Bahrain Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Bahrain, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Bahrain, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Manama, bordering countries like none, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Bahrain, Manama Google maps, Driving Directions Bahrain, Printable Road Map.

About Bahrain in a nutshell
- The 16 Hawar Islands were awarded to Bahrain in 2001 after a lengthy dispute with Qatar.
- Conventional short form of the name: Bahrain
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Bahrain
- Local long form: Mamlakat al Bahrayn
- Local short form: Al Bahrayn
- Former name(s): Dilmun, Tylos, Awal, Mishmahig, Bahrayn, State of Bahrain
- Etymology: the name means the two seas in Arabic and refers to the water bodies surrounding the archipelago.
- The legal system in Bahrain: mixed legal system of Islamic (sharia) law, English common law, Egyptian civil, criminal, and commercial codes; customary law.
- Climate: Summers are hot and humid. Winters are mild. Low rainfall. The key social division is between
- The national symbols are a red field surmounted by a white serrated band with five white points; national colors: red, white.
- Internet TLD: .bh
Background
In 1783, the Sunni Al-Khalifa family took power in Bahrain. It entered into a series of treaties with the UK during the 19th century, making Bahrain a British protectorate to secure these holdings. The archipelago attained its independence in 1971. A steady decline in oil production and reserves since 1970 prompted Bahrain to diversify its economy in developing petroleum processing and refining, aluminum production, and hospitality and retail sectors. It has also become a leading regional banking center, especially Islamic finance. Bahrain’s small size, central location among Gulf countries, economic dependence on Saudi Arabia, and proximity to Iran require it to play a delicate balancing act in foreign affairs among its larger neighbors. Its foreign policy activities usually fall in line with Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
The Sunni royal family has long struggled to manage relations with its large Shia-majority population. In early 2011, amid Arab uprisings elsewhere in the region, the Bahraini Government confronted similar pro-democracy and reform protests at home with police and military action, including deploying Gulf Cooperation Council security forces to Bahrain. Failed political talks prompted opposition political societies to boycott 2014 legislative and municipal council elections.
In 2018, a law preventing members of political societies dissolved by the courts from participating in elections effectively sidelined the majority of opposition figures from taking part in national elections. As a result, most members of parliament are independents. Ongoing dissatisfaction with the political status quo continues to factor into sporadic clashes between demonstrators and security forces. On 15 September 2020, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates signed peace agreements (the Abraham Accords) with Israel brokered by the US in Washington DC. Bahrain and the UAE thus became the third and fourth Middle Eastern countries, along with Egypt and Jordan, to recognize Israel.
Geography
All islands are low-lying. The largest, Bahrain Island, is mainly sandy plains and salt marshes.
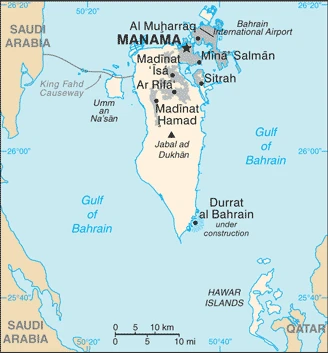
Bahrain is an archipelago of 49 islands between the Qatar peninsula and the Saudi Arabian mainland. Only three of the islands are inhabited. It was the first Gulf emirate to export oil.
This state is located in the Middle East, an archipelago in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia, under the coordinates of 26 00 N, 50 33 E, covering an area of 760 sq km with a coastline of 161 km. Bahrain is 3.5 times the size of Washington, DC.
Mostly low desert plain rising gently to the low central escarpment, with Jabal ad dukhan 135 m as the highest point of Bahrain, while Persian Gulf 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 61 meters throughout the country. With a total of 760 sq km, Bahrain has 760 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
Close to primary Middle Eastern petroleum sources; strategic location in the Persian Gulf, through which much of the Western world’s petroleum must transit to reach the open ocean.
The climate in Bahrain is as follows: Arid, mild, pleasant winters, sweltering, humid summers.
When you visit Bahrain, the natural hazards shall be considered: Periodic droughts; dust storms.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Bahrain: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Bahraini people: desertification resulting from the degradation of limited arable land, periods of drought, and dust storms; coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, and distribution stations; lack of freshwater resources (groundwater and seawater are the only sources for all water needs); lowered water table leaves aquifers vulnerable to saline contamination; desalinization provides some 90% of the country’s freshwater.
