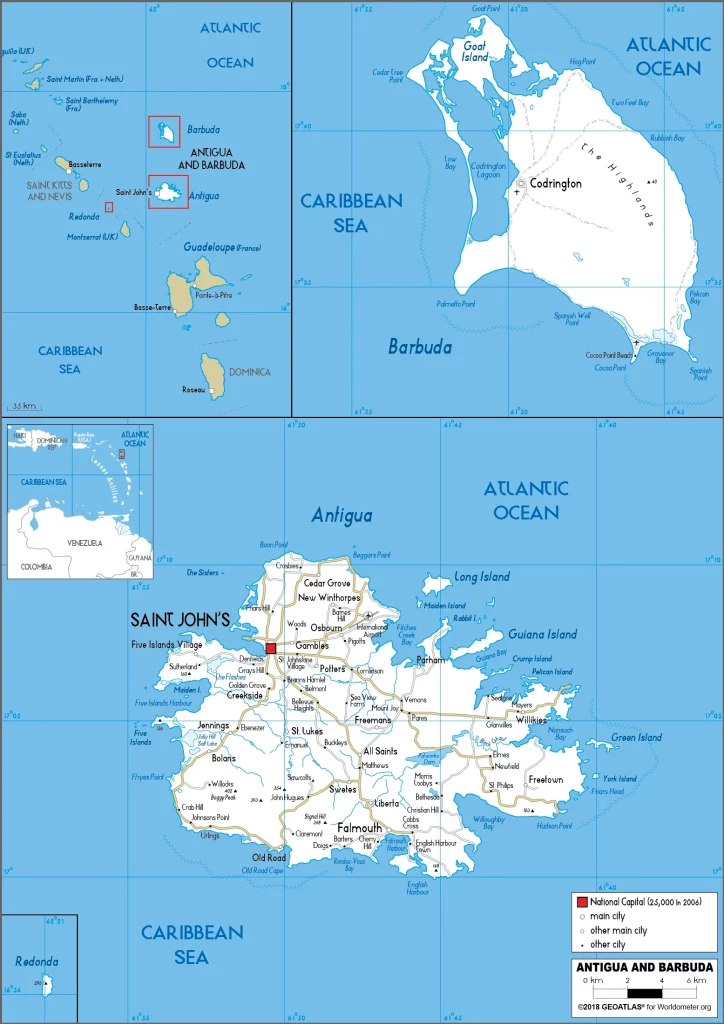
Antigua and Barbuda Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Antigua and Barbuda, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Antigua and Barbuda, Central America, and the Caribbean (35 countries) showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Saint Johns, bordering countries like none, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Antigua and Barbuda, Saint Johns Google maps, Driving Directions Antigua and Barbuda, Printable Road Map.

About Antigua and Barbuda in a nutshell
- In 1865, Redonda was “claimed” by an eccentric Englishman as a kingdom for his son.
- Conventional short form of the name: Antigua and Barbuda
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Etymology: the name Arctic comes from the Greek word arktikos meaning near the bear or northern, and that word derives from arktos, meaning bear; the name refers either to the constellation Ursa Major, the Great Bear, which is prominent in the northern celestial sphere, or to the constellation Ursa Minor, the Little Bear, which contains Polaris, the North (Pole) Star.
- The legal system in Antigua and Barbuda: common law based on the English model.
- Climate: Tropical, moderated by trade winds and sea breezes. Humidity and rainfall are low for the region.
- The national symbols are fallow deer; national colors: red, white, blue, black, yellow.
- Internet TLD: .ag
Background
The Siboney were the first people to inhabit the islands of Antigua and Barbuda in 2400 B.C., but Arawak Indians populated the islands when COLUMBUS landed on his second voyage in 1493. An English colony succeeded early Spanish and French settlements in 1667. Slavery, established to run the sugar plantations in Antigua, was abolished in 1834. The islands became an independent state within the British Commonwealth of Nations in 1981. On 6 September 2017, Hurricane Irma passed over the island of Barbuda, devastating the island and forcing the evacuation of the population to Antigua. Almost all the structures on Barbuda were destroyed, and the vegetation stripped, but Antigua was spared the worst.
