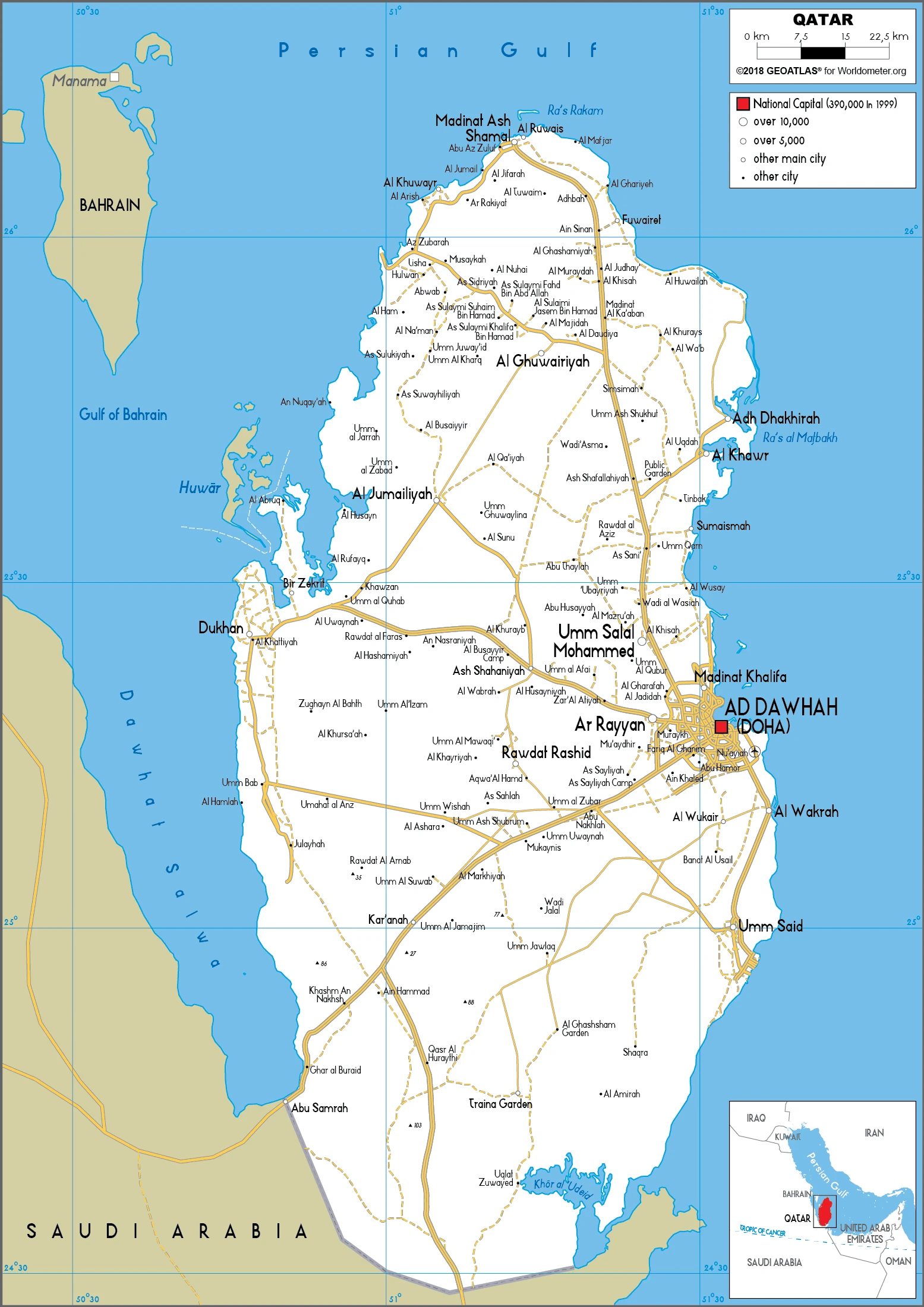
Qatar Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Qatar, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Qatar, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Doha, bordering countries like Saudi Arabia, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Qatar, Doha Google maps, Driving Directions Qatar, Printable Road Map.

About Qatar in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Qatar
- The conventional long form of the name: State of Qatar
- Local long form: Dawlat Qatar
- Local short form: Qatar
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the origin of the name is uncertain, but it dates back at least 2,000 years since the term Catharrei was used to describe the inhabitants of the peninsula by Pliny the Elder (1st century A.D.), and a Catara peninsula is depicted on a map by Ptolemy (2nd century A.D.).
- The legal system in Qatar: mixed legal system of civil law and Islamic (sharia) law (in family and personal matters).
- Climate: Hot and humid. Temperatures in summer can soar to over 104°F (40°C). Rainfall is rare.
- The national symbols are a maroon field surmounted by a white serrated band with nine white points; the national colors: are maroon and white.
- Internet TLD: .qa
Qatar is a country on the Arabian Peninsula. It has a small peninsula on the northeastern coast and shares its only land border with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the gulf of Bahrain separating it from nearby Bahrain. The capital is Doha, where over 80% of Qatar’s population lives. Qatar is a high-income country with the world’s third-highest GDP (PPP) per capita. It has the third-highest HDI in the Arab world. Qatar is an oil and natural gas exporter, and its inhabitants generate the world’s highest carbon dioxide emissions per capita.
