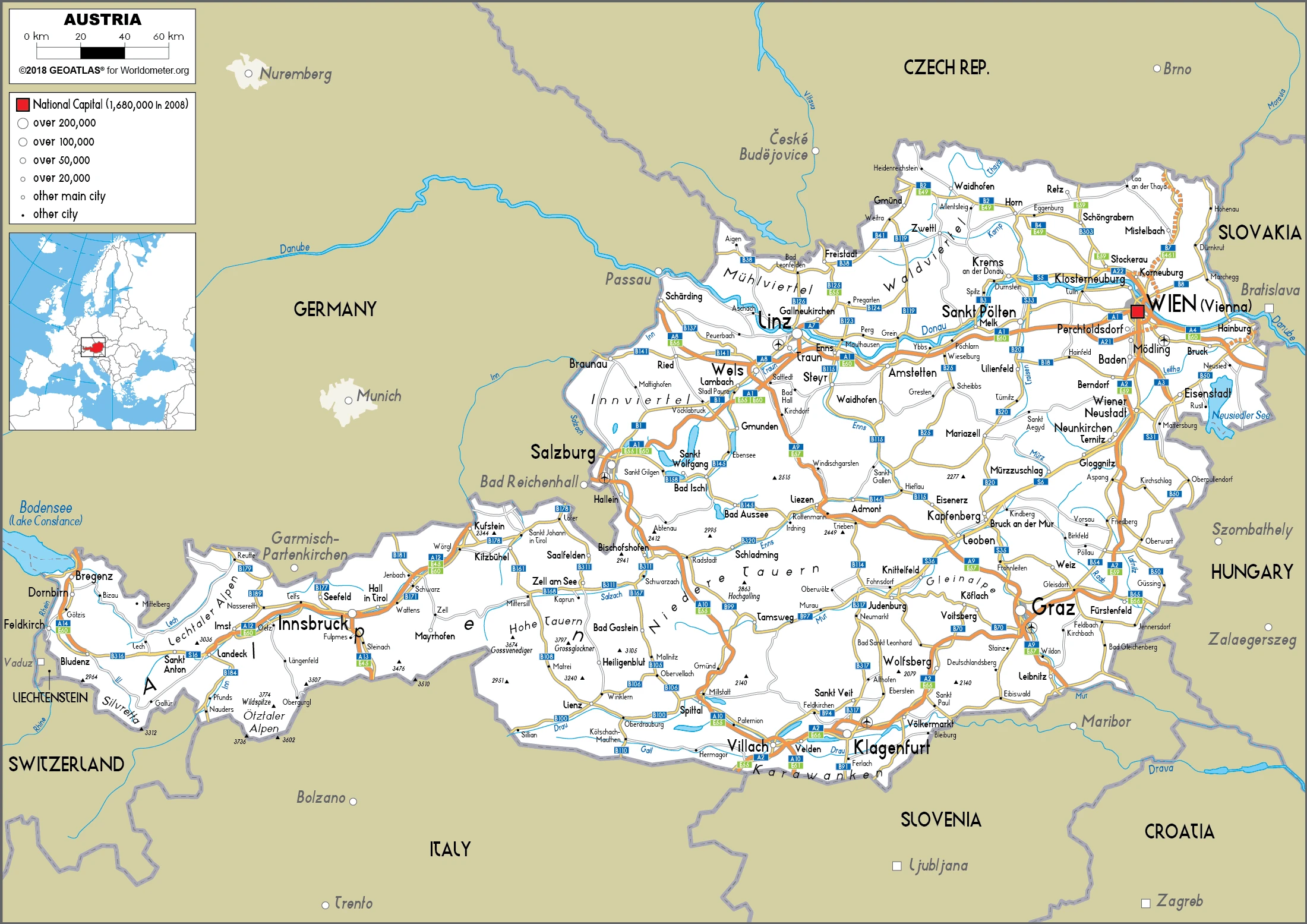
Austria Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Austria, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Austria, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, and details about its capital city Vienna, and bordering countries like the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Austria, Vienna Google maps, Driving Directions Austria, Printable Road Map.

About Austria in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Austria
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Austria
- Local long form: Republik Oesterreich
- Local short form: Oesterreich
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the name Oesterreich means eastern realm or eastern march and dates to the 10th century; the designation refers to the fact that Austria was the easternmost extension of Bavaria and, in fact, of all the Germans; the word Austria is a Latinization of the German name.
- The legal system in Austria: civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts by the Constitutional Court.
- Climate: Temperate continental climate. The western Alpine regions have colder winters and more rainfall.
- The national symbols are eagle, edelweiss, Alpine gentian; national colors: red, white.
- Internet TLD: .at
Austria is positioned at the crossroads of Europe, just as it was during the heyday of Austria-Hungary. Its capital, Vienna, is on the edge of western Europe and its recent revival as an important international city. In Austria, there is plenty to do, from exploring historic castles and palaces to skiing on world-class alpine slopes.
