Fiji Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Fiji, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Fiji, Oceania (27 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Suva (on Viti Levu), bordering countries like none, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Oceanian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Fiji, Suva (on Viti Levu) Google maps, Driving Directions Fiji, Printable Road Map.

About Fiji in a nutshell
- Both Fijians and Indians practice fire-walking; Indians walk on hot embers, Fijians on heated stones.
- Conventional short form of the name: Fiji
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Fiji
- Local long form: Republic of Fiji / Matanitu ko Viti
- Local short form: Fiji / Viti
- Etymology: the Fijians called their home Viti, but the neighboring Tongans called it Fisi, and in the Anglicized spelling of the Tongan pronunciation – promulgated by explorer Captain James COOK – the designation became Fiji.
- The legal system in Fiji: common law system based on the English model.
- Climate: Tropical. High temperatures all year round. Cyclones are a hazard.
- The national symbols are Fijian canoe; national color: light blue.
- Internet TLD: .fj
Background
Austronesians settled Fiji around 1000 B.C., followed by successive waves of Melanesians starting around the first century A.D. Fijians traded with Polynesian groups in Samoa and Tonga. By about 900, much of Fiji was in the Tui Tongan Empires’ sphere of influence. The Tongan influence declined significantly by 1200 while Melanesian seafarers periodically arrived in Fiji, further mixing Melanesian and Polynesian cultural traditions. Dutch explorer Abel TASMAN was the first European to spot Fiji in 1643, followed by British explorer James COOK in 1774. Captain William BLIGH plotted the islands in 1789. In the 1800s, merchants, traders, and whalers frequented the islands, and the first missionaries arrived in 1835. Rival kings and chiefs competed for power, aided by Europeans and their weapons, and in 1865, Seru Epenisa CAKOBAU united many groups into the Confederacy of Independent Kingdoms of Viti. The arrangement proved weak, and a subsequent attempt in 1871 to centralize power as the Kingdom of Fiji also faltered. Fearing a hostile takeover by a foreign power, CAKOBAU ceded Fiji to the U.K. in 1874.
The first British governor set up a plantation-style economy and brought in more than 60,000 Indians as indentured laborers. Most of them chose to stay in Fiji rather than return to India when their contracts expired. In the early 1900s, society was divided along ethnic lines, with iTaukei (indigenous Fijians), Europeans, and Indo-Fijians living in separate areas and maintaining their languages and traditions. ITaukei fears of an Indo-Fijian takeover of government delayed independence through the 1960s. Fiji achieved independence in 1970 with agreements in place to allocate parliamentary seats by ethnic groups. Long-serving Prime Minister Kamisese MARA essentially balanced these ethnic divisions, but concerns about growing Indo-Fijian political influence led to two coups in 1987. A new constitution in 1990 cemented iTaukei’s control of politics, leading thousands of Indo-Fijians to leave.
A reformed constitution in 1997 was more equitable and led to the election of an Indo-Fijian prime minister in 1999, who was ousted in a coup the following year. In 2005, the new prime minister put forward a bill that would grant pardons to the coup perpetrators, leading Commodore Josaia BAINIMARAMA to launch a coup in 2006. BAINIMARAMA appointed himself prime minister in 2007 and continues to hold the position after 2014 and 2018 that international observers deemed credible. With a well-developed infrastructure, Fiji has become a hub for the Pacific, hosting the secretariat for the Pacific Islands Forum and the main campus of the University of the South Pacific. In addition, Fiji is a center for Pacific tourism, and Nadi International Airport is the busiest airport in a pacific island country.
Geography
Main islands are mountainous, fringed by coral reefs. The remaining is limestone and coral formations.
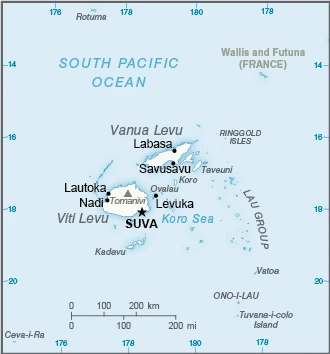
A volcanic archipelago in the South Pacific, with two large islands and 880 islets. Tensions between native Fijians and the Indian minority have sparked a succession of coups.