Qatar, a hereditary monarchy run by the House of Thani since Mohammed bin Thani signed treaties with Britain in 1868, is one of the wealthiest countries in the world. Qatar was formerly under the Ottoman rule and was separated into a British protectorate until independence on 28 September 1971. Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani has the most authority and is head of state, appoints power to all executive roles, and controls the judiciary. Its constitution partially elects members to the Consultative Assembly. In the 21st century, Qatar emerged as a significant power in the Arab world through its resource wealth and by broadcasting Al Jazeera, one of the largest media groups in the world. Qatar is also planning to host the 2022 FIFA World Cup and the 2030 Asian Games, making it unique among other Arab countries.
There are three times as many men as women in Qatar.
Background
Ruled by the Al Thani family since the mid-1800s, Qatar, within the last 60 years, transformed itself from a poor British protectorate noted mainly for pearling into an independent state with significant oil and natural gas revenues. Former Amir HAMAD bin Khalifa Al Thani, who overthrew his father in a bloodless coup in 1995, ushered in wide-sweeping political and media reforms, unprecedented economic investment, and a growing Qatari regional leadership role, in part through the creation of the pan-Arab satellite news network Al-Jazeera and Qatar’s mediation of some regional conflicts. In the 2000s, Qatar resolved its longstanding border disputes with both Bahrain and Saudi Arabia and, by 2007, had attained the highest per capita income in the world. Qatar did not experience domestic unrest or violence like other Near Eastern and North African countries in 2011 due to its immense wealth and patronage network. In mid-2013, HAMAD peacefully abdicated, transferring power to his son, the current Amir TAMIM bin Hamad.
TAMIM is popular with the Qatari public for his role in shepherding the country through an economic embargo by some other regional countries, for his efforts to improve the country’s healthcare and education systems, and for his expansion of the country’s infrastructure in anticipation of Doha’s hosting of the 2022 World Cup. Recently, Qatar’s relationships with its neighbors have been tense, although, since the fall of 2019, there have been signs of improved prospects for a thaw. Following the outbreak of regional unrest in 2011, Doha prided itself on its support for many popular revolutions, particularly in Libya and Syria. This stance was detrimental to Qatar’s relations with Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), which temporarily recalled their respective ambassadors from Doha in March 2014. TAMIM later oversaw a warming of Qatar’s relations with Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE in November 2014 following Kuwaiti mediation and signing of the Riyadh Agreement. This reconciliation, however, was short-lived. In June 2017, Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE (the Quartet) cut diplomatic and economic ties with Qatar in response to alleged violations of the agreement, among other complaints.
Geography
Flat, semiarid desert with dunes and salt pans. Vegetation is limited to small patches of scrub.
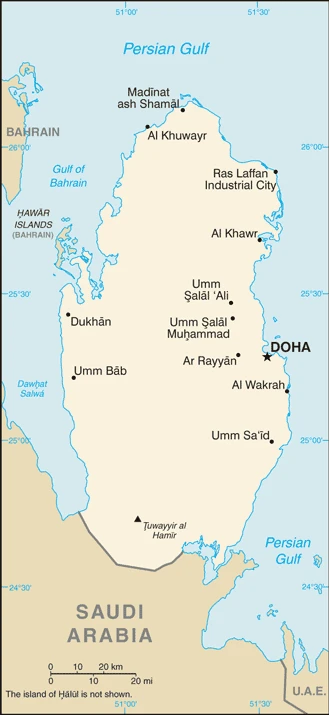
Qatar projects from the Arabian Peninsula into the Persian Gulf. A founding member of OPEC, it is one of the region’s wealthiest states due to oil and natural gas exports.
This state is located in the Middle East, a peninsula bordering the Persian Gulf and Saudi Arabia, under the coordinates of 25 30 N, 51 15 E, covering an area of 11,586 sq km with a coastline of 563 km. Qatar is Almost twice the size of Delaware, slightly smaller than Connecticut.
Qatar has 87 km of land boundaries and borders (1 nation): Saudi Arabia has 87 km.
Mostly flat and barren desert, with Tuwayyir al Hamir 103 m as the highest point of Qatar, while Persian Gulf 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation of 28 m throughout the country. With 11,586 sq km, Qatar has 11,586 sq km of land and 0 sq km of water surface area.
The peninsula is strategically located near significant petroleum deposits in the central Persian Gulf.
The climate in Qatar is as follows: Arid, mild, pleasant winters, very hot, humid summers.
When you visit Qatar, the natural hazards shall be considered: Haze, dust storms, and sandstorms are common.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Qatar: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Qatari people: air, land, and water pollution are significant environmental issues; limited natural freshwater resources are increasing dependence on large-scale desalination facilities; other issues include conservation of oil supplies and preservation of the natural wildlife heritage.