Google Maps Bahrain
The capital and other divisions
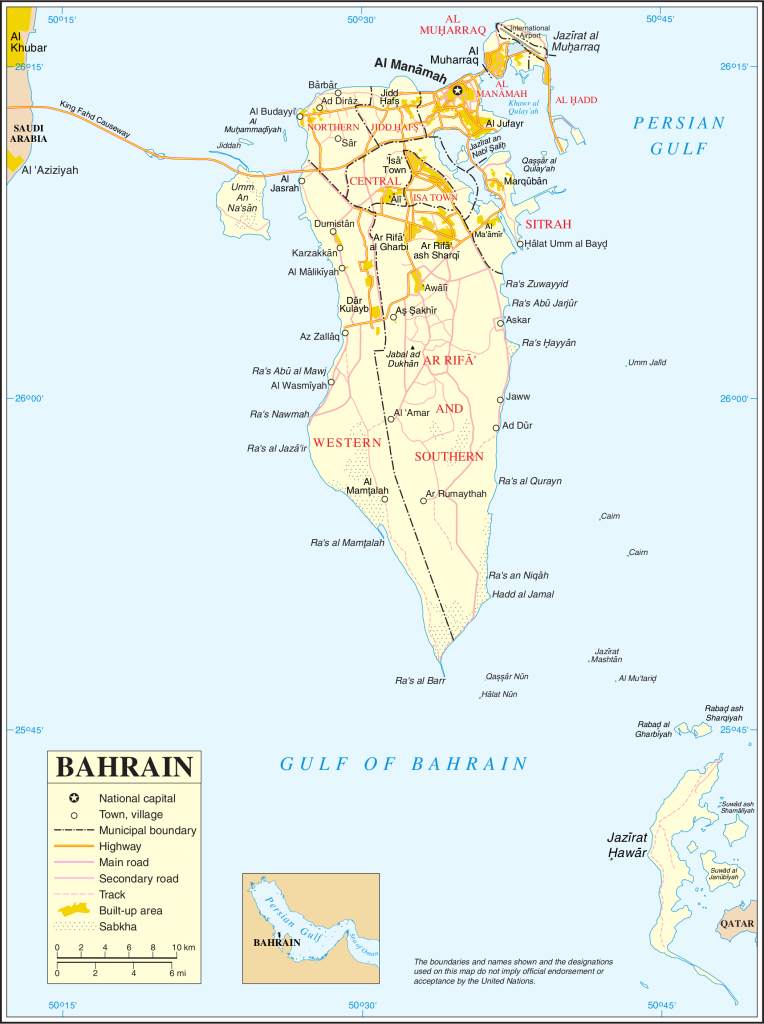
Capital city: Manama found under the coordinates 26 14 N, 50 34 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Manama is an Arabic word that means “hope”. This week, the nation of Bahrain will be hosting the annual Manama Dialogue: A Forum to discuss global issues. The forum is organized by the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and hosted by its Ministry of Foreign Affairs in collaboration with the Ministry of Interior.
Bahrain became independent on 15 August 1971 (from the UK), and its national holiday is National Day, 16 December (1971).
Administrative divisions: 4 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah); Asimah (Capital), Janubiyah (Southern), Muharraq, Shamaliyah (Northern) note: each governorate administered by an appointed governor.
People and society
The critical social division is between the Shiand Sunni minority. Sunnis hold the best jobs in bureaucracy and business. Bahrain is socially liberal. The al-Khalifa family has ruled since 1783 but transformed Bahrain into a constitutional monarchy in 2002. Protests calling for greater democracy rocked the country since the 2011 “Arab Spring”.
The population in Bahrain is 1,526,929 (July 2021 estimate). Note: immigrants make up approximately 45% of the total population, according to UN data (2019), with an average of 0.9% (2021 estimate) change. That means Bahrain is the No. 154 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 32.9 years median age (34.4 years for males and 34.4 years for women), Bahrain ranks No. 102 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Bahraini(s) (noun) or Bahraini (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Bahraini 46%, Asian 45.5%, other Arab 4.7%, African 1.6%, European 1%, other 1.2% (includes Gulf Co-operative country nationals, North and South Americans, and Oceanians) (2010 estimate).