Geography
Mainly low-lying limestone and coral islands with some higher volcanic areas. Antiguas coast is indented with bays and harbors.
A former colony of Spain, France, and the U.K., Antigua, and Barbuda lies at the outer edge of the Leeward Islands group in the Caribbean and includes the uninhabited islet of Redonda.
This state is located in the Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico, under the coordinates of 17 03 N, 61 48 W, covering an area of 15.558 million sq km with a coastline of 153 km. Antigua and Barbuda is 2.5 times the size of Washington, DC.
Mainly low-lying limestone and coral islands, with some higher volcanic areas arctic ocean central surface covered by a perennial drifting polar icepack that, on average, is about 3 m thick, although pressure ridges may be three times that thickness, the icepack is surrounded by open seas during the summer, but more than doubles in size during the winter and extends to the encircling landmasses, the ocean floor is about 50% continental shelf (highest percentage of any ocean) with the remainder a central basin interrupted by three submarine ridges (alpha cordillera, nansen cordillera, and lomonosov ridge) major surface currents: two major, slow-moving, wind-driven currents (drift streams) dominate: a clockwise drift pattern in the beaufort gyre in the western part of the arctic ocean and a nearly straight line transpolar drift stream that moves eastward across the ocean from the new siberian islands (russia) to the fram strait (between greenland and svalbard), sea ice that lies close to the center of the gyre can complete a 360 degree circle in about 2 years, while ice on the gyre periphery will complete the same circle in about 7-8 years, sea ice in the transpolar drift crosses the ocean in about 3 years, with Sea level as the highest point of Antigua and Barbuda, while Molloy Deep -5,577 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at N/A throughout the country. With 15.558 million sq km, Antigua and Barbuda has 442.6 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
Antigua has a deeply indented shoreline with many natural harbors and beaches; Barbuda has a sizeable western harbor.
The climate in Antigua and Barbuda is as follows: Tropical maritime, slight seasonal temperature variation.
When you visit Antigua and Barbuda, the natural hazards are hurricanes and tropical storms (July to October); periodic droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Antigua and Barbuda: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Antiguan, Barbudan people: water management – a significant concern because of limited natural freshwater resources – is further hampered by the clearing of trees to increase crop production, causing rainfall to run off quickly.
Google Maps Antigua and Barbuda
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Saint Johns found under the coordinates 17 07 N, 61 51 W, applying the time zone UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
One of the most popular destinations in Antigua, Saint John, is a small village that boasts its own distinct culture. With picturesque views across the Caribbean Sea, it provides an ideal spot to relax by the water’s edge and enjoy everything from snorkeling to whale watching.
Antigua and Barbuda became independent on 1 November 1981 (from the U.K.), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 1 November (1981).
Administrative divisions: 6 parishes and 2 dependencies; Barbuda, Redonda, Saint George, Saint John, Saint Mary, Saint Paul, Saint Peter, Saint Philip.
People and society
The population is almost entirely of African origin, with small Europeans and South Asians. Womens status has risen as a result of greater access to education. Wealth disparities are small. The Bird family dominated politics from 1960 but lost power to the United Progressive Party (UPP) in 2004.
The population in Antigua and Barbuda is 99,175 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.17% (2021 estimate) change. That means Antigua and Barbuda is the No. 196 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 32.7 years median age (30.7 years for males and 30.7 years for women), Antigua and Barbuda ranks No. 106 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Antiguan(s), Barbudan(s) (noun) or Antiguan, Barbudan (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: African descent 87.3%, mixed 4.7%, Hispanic 2.7%, White 1.6%, other 2.7%, unspecified 0.9% (2011 estimate). Note: data represent population by ethnic group.