Google Maps Qatar
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Doha found under the coordinates 25 17 N, 51 32 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Doha is the capital of Qatar, a country in the Persian Gulf. It is a vital hub for business, trade, and finance. Its port is one of the most important in the region and plays a crucial role in Qatar’s economy due to its strategic location. In particular, it has been a popular destination for Western businesses looking to establish a foothold within the region. Doha’s main feature is its harbor, built by dredging from the Persian Gulf.
Qatar became independent on 3 September 1971 (from the U.K.), and its national holiday is National Day, 18 December (1878), the anniversary of the Al Thani family’s accession to the throne; Independence Day, 3 September (1971).
Administrative divisions: 8 municipalities (baladiyat, singular – baladiyah); Ad Dawhah, Al Khawr wa adh Dhakhirah, Al Wakrah, Ar Rayyan, Ash Shamal, Ash Shihaniyah, Az Zaayin, Umm Salal.
People and society
Only one in five residents is native-born; the rest are guest workers from across the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and North Africa. Qataris were once nomadic Bedouins, but since the advent of oil wealth, most now live in Doha and its suburbs, leaving the north dotted with abandoned villages. Women enjoy relative freedom; most wear the veil.
The population in Qatar is 2,479,995 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.23% (2021 estimate) change. That means Qatar is the No. 143 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 33.7 years median age (35 years for males and 35 years for women), Qatar ranks No. 96 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Qatari(s) (noun) or Qatari (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: non-Qatari 88.4%, Qatari 11.6% (2015 estimate).
They speak Arabic (official language), English commonly used as a second language languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 65.2%, Christian 13.7%, Hindu 15.9%, Buddhist 3.8%, folk religion <0.1%, Jewish <0.1%, other <1%, unaffiliated <1% (2020 estimate). We can conclude the following about the population in Qatar: Most of the population is clustered in or around the capital of Doha on the eastern side of the peninsula. In Qatar, we are talking about 99.3% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: Ar-Rayyan 750,000, 646,000 Doha (capital city) (2021).
Industry
There is a steady supply of crude oil, substantial natural gas reserves, and related industries. All other raw materials and most foods are imported. Strong GDP growth in 2004-2011. The economy is heavily dependent on a foreign workforce.
Qatar’s oil and natural gas resources are the country’s main economic engine and government revenue source, driving Qatar’s high economic growth and per capita income levels, robust state spending on public entitlements, and booming construction spending, particularly as Qatar prepares to host the World Cup in 2022. Although the Government has maintained high capital spending levels for ongoing infrastructure projects, low oil and natural gas prices have led the Qatari Government to tighten some spending to help stem its budget deficit. Qatar’s reliance on oil and natural gas is likely to persist for the foreseeable future. Proved natural gas reserves exceed 25 trillion cubic meters – 13% of the world total and, among countries, third-largest. Proved oil reserves exceed 25 billion barrels, allowing production to continue at current levels for about 56 years. Despite oil and natural gas dominance, Qatar has made significant gains in strengthening non-oil sectors, such as manufacturing, construction, and financial services, leading non-oil GDP to steadily rise in recent years to just over half the total. Following trade restrictions imposed by Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Bahrain, and Egypt in 2017, Qatar established new trade routes with other countries to maintain access to imports.
Qatar is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, fish, and natural gas.
The main industrial sectors are liquefied natural gas, crude oil production and refining, ammonia, fertilizer, petrochemicals, steel reinforcing bars, cement, and commercial ship repair.
The country’s export sectors are robust in natural gas, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, ethylene polymers, and fertilizers (2019), partnering with these nations: Japan 17%, South Korea 16%, India 14%, China 13%, Singapore 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $70.93 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Qatar’s position of 50.
Land use in Qatar: 0% (2018 estimate) forest, 94.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 1.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 5.6% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.2% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 4.3% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 130 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Qatar are tomatoes, dates, camel milk, sheep milk, goat milk, pumpkins/gourds, mutton, poultry, milk, and eggplants.
The country typically needs to import: aircraft, gas turbines, cars, jewelry, and iron piping (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 15%, France 13%, the United Kingdom 9%, China 9%, Germany 5%, Italy 5% (2019) in a sum value of $59.06 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $66.77 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $65.81 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Qatar 53.
Qatar Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Qatar, the Middle East, the peninsula bordering the Persian Gulf, and Saudi Arabia. We published some basic information about its capital Doha, and the Qatari nation.
Are you interested in visiting Qatar and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Qatar below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Qatar
Did you know about Qatar?
Qatar is a small country located in the Middle East. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain. Qatar has a population of 2.6 million people. The official languages of Qatar are Arabic and English. The currency of Qatar is the Qatari riyal. Qatar is a Muslim country, and Islam is the official religion.
Doha is the capital and largest city of Qatar. It is located on the coast of the Persian Gulf and has a population of over 2.4 million people. Doha is Qatar’s economic and financial center and its principal transportation hub. The city is home to many major businesses, including Qatar Airways, Qatar Petroleum, and the Qatar Stock Exchange. Doha is also a popular tourist destination due to its beautiful beaches, luxury hotels, and vibrant nightlife.
After virtually visiting Qatar, you may also be interested in the neighboring country: Saudi Arabia.
If you liked our Google map and Qatar information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.