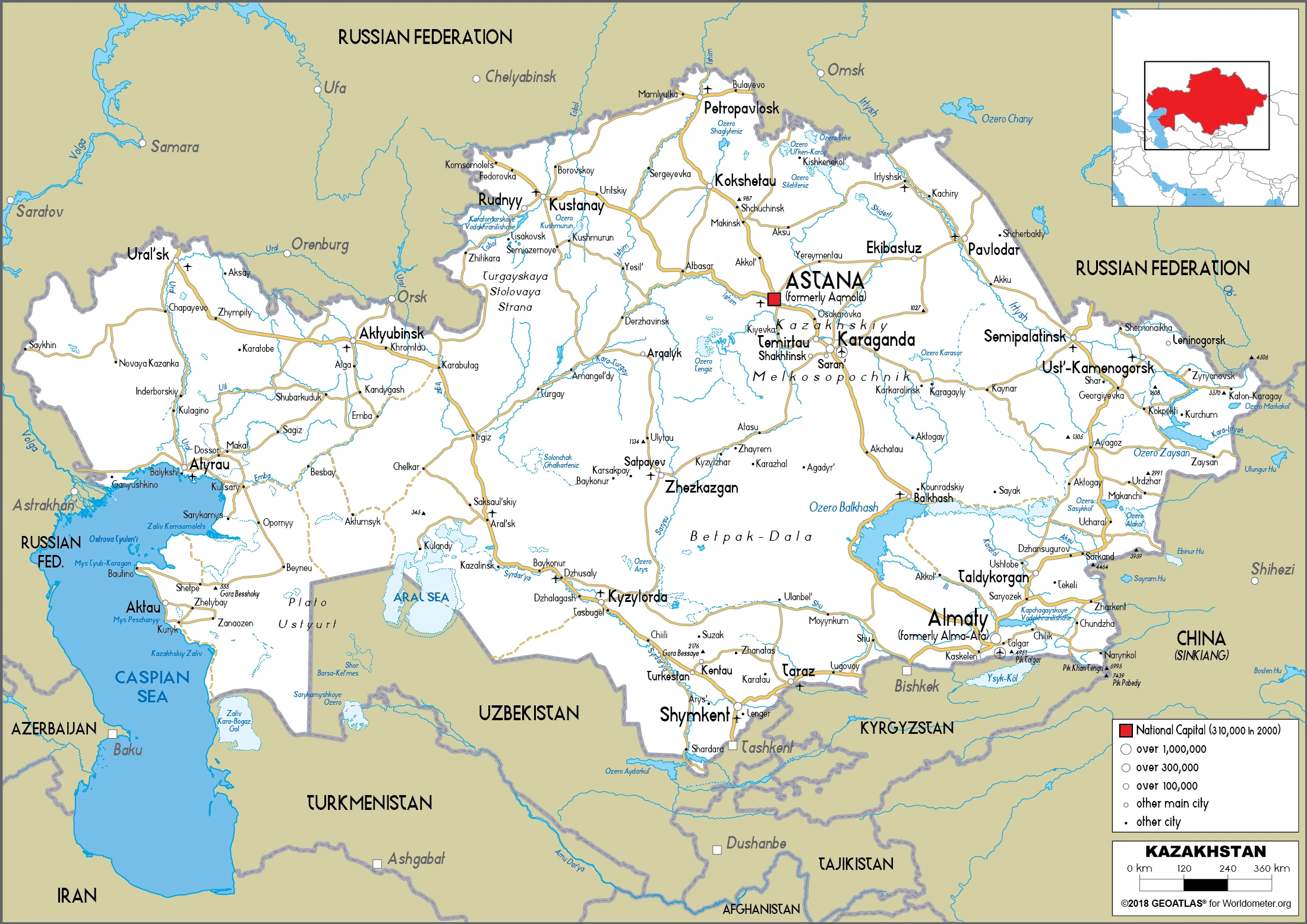
Kazakhstan Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Kazakhstan, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Kazakhstan, Asia (22 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Nur-Sultan, bordering countries like China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Kazakhstan, Nur-Sultan Google maps, Driving Directions Kazakhstan, Printable Road Map.

About Kazakhstan in a nutshell
- The Soviet-built Baykonyr space center is still an important launch site for international missions.
- Conventional short form of the name: Kazakhstan
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Kazakhstan
- Local long form: Qazaqstan Respublikasy
- Local short form: Qazaqstan
- Former name(s): Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
- Etymology: the name Kazakh derives from the Turkic word kaz meaning to wander, recalling the Kazakhs nomadic lifestyle; the Persian suffix -stan means place of or country, so the word Kazakhstan literally means Land of the Wanderers.