Around two-thirds of Austria is covered by the jagged chains of the Austro-Croatian limestone Alps glaciers. In the northern foothills, the landscape is varied with rolling hills and vast basins sloping down to the broad Danube valley, and in the east, the Vienna Basin, the Alpine hills, and the slopes of Lake Fertő. The Fertő/Neusiedlersee cultural landscape, which bears the imprint of 8,000 years of different cultures, is a World Heritage Site shared with Hungary. It is no coincidence that Austria has eight World Heritage Sites Austria are three cultural landscapes in three of Austria’s eight World Heritage Sites. Hallstatt, Dachstein, and Salzkammergut, human activity traces of human activity are believed to date back to prehistoric times: salt was mined here in the 2nd millennium BC.
The Wachau, in the Danube valley, is a cultural region where town planning and viticulture are in harmony. And the fact that this landscape has been inhabited since time immemorial is demonstrated by the discovery of a small statue of the ‘Venus of Willendorf’ nearby. The historical centers and old town centers of the three most populous Austrian cities of Vienna, Graz, and Salzburg have been influenced by the empires’ different periods and architectural styles from Roman times to the end of the 19th century. From the 18th century until 1918, the summer residence of the Habsburg monarchs was the Schönbrunn Palace, a rival to the French Palace of Versailles. The world’s first zoo was established in 1752 and has been open to visitors ever since. Built between 1848 and 1854, the Semmering Railway is still in operation today and was an engineering masterpiece.
Many of the worlds great composers were Austrian, including Mozart, Haydn, Schubert, and Strauss.
Background
Once the center of power for the large Austro-Hungarian Empire, Austria was reduced to a small republic after World War I. Following annexation by Nazi Germany in 1938 and subsequent occupation by the victorious Allies in 1945, Austria’s status remained unclear for a decade. A State Treaty signed in 1955 ended the occupation, recognized Austria’s independence, and forbade unification with Germany. A constitutional law that same year declared the country’s perpetual neutrality as a condition for Soviet military withdrawal. The Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991 and Austria’s entry into the EU in 1995 have altered the meaning of this neutrality. A prosperous, democratic country, Austria entered the EU Economic and Monetary Union in 1999.
Geography
Mainly mountainous. Alps and foothills cover the west and south. Lowlands in the east are part of the Danube River basin.
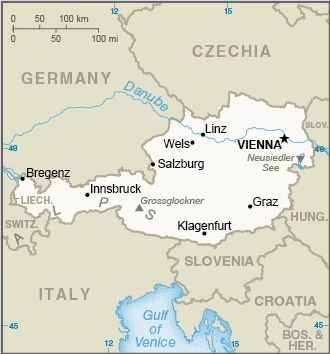
Bordering eight countries in the heart of Europe, Austria was created in 1918 after the collapse of the Habsburg Empire. Neutral after World War II, it joined the EU in 1995.
This state is located in Central Europe, north of Italy and Slovenia, under the coordinates of 47 20 N, 13 20 E, covering an area of 83,871 sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). Austria is About the size of South Carolina, slightly more than two-thirds the size of Pennsylvania.
Austria has 2,524 km of land boundaries and borders (8 nations): the Czech Republic 402 km, Germany 801 km, Hungary 321 km, Italy 404 km, Liechtenstein 34 km, Slovakia 105 km, Slovenia 299 km, Switzerland 158 km.
Mostly mountains (alps) in the west and south, mostly flat or gently sloping along the eastern and northern margins, with Grossglockner 3,798 m as the highest point of Austria, while Neusiedler See 115 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 910 m throughout the country. With 83,871 sq km, Austria has 82,445 sq km of land and 1,426 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Constance (shared with Switzerland and Germany) – 540 sq km (a freshwater lake), N/A (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Danube (shared with Germany, Slovakia, Czechia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania m) – 2,888 km. The significant watersheds for Austria are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Rhine-Maas (198,735 sq km), (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km).
Landlocked; strategic location at the crossroads of central Europe with many easily traversable Alpine passes and valleys; the major river is the Danube; the population is concentrated on eastern lowlands because of steep slopes, poor soils, and low temperatures elsewhere.
The climate in Austria is as follows: Temperate, continental, cloudy, cold winters with frequent rain and some snow in lowlands and snow in the mountains, moderate summers with occasional showers.
When you visit Austria, the natural hazards shall be considered: Landslides, avalanches, and earthquakes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Austria: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Austrian people: some forest degradation caused by air and soil pollution; soil pollution results from the use of agricultural chemicals; air pollution results from emissions by coal- and oil-fired power stations and industrial plants and from trucks transiting Austria between northern and southern Europe; water pollution; the Danube, as well as some of Austria’s other rivers and lakes, are threatened by pollution.
Google Maps Austria
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Vienna found under the coordinates 48 12 N, 16 22 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Vienna is a beautiful city with lots of culture and history from the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It’s also home to lots of architecture and museums. Its culture is one that you’ll want to experience!