This state is located in Oceania, an island group in the South Pacific Ocean, about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand, under the coordinates of 18 00 S, 175 00 E, covering an area of 18,274 sq km with a coastline of 1,129 km. Fiji is Slightly smaller than New Jersey.
Primarily mountains of volcanic origin, with Tomanivi 1,324 m as the highest point of Fiji, while Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at N/A throughout the country. With a total of 18,274 sq km, Fiji has 18,274 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
Consists of 332 islands, approximately 110 of which are inhabited, and more than 500 islets.
The climate in Fiji is as follows: Tropical marine, only slight seasonal temperature variation.
When you visit Fiji, the natural hazards shall be considered: Cyclonic storms can occur from November to January.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Fiji: degree of risk: high (2020), bacterial diarrhea, malaria.
Current environmental issues affecting the Fijian people: the widespread practice of waste incineration is a significant contributor to air pollution in the country, as are vehicle emissions in urban areas; deforestation and soil erosion are significant problems; a contributory factor to erosion is the clearing of land by bush burning, a widespread practice that threatens biodiversity.
Google Maps Fiji
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Suva (on Viti Levu) found under the coordinates 18 08 S, 178 25 E, applying the time zone UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in November; ends second Sunday in January.
Suva is the capital and largest city in Fiji, located on the island of Viti Levu. Suva is the primary port for Fiji’s international trade and one of the Pacific region’s most important and prominent cities.
Fiji became independent on 10 October 1970 (from the U.K.), and its national holiday is Fiji (Independence) Day, 10 October (1970).
Administrative divisions: 14 provinces and 1 dependency; Ba, Bua, Cakaudrove, Kadavu, Lau, Lomaiviti, Macuata, Nadroga and Navosa, Naitasiri, Namosi, Ra, Rewa, Rotuma, Serua, Tailevu.
People and society
The British introduced workers from India in the late 19th century, and by 1946 their descendants outnumbered the ethnic Fijians. Ethnic-Fijian nationalism is strong. Many Indo-Fijians left after the 1987 coup, restoring ethnic Fijians to a majority. The first Indo-Fijian-dominated government was ousted in 2000. The army led another coup in 2006: elections were held in 2014. Women are lobbying for more rights.
The population in Fiji is 939,535 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.46% (2021 estimate) change. That means Fiji is the No. 161 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 29.9 years median age (29.7 years for males and 29.7 years for women), Fiji ranks No. 125 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Fijian(s) (noun) or Fijian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: iTaukei 56.8% (predominantly Melanesian with a Polynesian admixture), Indo-Fijian 37.5%, Rotuman 1.2%, other 4.5% (European, part European, other Pacific Islanders, Chinese) (2007 estimate). Note: a 2010 law replaces Fijian with iTaukei when referring to Fiji’s original and native settlers.
They speak English (official language), iTaukei (official language), Fiji Hindi (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 45% (Methodist 34.6%, Assembly of God 5.7%, Seventh Day Adventist 3.9%, and Anglican 0.8%), Hindu 27.9%, other Christian 10.4%, Roman Catholic 9.1%, Muslim 6.3%, Sikh 0.3%, other 0.3%, none 0.8% (2007 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Fiji: Approximately 70% of the population lives on the island of Viti Levu. Roughly half of the population lives in urban areas. In Fiji, we are talking about 57.7% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 178,000 Suva (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Tourism was the leading sector, though damaged by instability. Coups have also caused international isolation. All sectors are struggling: sugar production, gold mining, textiles, timber, and commercial fishing.
Fiji, endowed with forest, mineral, and fish resources, is one of the most developed and connected of the Pacific island economies. Earnings from the tourism industry, with an estimated 842,884 tourists visiting in 2017, and remittances from Fijians working abroad are the country’s largest foreign exchange-earners. Bottled water exports to the U.S. are Fijis’ largest domestic export. Fijis sugar sector remains a significant industry and a major export, but crops and one of the sugar mills suffered damage during Cyclone Winston in 2016. Fijis trade imbalance continues to widen with increased imports and sluggish performance of domestic exports. The return to parliamentary democracy and successful elections in September 2014 improved investor confidence. Still, increasing bureaucratic regulation, new taxes, and lack of consultation with relevant stakeholders brought four consecutive years of decline for Fiji on the World Bank Ease of Doing Business index. Private sector investment in 2017 approached 20% of GDP, compared to 13% in 2013.