- The legal system in Kazakhstan: civil law system influenced by Roman-Germanic law and by the theory and practice of the Russian Federation.
- Climate: Dry continental. Temperature variations between desert south and northern steppes are large. Winters are mildest near the Caspian Sea.
- The national symbols are golden eagle; national colors: blue, yellow.
- Internet TLD: .kz
Kazakhstan’s oldest cultural and historical remains are found in the Tamgaly Gorge in the arid Chu-lli Mountains. Some 5,000 Sikh carvings and fish tombs in the area record the culture of four millennia of pastoral societies from the 2nd millennium BC to the early 20th century. The Khoja Ahmed Jasavi Mausoleum in Jasi (now Turkestan), built between 1389 and 1405 during the Timurid Empire, is one of the most significant and best-preserved architectural monuments of the empire. The Persian masters, who adopted new architectural and structural techniques, later adopted the same method in constructing the empire’s capital, Samarkand. Both sites are universal treasures of humanity.
Background
Ethnic Kazakhs, a mix of Turkic and Mongol nomadic tribes with additional Persian cultural influences, migrated to the region in the 15th century. Russia conquered the area in the 18th and 19th centuries, and Kazakhstan became the Soviet Republic in 1925. Repression and starvation associated with forced agricultural collectivization led to many deaths in the 1930s. During the 1950s and 1960s, the agricultural Virgin Lands program led to many settlers (mostly ethnic Russians and other nationalities). At Kazakhstan’s independence in 1991, ethnic Kazakhs were a minority. Non-Muslim ethnic minorities departed Kazakhstan in large numbers from the mid-1990s through the mid-2000s, and a national program has repatriated about a million ethnic Kazakhs (from Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Mongolia, and the Xinjiang region of China) back to Kazakhstan. As a result of this shift, the ethnic Kazakh share of the population now exceeds two-thirds. Kazakhstan’s economy is the largest in the Central Asian states, mainly due to the country’s vast natural resources. Current issues include: diversifying the economy, obtaining membership in global and regional international economic institutions, enhancing Kazakhstan’s economic competitiveness, and strengthening relations with neighboring states and foreign powers.
Geography
Mainly steppe. Volga Delta and the Caspian Sea in the west. Central plateau. The inhospitable Altai Mountains in the east. Semidesert in the south.
Kazakhstan was the last of the former Soviet republics to declare independence. Foreign investment in the oil and natural gas sector strengthens its regional power.
This state is located in Central Asia, northwest of China. A small portion west of the Ural (Oral) River in easternmost Europe, under the coordinates of 48 00 N, 68 00 E, covering an area of 2,724,900 sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). Kazakhstan is Slightly less than four times the size of Texas.
Kazakhstan has 13,364 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (5 nations): China 1765 km, Kyrgyzstan 1212 km, Russia 7644 km, Turkmenistan 413 km, Uzbekistan 2330 km.
Vast flat steppe extending from the Volga in the west to the Altai mountains in the east and from the plains of western Siberia in the north to oases and deserts of Central Asia in the south, with Pik Khan-Tengri 6,995 m as the highest point of Kazakhstan, while Qauyndy Oyysy -132 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 387 m throughout the country. With 2,724,900 sq km, Kazakhstan has 2,699,700 sq km of land and 25,200 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Ozero Balkhash – 22,000 sq km; Ozero Zaysan – 1,800 sq km (freshwater lake), Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Russia) – 374,000 sq km; Aral Sea (north) – 3,300 sq km; Ozero Alakol – 2,650 sq km; Ozero Teniz 1,590 sq km; Ozero Seletytenzi – 780 sq km; Ozero Sasykkol – 740 sq km (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Syr Darya (shared with Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan) – 3,078 km. The significant watersheds for Kazakhstan are Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Tarim Basin (1,152,448 sq km), Amu Darya (534,739 sq km), Syr Darya (782,617 sq km), Lake Balkhash (510,015 sq km).
The world’s largest landlocked country and one of only two countries that extends into two continents (Azerbaijan), Russia leased approximately 6,000 sq km of territory enclosing the Baikonur Cosmodrome; in January 2004, Kazakhstan and Russia extended the lease to 2050.
The climate in Kazakhstan is as follows: Continental, cold winters and hot summers, arid and semiarid.
