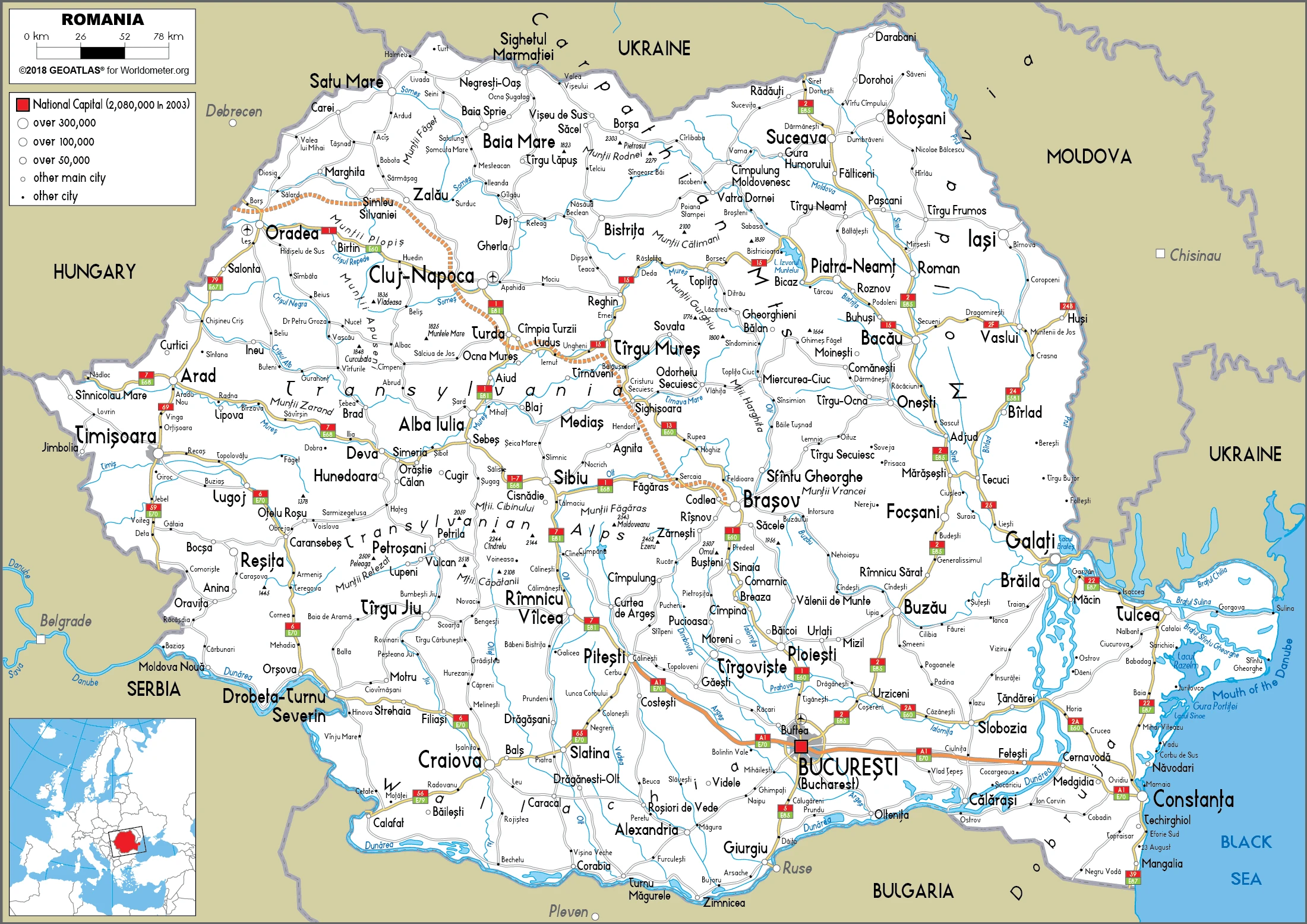
Romania Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Romania, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Romania, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Bucharest, bordering countries like Bulgaria, Hungary, Moldova, Serbia, Ukraine, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Romania, Bucharest Google maps, Driving Directions Romania, Printable Road Map.