They speak English (official language), Antiguan creole languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 68.3% (Anglican 17.6%, Seventh Day Adventist 12.4%, Pentecostal 12.2%, Moravian 8.3%, Methodist 5.6%, Wesleyan Holiness 4.5%, Church of God 4.1%, Baptist 3.6%), Roman Catholic 8.2%, other 12.2%, unspecified 5.5%, none 5.9% (2011 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Antigua and Barbuda: The island of Antigua is home to approximately 97% of the population. Nearly the entire population of Barbuda lives in Codrington. In Antigua and Barbuda, we are talking about 24.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 21,000 Saint Johns (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Tourism is the primary source of revenue and the biggest provider of jobs. Financial services and Internet gambling are expanding. High debt.
Tourism dominates Antigua and Barbuda’s economy, accounting for nearly 60% of GDP and 40% investment. The dual-island nation’s agricultural production is focused on the domestic market and constrained by a limited water supply and a labor shortage stemming from the lure of higher wages in tourism and construction. Manufacturing comprises an enclave-type assembly for export with major products being bedding, handicrafts, and electronic components., Like other countries in the region, Antiguas economy was severely hit by the global economic recession in 2009. The country suffered from the collapse of its largest private-sector employer, a steep decline in tourism, a rise in debt, and a sharp economic contraction between 2009 and 2011. Antigua has not yet returned to its pre-crisis growth levels. Barbuda suffered significant damages after hurricanes Irma and Maria passed through the Caribbean in 2017., In the medium term, prospects for economic growth will continue to depend on tourist arrivals from the US, Canada, and Europe. They could be disrupted by potential damage from natural disasters. The new government, elected in 2014 and led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne, faces significant fiscal challenges. The government places some hope in a new Citizenship by Investment Program to reduce public debt levels and spur growth and a resolution of a WTO dispute with the U.S.
Antigua and Barbuda are rich in natural resources: Pleasant climate fosters tourism.
The main industrial sectors are typically tourism, construction, light manufacturing (clothing, alcohol, household appliances).
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in ships, refined petroleum, precious/semi-precious metal scraps, rice, and corn (2019), partnering with Poland 37%, Suriname 33%, and the United Arab Emirates 8% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.15 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Antigua and Barbuda’s position of 175.
Land use in Antigua and Barbuda: 18.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 60.8% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 20.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 2.3% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 9% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1.3 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Antigua and Barbuda are tropical fruit, milk, mangoes/guavas, melons, tomatoes, pineapples, lemons, limes, eggplants, onions.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, ships, cars, precious/semi-precious metals, recreational boats (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 39%, Poland 16%, China 7% (2019) in a sum value of $1.12 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $503.4 million (2016 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Antigua and Barbuda 188.
Antigua and Barbuda Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Antigua and Barbuda, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east-southeast of Puerto Rico. We published basic information about Saint Johns’s capital and the Antiguan, Barbudan nation.
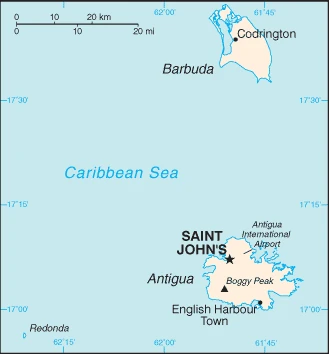
Are you interested in visiting Antigua and Barbuda and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Antigua and Barbuda below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Antigua and Barbuda
Did you know about Antigua and Barbuda?
Antigua and Barbuda are two islands in the Caribbean with some unique historical sites worth visiting. Nelson’s Dockyard National Park on Antigua is an old military base. Barbuda is home to the centuries-old Codrington Plantation House, where visitors can see how enslaved people would have lived.
After virtually visiting Antigua and Barbuda, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Anguilla, Dominica, Guadeloupe, Monserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis.
If you liked our Google map and Antigua and Barbuda information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.