When you visit Kazakhstan, the natural hazards shall be considered: Earthquakes in the south; mudslides around Almaty.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Kazakhstan: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Kazakhstani people: radioactive or toxic chemical sites associated with former defense industries and test ranges scattered throughout the country pose health risks for humans and animals; industrial pollution is severe in some cities; because the two main rivers that flowed into the Aral Sea have been diverted for irrigation, it is drying up and leaving behind a harmful layer of chemical pesticides and natural salts; these substances are then picked up by the wind and blown into noxious dust storms; pollution in the Caspian Sea; desertification; soil pollution from overuse of agricultural chemicals and salination from poor infrastructure and wasteful irrigation practices.
Google Maps Kazakhstan
The capital and other divisions
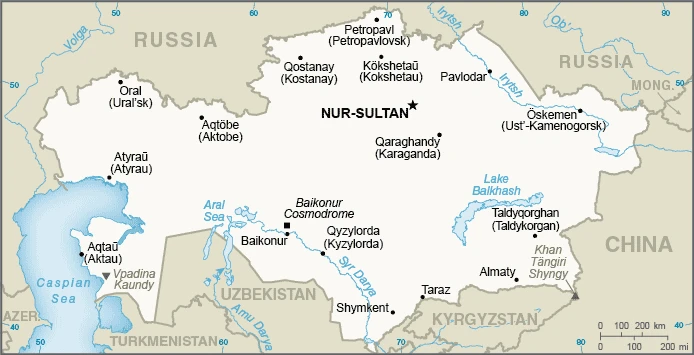
Capital city: Nur-Sultan found under the coordinates 51 10 N, 71 25 E, applying the time zone UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital of the Kazakhstani country, Nur-Sultan, is a city with a painful past. It’s been a battleground where Russians and Kazakhs have battled for centuries. Kazakhstan is a country with many different sights and aspects of Kazakh culture worth exploring.
Kazakhstan became independent on 16 December 1991 (from the Soviet Union), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 16 December (1991).
Administrative divisions: 14 provinces (oblyslar, singular – oblys) and 4 cities (qalalar, singular – qala); Almaty (Taldyqorghan), Almaty, Aqmola (Kokshetau), Aqtobe, Atyrau, Batys Qazaqstan West Kazakhstan (Oral), Bayqongyr, Mangghystau (Aqtau), Nur-Sultan, Pavlodar, Qaraghandy, Qostanay, Qyzylorda, Shyghys Qazaqstan East Kazakhstan (Oskemen), Shymkent, Soltustik Qazaqstan North Kazakhstan (Petropavl), Turkistan, Zhambyl (Taraz) note: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses); in 1995, the government’s of Kazakhstan and Russia entered into an agreement whereby Russia would lease for a period of 20 years an area of 6,000 sq km enclosing the Baikonur space launch facilities and the city of Bayqongyr (Baikonur, formerly Leninsk); in 2004, a new agreement extended the lease to 2050.
People and society
Kazakhstans ethnic diversity arose mainly from forced settlements there during Soviet times. Since independence, the proportion of ethnic Russians has dropped. Many emigrated, while ethnic Kazakhs arrived from neighboring states. Very few Kazakhs maintain a traditional nomadic lifestyle, but Islam and loyalty to clans remain strong. There are significant disparities in wealth.
The population in Kazakhstan is 19,245,793 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.81% (2021 estimate) change. That means Kazakhstan is the No. 64 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 31.6 years median age (30.3 years for males and 30.3 years for women), Kazakhstan ranks No. 114 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Kazakhstani(s) (noun) or Kazakhstani (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Kazakh (Qazaq) 68%, Russian 19.3%, Uzbek 3.2%, Ukrainian 1.5%, Uighur 1.5%, Tatar 1.1%, German 1%, other 4.4% (2019 estimate).
They speak Kazakh (official language, Qazaq) 83.1% (understand spoken language) and trilingual (Kazakh, Russian, English) 22.3% (2017 estimate); Russian (official language, used in everyday business, designated the language of interethnic communication) 94.4% (understand spoken language) (2009 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 70.2%, Christian 26.2% (mainly Russian Orthodox), other 0.2%, atheist 2.8%, unspecified 0.5% (2009 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Kazakhstan: Most of the country displays a low population density, particularly the interior. Population clusters appear in urban agglomerations in the country’s far northern and southern portions. In Kazakhstan, we are talking about 57.8% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.928 million, Almaty, 1.212 million, Nur-Sultan (capital city), 1.093 million, Shimkent (2021).
Industry
Vast mineral resources: natural gas, oil, bismuth, uranium, and cadmium. Oil pipelines to China and the Black Sea. Many Western investors. Wheat exported. The sale of farmland has been legal only since 2003.