About Romania in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Romania
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Local long form: none
- Local short form: Romania
- Former name(s): Kingdom of Romania, Romanian Peoples Republic, Socialist Republic of Romania
- Etymology: the name derives from the Latin Romanus meaning citizen of Rome and was used to stress the common ancient heritage of Romanias three main regions – Moldavia, Transylvania, and Wallachia – during their gradual unification between the mid-19th century and early 20th century.
- The legal system in Romania: civil law system.
- Climate: Continental. Summers are hot and humid, winters are cold and snowy. Very heavy spring rains.
- The national symbols are golden eagle; national colors: blue, yellow, red.
- Internet TLD: .ro
In Romania, which joined the EU on 1 January 2007, 13 national parks and more than half a thousand protected areas are trying to protect the treasures of wildlife. The Danube Delta is a wetland of international importance among the national parks and has been on the World Heritage List since 1991. The protected area of 5,800 km2-e$ is home to 60% of the world’s population of the turtle-peccorant, and the Danube Delta is also home to the enormous contiguous reed bed on the planet.
The ruins of a late Iron Age Dacian fortress in the Southern Carpathians are the oldest World Heritage Sites. The historical center of Sighisoara, built in the 12th century, the fortified church villages of the Transylvanian Saxons, built in the 14th-16th centuries and spread over five counties, are universal treasures of the Transylvanian Basin, the Byzantine-style monastery churches of Moldavia in the 16th century, the Orthodox wooden churches of Maramures and the Byzantine-influenced 17th-century monastery of Horezu in the Havasalföld are among the ecclesiastical monuments. Thanks to the former volcanic activity, Transylvania’s ‘health tourism’ appeal is enhanced by the mineral-rich wine springs of Borszék and Tusnádfürdő, situated in the source areas of the Mures, the Küküllő, and the Olt.
In 2001, Romania became the last country in Europe to lift its ban on homosexuality.
Background
The principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia – for centuries under the suzerainty of the Turkish Ottoman Empire – secured their autonomy in 1856. They were de facto-linked in 1859 and formally united in 1862 under the new name of Romania. The country gained recognition of its independence in 1878. During World War I, it joined the Allied Powers and acquired new territories – most notably Transylvania – following the conflict. In 1940, Romania allied with the Axis powers and participated in the 1941 German invasion of the USSR. Three years later, overrun by the Soviets, Romania signed an armistice. The post-war Soviet occupation led to the formation of a communist people’s republic in 1947 and the king’s abdication. The decades-long rule of dictator Nicolae CEAUSESCU, who took power in 1965, and his Securitate police state became increasingly oppressive and draconian through the 1980s. CEAUSESCU was overthrown and executed in late 1989. Former communists dominated the government until 1996, when they were swept from power. Romania joined NATO in 2004 and the EU in 2007.
Geography
The Carpathian Mountains encircle the Transylvanian plateau. Vast plains to the south and east. Danube River forms the southern border.
Once dominated by Poles, Hungarians, and Ottomans, Romania has been slowly converting to a market economy since the 1989 overthrow of its communist regime. It joined the EU in 2007.
This state is located in Southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Bulgaria and Ukraine, under the coordinates of 46 00 N, 25 00 E, covering an area of 238,391 sq km with a coastline of 225 km. Romania is Twice the size of Pennsylvania, slightly smaller than Oregon.
Romania has 2,844 km of land boundaries in total and borders (5 nations): Bulgaria 605 km, Hungary 424 km, Moldova 683 km, Serbia 531 km, Ukraine 601 km.
Central Transylvanian basin is separated from the Moldavian Plateau on the east by the eastern Carpathian mountains and separated from the Walachian Plain on the south by the Transylvanian Alps, with Moldoveanu 2,544 m as the highest point of Romania, while the Black Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 414 m throughout the country. With a total of 238,391 sq km, Romania has 229,891 sq km of land and 8,500 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: The principal rivers are: the Danube (shared with Germany, Austria, Slovakia, Czechia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine) – 2,888 km. The significant watersheds for Romania are the Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km).