Austria became independent on no official date of independence: 976 (Margravate of Austria established); 17 September 1156 (Duchy of Austria founded); 6 January 1453 (Archduchy of Austria acknowledged); 11 August 1804 (Austrian Empire proclaimed); 30 March 1867 (Austro-Hungarian dual monarchy established); 12 November 1918 (the First Republic proclaimed); 27 April 1945 (the Second Republic proclaimed), and its national holiday is National Day (commemorates the passage of the law on permanent neutrality), 26 October (1955).
Administrative divisions: 9 states (Bundeslaender, singular – Bundesland); Burgenland, Kaernten (Carinthia), Niederoesterreich (Lower Austria), Oberoesterreich (Upper Austria), Salzburg, Steiermark (Styria), Tirol (Tyrol), Vorarlberg, Wien (Vienna).
People and society
Though Austrians speak German, they like to stress their distinctive identity to Germany. Vienna is a major cultural center. Minorities are few; some ethnic Croats, Slovenes, and Hungarians, plus refugees from the conflict in former Yugoslavia. Though strongly Roman Catholic, Austrian society is less conservative than some southern German Länder. Class divisions remain strong.
The population in Austria is 8,884,864 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.32% (2021 estimate) change. That means Austria is the No. 97 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 44.5 years median age (43.1 years for males and 43.1 years for women), Austria ranks No. 14 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Austrian(s) (noun) or Austrian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Austrian 80.8%, German 2.6%, Bosnian and Herzegovinian 1.9%, Turkish 1.8%, Serbian 1.6%, Romanian 1.3%, other 10% (2018 estimate). Note: data represent population by country of birth.
They speak German (official language nationwide) 88.6%, Turkish 2.3%, Serbian 2.2%, Croatian (official language in Burgenland) 1.6%, other (includes Slovene, official in southern Carinthia, and Hungarian, official in Burgenland) 5.3% (2001 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Catholic 57%, Eastern Orthodox 8.7%, Muslim 7.9%, Evangelical Christian 3.3%, other/none/unspecified 23.1% (2018 estimate) note: data on Muslim is a 2016 estimate; data on other/none/unspecified are from 2012-2018 estimates.
We can conclude the following about the population in Austria: The northern and eastern portions of the country are more densely populated. Nearly two-thirds of the populace lives in urban areas. In Austria, we are talking about 59% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.945 million, Vienna (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Large manufacturing base, despite lack of energy resources. The skilled labor force is key to high-tech exports. Eurozone member. Limited GDP growth has returned since the 2009 recession.
Austria is a well-developed market economy with a skilled labor force and a high standard of living. It is closely tied to other EU economies, especially Germany, and the US, its third-largest trade partner. Its economy features a large service sector, a sound industrial sector, and a small but highly developed agricultural sector., Austrian economic growth strengthened in 2017, with a 2.9% increase in GDP. Austrian exports, accounting for around 60% of the GDP, were up 8.2% in 2017. Austria’s unemployment rate fell from 0.3% to 5.5%, which is low by European standards but still at its second-highest rate since World War II, driven by an increased number of refugees and EU migrants entering the labor market. Austria’s fiscal position compares favorably with other euro-zone countries. The budget deficit stood at a low of 0.7% of GDP in 2017, and public debt declined again to 78.4% of GDP in 2017 after reaching a post-war high of 84.6% in 2015. The Austrian government has announced its plans to balance the fiscal budget in 2019. Several external risks, such as the Austrian bank’s exposure to Central and Eastern Europe, the refugee crisis, and continued unrest in Russia/Ukraine, eased in 2017 but are still a factor for the Austrian economy. Exposure to the Russian banking sector and a deep energy relationship with Russia present additional risks., Austria elected a new pro-business government in October 2017 that campaigned on promises to reduce bureaucracy, improve public sector efficiency, reduce labor market protections, and provide positive investment incentives.
Austria is rich in the following natural resources: Oil, coal, lignite, timber, iron ore, copper, zinc, antimony, magnesite, tungsten, graphite, salt, and hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are construction, machinery, vehicles and parts, food, metals, chemicals, lumber and paper, electronics, and tourism.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in cars, packaged medical supplies, vehicle parts, medical vaccines/cultures, and flavored water (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 28%, United States 7%, Italy 6%, Switzerland 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $226.79 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Austria’s position of 28.
Land use in Austria: 47.2% (2018 estimate) forest, 14.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 16.5% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 38.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 21.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1,170 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Austria are milk, maize, sugar beet, wheat, barley, potatoes, pork, triticale, grapes, and apples.
The country typically needs to import: cars, vehicle parts, broadcasting equipment, refined petroleum, and packaged medical supplies (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 39%, Italy 7%, Czechia 5% (2019) in a sum value of $211.85 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $232.8 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $238.79 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Austria 29.
Austria Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Austria, Central Europe, the north of Italy, and Slovenia. We published some basic information about its capital Vienna, and the Austrian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Austria and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Austria below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Austria
Did you know about Austria?
Did you know that Austria has the lowest unemployment rate in the European Union? Furthermore, it has one of the highest rates of income equality. To maintain this balance, Austria’s economic policies focus on achieving growth while ensuring workers are paid fairly, and inequality is at a minimum.
After virtually visiting Austria, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Switzerland.
If you liked our Google map and Austria information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.