They speak Arabic (official language), English, Farsi, Urdu languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 73.7%, Christian 9.3%, Jewish 0.1%, other 16.9% (2017 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Bahrain: Smallest population of the gulf states, but urbanization rate exceeds 90%. The largest settlement concentration is found on the far northern end of the island in and around Manamah and al Muharram. In Bahrain, we are talking about 89.6% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 664,000 Manama (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Main exports are refined petroleum and aluminum products. As oil reserves run out, natural gas is of increasing importance. The global banking crisis hit the Major Middle East offshore banking center in 2008-2009.
Oil and natural gas play a dominant role in Bahrain’s economy. Despite the Government’s past efforts to diversify the economy, oil still comprises 85% of Bahraini budget revenues. Lower world energy prices have generated sizable budget deficits in the last few years – about 10% of GDP in 2017 alone. Bahrain has few options for covering these deficits, with low foreign assets and fewer oil resources than its GCC neighbors. The three major US credit agencies downgraded Bahrain’s sovereign debt rating to junk status in 2016, citing persistently low oil prices and the Government’s high debt levels.
Nevertheless, Bahrain raised about $4 billion by issuing foreign currency-denominated debt in 2017. Another significant economic activity is aluminum production – Bahrain’s second-biggest export after oil and gas finance and construction. Bahrain seeks new natural gas supplies as feedstock to support its expanding petrochemical and aluminum industries. In April 2018, Bahrain announced it had found a significant oil field off the country’s west coast, but is still assessing how much of the oil can be extracted profitably., In addition to addressing its current fiscal woes, Bahraini authorities face the long-term challenge of boosting Bahrain’s regional competitiveness , especially regarding the industry, finance, and tourism , and reconciling revenue constraints with popular pressure to maintain generous state subsidies and a large public sector.
Since 2015, the Government lifted subsidies on meat, diesel, kerosene, and gasoline and has begun to phase in higher prices for electricity and water. As part of its diversification plans, Bahrain implemented a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the US in August 2006, the first FTA between the US and a Gulf state. It plans to introduce a Value Added Tax (VAT) by 2018.
Bahrain is rich in the following natural resources: Oil, associated and nonassociated natural gas, fish, pearls.
The main industrial sectors are petroleum processing and refining, aluminum smelting, iron pelletization, fertilizers, Islamic and offshore banking, insurance, ship repairing, tourism.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in refined petroleum, aluminum, and plating, crude petroleum, iron ore, gold (2019), partnering with these nations: United Arab Emirates 31%, Saudi Arabia 12%, Japan 8%, United States 8% (2019). The export trade resulted in $30.1 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Bahrain’s position of 70.
Land use in Bahrain: 0.7% (2018 estimate) forest, 88% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 11.3% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 3.9% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 5.3% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 40 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Bahrain are mutton, dates, milk, poultry, tomatoes, fruit, sheep offals, sheepskins, eggs, pumpkins.
The country typically needs to import: cars, iron ore, jewelry, gold, gas turbines (2019), partnering with the following nations: United Arab Emirates 27%, China 11%, Saudi Arabia 7%, United States 5%, Brazil 5%, Japan 5%, India 5% (2019) in a sum value of $27.19 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $22.132 billion (2017 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Bahrain 73.
Bahrain Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Bahrain, the Middle East, archipelago in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia. We published some basic information about its capital Manama, and the Bahraini nation.
Are you interested in visiting Bahrain and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Bahrain below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Bahrain
Did you know about Bahrain?
Bahrain is one of the smallest countries in the Middle East. From Bahrain, you can see the light blue water and get a glimpse of some of the most picturesque landscapes on earth.
Bahrain is a country in the Middle East that borders Saudi Arabia. It is one of the oldest countries globally, dating back to around 2000 BCE. Bahrain was ruled by various kingdoms throughout history, with many different influences from other parts of the world. Islam heavily influences the country’s culture, and it is known for its Arabic cuisine.
After virtually visiting Bahrain, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Qatar or Saudi Arabia.
If you liked our Google map and Bahrain information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.