Fiji is rich in the following natural resources: Timber, fish, gold, copper, offshore oil potential, hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are typically tourism, sugar processing, clothing, copra, gold, silver, lumber.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in the water, refined petroleum, fish, raw sugar, gold (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 29%, Australia 14%, New Zealand 7%, Japan 6%, Tonga 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.23 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Fiji’s position of 171.
Land use in Fiji: 55.7% (2018 estimate) forest, 21% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 23.3% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 4.7% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 9.6% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 40 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Fiji are sugar cane, cassava, taro, poultry, vegetables, coconuts, eggs, milk, ginger, sweet potatoes.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, aircraft, cars, wheat, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: Singapore 18%, Australia 13%, China 13.8%, New Zealand 11%, France 11%, South Korea 8% (2017) in a sum value of $1.97 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $3.21 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $3.1 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Fiji 175.
Fiji Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Fiji, Oceania, island group in the South Pacific Ocean, about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand. We published some basic information about its capital Suva (on Viti Levu), and the Fijian nation.
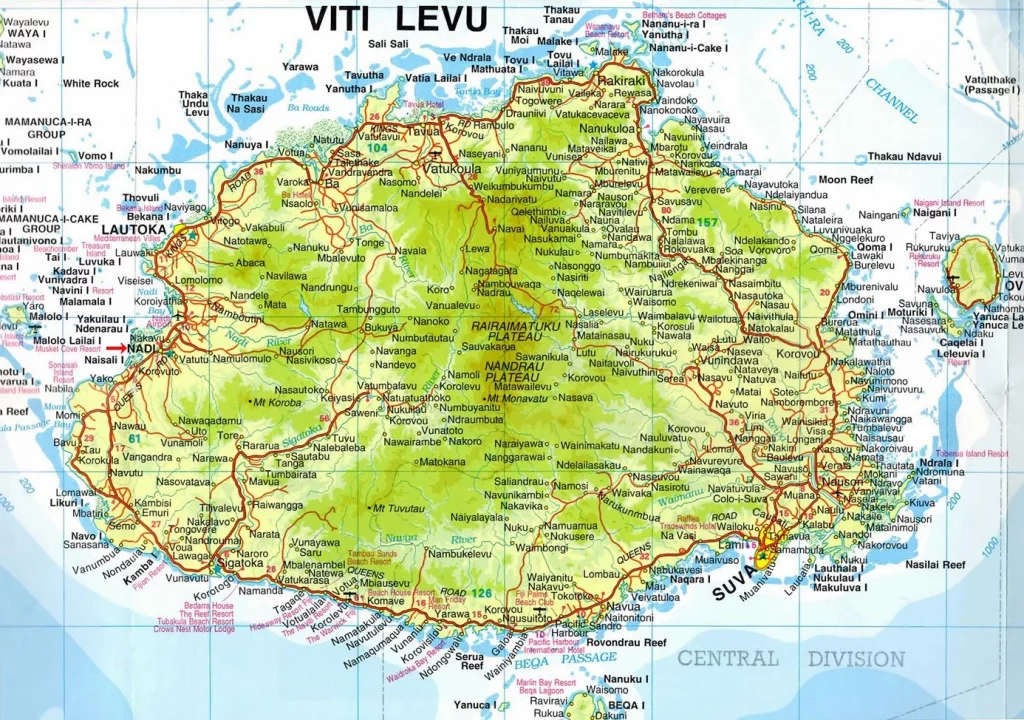
Are you interested in visiting Fiji and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Fiji below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Fiji
Did you know about Fiji?
Did you know about the Federated States of Fiji? It is a country in the Pacific Ocean known for its pristine water, spouting volcanoes, and lush rainforests. The country’s culture is a fusion of indigenous Fijian customs with modern influences from other cultures.
After visiting Fiji, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and Fiji information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.