Kazakhstan’s vast hydrocarbon and mineral reserves form the backbone of its economy. Geographically the largest of the former Soviet republics, excluding Russia Kazakhstan, g possesses substantial fossil fuel reserves and other minerals and metals, such as uranium, copper, and zinc. It also has a large agricultural sector featuring livestock and grain. The government realizes that its economy suffers from an overreliance on oil and extractive industries and has made initial attempts to diversify its economy by targeting sectors like transport, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications, petrochemicals, and food processing for more significant development and investment. It also adopted a Subsoil Code in December 2017 intending to increase exploration and investment in the hydrocarbon, and particularly mining, sectors., Kazakhstan’s oil production and potential are expanding rapidly. A $36.8 billion expansion of Kazakhstan’s premiere Tengiz oil field by Chevron-led Tengizchevroil should be complete in 2022. Meanwhile, the super-giant Kashagan field finally launched production in October 2016 after years of delay and an estimated $55 billion in development costs.
Kazakhstan’s total oil production in 2017 climbed 10.5%., Kazakhstan is landlocked and depends on Russia to export its oil to Europe. It also exports oil directly to China. In 2010, Kazakhstan joined Russia and Belarus to establish a Customs Union to boost foreign investment and improve trade. The Customs Union evolved into a Single Economic Space in 2012 and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) in January 2015. Supported by rising commodity prices, Kazakhstan’s exports to EAEU countries increased 30.2% in 2017. Imports from EAEU countries grew by 24.1%. The economic downturn of its EAEU partner, Russia, and the decline in global commodity prices from 2014 to 2016 contributed to an economic slowdown in Kazakhstan. In 2014, Kazakhstan devalued its currency, the tenge, and announced a stimulus package to cope with its economic challenges. In the face of further decline in the ruble, oil prices, and the regional economy, Kazakhstan announced in 2015 it would replace its currency band with a floating exchange rate, leading to a sharp fall in the tenge’s value.
Since reaching a low of 391 to the dollar in January 2016, the tenge has modestly appreciated, helped by somewhat higher oil prices. While growth slowed to about 1% in 2015 and 2016, a moderate recovery in oil prices, relatively stable inflation and foreign exchange rates, and the start of production at Kashagan helped push 2017 GDP growth to 4%. Despite some positive institutional and legislative changes in the last several years, investors remain concerned about corruption, bureaucracy, and arbitrary law enforcement, especially at the regional and municipal levels. An additional concern is the condition of the country’s banking sector, which suffers from poor asset quality and a lack of transparency. Investors also question the potentially harmful effects on the economy of a contested presidential succession as Kazakhstan’s first president, Nursultan NAZARBAYEV, turned 77 in 2017.
Kazakhstan is rich in the following natural resources: Major petroleum deposits, natural gas, coal, iron ore, manganese, chrome ore, nickel, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, lead, zinc, bauxite, gold, uranium.
The main industrial sectors are oil, coal, iron ore, manganese, chromite, lead, zinc, copper, titanium, bauxite, gold, silver, phosphates, sulfur, uranium, iron, and steel; tractors and other agricultural machinery, electric motors, construction materials.
The country’s export sectors are robust in crude petroleum, natural gas, copper, iron alloys, radioactive chemicals (2019), partnering with these nations: China 13%, Italy 12%, Russia 10%, Netherlands 7%, France 6%, South Korea 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $51.75 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Kazakhstan’s position of 55.
Land use in Kazakhstan: 1.2% (2018 estimate) forest, 21.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 8.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 77.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 68.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 20,660 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Kazakhstan are wheat, milk, potatoes, barley, watermelons, melons, linseed, onions, maize, sunflower seed.
The country typically needs to import: packaged medicines, natural gas, cars, broadcasting equipment, aircraft (2019), partnering with the following nations: Russia 34%, China 24% (2019) in a sum value of $44.3 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $51.5 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $46.23 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Kazakhstan 64.
Kazakhstan Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Kazakhstan, Central Asia, northwest of China. There is a small portion west of the Ural (Oral) River in easternmost Europe. We published some basic information about its capital Nur-Sultan, and the Kazakhstani nation.
Are you interested in visiting Kazakhstan and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Kazakhstan below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Kazakhstan
Did you know about Kazakhstan?
Kazakhstan is the ninth largest country in the world by area. Kazakhstan has diverse geography ranging from forests to deserts. The country has an arid climate, and its economy relies on uranium mining and oil production. It borders other countries like Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, China, and Russia.
After virtually visiting Kazakhstan, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
If you liked our Google map and Kazakhstan information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.