competitive regionally but have raised tensions with trade unions, which have called for extended strikes. In 2017, Belgium approved a tax reform plan to ease corporate rates from 33% to 29% by 2018 and down to 25% by 2020. The tax plan also included benefits for innovation and SMEs, intended to spur competitiveness and private investment.
Belgium is rich in the following natural resources: Construction materials, silica sand, carbonates, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically engineering and metal products, motor vehicle assembly, transportation equipment, scientific instruments, processed food and beverages, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, base metals, textiles, glass, petroleum.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars and vehicle parts, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, medical cultures/vaccines, diamonds, and natural gas (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 17%, France 14%, Netherlands 13%, United Kingdom 8%, United States 6%, Italy 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $414.79 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Belgium’s position of 17.
Land use in Belgium: 22.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 33.5% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 27.2% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 44.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 16.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 230 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Belgium are sugar beet, milk, potatoes, wheat, pork, lettuce, poultry, maize, barley, pears.
The country typically needs to import: cars, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, medical cultures/vaccines, diamonds, and natural gas (2019), partnering with the following nations: Netherlands 16%, Germany 13%, France 10%, United States 8%, Ireland 5%, China 5% (2019) in a sum value of $412.85 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $433.04 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $452.53 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Belgium 15.
Belgium Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Belgium, Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between France and the Netherlands. We published some basic information about its capital Brussels, and the Belgian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Belgium and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Belgium below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Belgium
Did you know about Belgium?
Belgium has been there for centuries and is known as the regional economic center for Europe. Belgium has a very diverse population and is bilingual: Flemish and French.
Due to their history with France and Netherlands, Belgians typically eat dishes comparable to French or Dutch cuisine.
After virtually visiting Belgium, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: France, Germany, Luxembourg, Netherlands.
The capital city of Brussels is home to many international institutions, including NATO and the European Union. The port of Antwerp handles much of Belgium’s trade with other countries in Europe.
If you liked our Google map and Belgium information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.