Controls the most easily traversable land route between the Balkans, Moldova, and Ukraine; the Carpathian Mountains dominate the center of the country, while the Danube River forms much of the southern boundary with Serbia and Bulgaria.
The climate in Romania is as follows: Temperate, cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow and fog, sunny summers with frequent showers and thunderstorms.
When you visit Romania, the natural hazards shall be considered: Earthquakes, most severe in the south and southwest; geologic structure and climate promote landslides.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Romania: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Romanian people: soil erosion, degradation, and desertification; water pollution; air pollution in the south from industrial effluents; contamination of Danube delta wetlands.
Google Maps Romania
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Bucharest found under the coordinates 44 26 N, 26 06 E, applying the time zone UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Bucharest is the capital and largest city of Romania and its cultural, industrial, and financial center. The city is situated at the confluence of the rivers Olt and Somes in the western part of Romania. A UNESCO World Heritage Site, Bucharest was listed in 2005 on the World Cultural Heritage list as “the first European Capital of Culture,” with its historical center inscribed in 2003 as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Romania became independent on 9 May 1877 (independence proclaimed from the Ottoman Empire; 13 July 1878 (independence recognized by the Treaty of Berlin); 26 March 1881 (kingdom proclaimed); 30 December 1947 (republic proclaimed), and its national holiday is Unification Day (unification of Romania and Transylvania), 1 December (1918).
Administrative divisions: 41 counties (judete, singular – judet) and 1 municipality (municipiu); Alba, Arad, Arges, Bacau, Bihor, Bistrita-Nasaud, Botosani, Braila, Brasov, Bucuresti (Bucharest), Buzau, Calarasi, Caras-Severin, Cluj, Constanta, Covasna, Dambovita, Dolj, Galati, Gorj, Giurgiu, Harghita, Hunedoara, Ialomita, Iasi, Ilfov, Maramures, Mehedinti, Mures, Neamt, Olt, Prahova, Salaj, Satu Mare, Sibiu, Suceava, Teleorman, Timis, Tulcea, Vaslui, Valcea, Vrancea.
People and society
Romanians are ethnically distinct from their Slav and Hungarian (Magyar) neighbors. Hungarians are the most significant minority, living mainly in Transylvania. They are protected by the influence of Hungary, unlike the Roma, who suffer discrimination. Net emigration (since EU membership) is slowing. Low birth rate.
The population in Romania is 21,230,362 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.38% (2021 estimate) change. That means Romania is the No. 60 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 42.5 years median age (41 years for males and 41 years for women), Romania ranks No. 34 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Romanian(s) (noun) or Romanian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Romanian 83.4%, Hungarian 6.1%, Romani 3.1%, Ukrainian 0.3%, German 0.2%, other 0.7%, unspecified 6.1% (2011 estimate). Note: Romani populations are usually underestimated in official statistics and may represent 511% of Romania’s population.
They speak Romanian (official language) 85.4%, Hungarian 6.3%, Romani 1.2%, other 1%, unspecified 6.1% (2011 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Eastern Orthodox (including all sub-denominations) 81.9%, Protestant (various denominations including Reformed and Pentecostal) 6.4%, Roman Catholic 4.3%, other (includes Muslim) 0.9%, none or atheist 0.2%, unspecified 6.3% (2011 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Romania: Urbanization is not exceptionally high, and a fairly even population distribution can be found throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populations. The country’s most significant minority, Hungarians, have a powerful presence in eastern Transylvania. In Romania, we are talking about 54.3% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.794 million, Bucharest (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Polluting, outdated heavy industry. Unmechanized agricultural sector. Textile and metal exports led to growth in the 2000s. High budget deficits exposed the economy in 20072009 global downturn: IMF bailout, austerity measures. Plans to join euro in 2019. Privatization continues.
Romania, which joined the EU on 1 January 2007, began the transition from communism in 1989 with a largely obsolete industrial base and a pattern of output unsuited to the country’s needs. Romania’s macroeconomic gains have only recently started to spur the creation of a middle class and address Romania’s widespread poverty. Corruption and red tape continue to permeate the business environment., After the global financial crisis, Romania signed a $26 billion emergency assistance package from the IMF, the EU, and other international lenders, but GDP contracted until 2011. In March 2011, Romania and the IMF/EU/World Bank signed a 24-month precautionary standby agreement worth $6.6 billion to promote fiscal discipline, encourage progress on structural reforms, and strengthen financial sector stability; no funds were drawn.
In September 2013, Romanian authorities and the IMF/EU agreed to a follow-on standby agreement worth $5.4 billion to continue reforms. This agreement expired in September 2015, and no funds were drawn. Progress on structural reforms has been uneven, and the economy still is vulnerable to external shocks. Economic growth rebounded in the 2013-2017 period, driven by strong industrial exports, excellent agricultural harvests, and, more recently, expansionary fiscal policies in 2016-2017 that nearly quadrupled Bucharest’s annual fiscal deficit, from +0.8% of GDP in 2015 to -3% of GDP in 2016 and an estimated -3.4% in 2017. Industry outperformed other sectors of the economy in 2017. Exports remained an engine of economic growth, led by trade with the EU, which accounts for roughly 70% of Romania’s trade. Domestic demand was the primary driver due to tax cuts and significant wage increases that began last year and continued in 2018. An aging population, emigration of skilled labor, significant tax evasion, insufficient health care, and an aggressive loosening of the fiscal package compromise Romania’s long-term growth and economic stability and are the economy’s top vulnerabilities.
Romania is rich in the following natural resources: petroleum (reserves declining), timber, natural gas, coal, iron ore, salt, arable land, and hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are electric machinery and equipment, auto assembly, textiles and footwear, light machinery, metallurgy, chemicals, food processing, petroleum refining, mining, timber, and construction materials.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars and vehicle parts, insulated wiring, refined petroleum, electrical control boards, seats (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 22%, Italy 10%, France 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $93.01 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Romania’s position of 41.
Land use in Romania: 28.7% (2018 estimate) forest, 10.6% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 39.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 60.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1.9% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 19.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 31,490 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Romania are maize, wheat, milk, sunflower seed, potatoes, barley, grapes, sugar beet, rapeseed, and plums/sloes.
The country typically needs to import: cars and vehicle parts, crude petroleum, packaged medicines, insulated wiring, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 19%, Italy 9%, Hungary 7%, Poland 6%, China 5%, France 5% (2019) in a sum value of $104.16 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $111.18 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $109.26 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Romania 39.
Romania Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Romania, Southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Bulgaria and Ukraine. We published some basic information about its capital Bucharest, and the Romanian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Romania and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Romania below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Romania
Did you know about Romania?
The principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia – for centuries under the suzerainty of the Turkish Ottoman Empire – secured their autonomy in 1856; they were de facto linked in 1859 and formally united in 1862 under the new name of Romania. The country gained recognition of its independence in 1878. In World War I, it joined the Allied Powers and acquired new territories – most notably Transylvania.
Romania is a beautiful country that is divided into eight regions. These include Wallachia, Moldavia, Transylvania, Dobruja, and Banat. Four of these regions are along the Danube River. The capital city is Bucharest, and it has 1.8 million inhabitants. Romania has many historical sights, including Bran Castle, which is surrounded by a 13th-century wall and was once home to Vlad the Impaler.
The country of Romania is filled with natural beauty and great cultural heritage. The city of Bucharest offers beautiful architecture with impressive sights like the Palace of Parliament and the National Museum of Art. You can also visit historic castles and churches.
After virtually visiting Romania, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Bulgaria, Hungary, Moldova, Serbia, and Ukraine.
If you liked our Google map and Romania information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.